A one-to-one relationships occurs when one entity is related to exactly one occurrence in another entity.
In this tutorial, we show you how to work with one-to-one table relationship in Hibernate, via XML mapping file (hbm).
Tools and technologies used in this tutorials :
Hibernate 3.6.3.Final
- MySQL 5.1.15
- Maven 3.0.3
- Eclipse 3.6
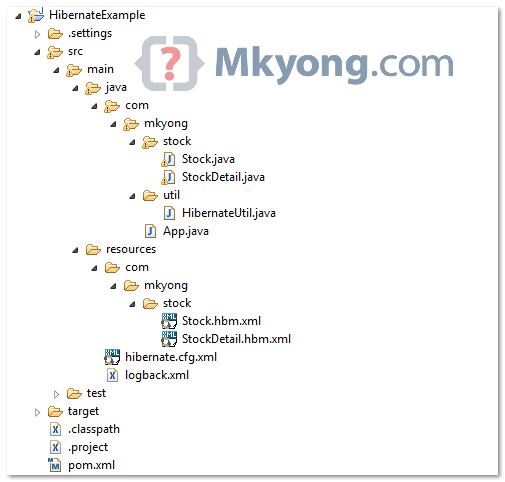
Project Structure
See the final project structure of this tutorial.
Project Dependency
Get hibernate.jar from JBoss repository, Maven will take care all the related dependencies for you.
File : pom.xml
<project ...>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>JBoss repository</id>
<url>http://repository.jboss.org/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<!-- MySQL database driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.15</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>3.6.3.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javassist</groupId>
<artifactId>javassist</artifactId>
<version>3.12.1.GA</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>1. “One-to-one” table relationship
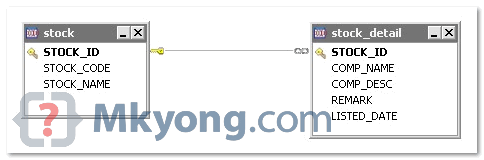
A one-to-one relationship table design, a STOCK table contains exactly one record in STOCK_DETAIL table. Both tables have the same Stock_Id as primary key. In STOCK_DETAIL table, Stock_Id is the primary key and also a foreign key to STOCK table. This is the common way of define “one-to-one” table relationship.
2. Hibernate Model Class
Create two model classes – Stock.java and StockDetail.java, to represent the above tables.
File : Stock.java
package com.mkyong.stock;
public class Stock implements java.io.Serializable {
private Integer stockId;
private String stockCode;
private String stockName;
private StockDetail stockDetail;
//constructor & getter and setter methods
}File : StockDetail.java
package com.mkyong.stock;
public class StockDetail implements java.io.Serializable {
private Integer stockId;
private Stock stock;
private String compName;
private String compDesc;
private String remark;
private Date listedDate;
//constructor & getter and setter methods
}3. Hibernate XML Mapping
Now, create two Hibernate mapping files (hbm) – Stock.hbm.xml and StockDetail.hbm.xml.
File : Stock.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!-- Generated 25 April 2011 7:52:33 PM by Hibernate Tools 3.4.0.CR1 -->
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.mkyong.stock.Stock" table="stock" catalog="mkyongdb">
<id name="stockId" type="java.lang.Integer">
<column name="STOCK_ID" />
<generator class="identity" />
</id>
<property name="stockCode" type="string">
<column name="STOCK_CODE" length="10" not-null="true" unique="true" />
</property>
<property name="stockName" type="string">
<column name="STOCK_NAME" length="20" not-null="true" unique="true" />
</property>
<one-to-one name="stockDetail" class="com.mkyong.stock.StockDetail"
cascade="save-update"></one-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>File : StockDetail.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!-- Generated 25 April 2011 7:52:33 PM by Hibernate Tools 3.4.0.CR1 -->
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.mkyong.stock.StockDetail" table="stock_detail"
catalog="mkyongdb">
<id name="stockId" type="java.lang.Integer">
<column name="STOCK_ID" />
<generator class="foreign">
<param name="property">stock</param>
</generator>
</id>
<one-to-one name="stock" class="com.mkyong.stock.Stock"
constrained="true"></one-to-one>
<property name="compName" type="string">
<column name="COMP_NAME" length="100" not-null="true" />
</property>
<property name="compDesc" type="string">
<column name="COMP_DESC" not-null="true" />
</property>
<property name="remark" type="string">
<column name="REMARK" not-null="true" />
</property>
<property name="listedDate" type="date">
<column name="LISTED_DATE" length="10" not-null="true" />
</property>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>Note
The main difficulty in this one-to-one relationship is ensuring both are assigned the same primary key. In StockDetail.hbm.xml, a special foreign identifier generator is declared, it will know get the primary key value from STOCK table. With constrained=”true”, it ensure the Stock must exists.
4. Hibernate Configuration File
Puts Stock.hbm.xml and StockDetail.hbm.xml in your Hibernate configuration file, and also MySQL connection details.
File : hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mkyongdb</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">password</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="com/mkyong/stock/Stock.hbm.xml" />
<mapping resource="com/mkyong/stock/StockDetail.hbm.xml" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>5. Run It
Run it, Hibernate will insert a row into the STOCK table and a row into the STOCK_DETAIL table.
File : App.java
package com.mkyong;
import java.util.Date;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import com.mkyong.stock.Stock;
import com.mkyong.stock.StockDetail;
import com.mkyong.util.HibernateUtil;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hibernate one to one (XML mapping)");
Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
Stock stock = new Stock();
stock.setStockCode("4715");
stock.setStockName("GENM");
StockDetail stockDetail = new StockDetail();
stockDetail.setCompName("GENTING Malaysia");
stockDetail.setCompDesc("Best resort in the world");
stockDetail.setRemark("Nothing Special");
stockDetail.setListedDate(new Date());
stock.setStockDetail(stockDetail);
stockDetail.setStock(stock);
session.save(stock);
session.getTransaction().commit();
System.out.println("Done");
}
}Output
Hibernate one to one (XML mapping)
Hibernate: insert into mkyongdb.stock (STOCK_CODE, STOCK_NAME) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into mkyongdb.stock_detail
(COMP_NAME, COMP_DESC, REMARK, LISTED_DATE, STOCK_ID) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)Done






















 566
566

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








