Socket通用TCP通信协议设计及实现(防止粘包,可移植,可靠)
引文
我们接收Socket字节流数据一般都会定义一个数据包协议。我们每次开发一个软件的通信模块时,尽管具体的数据内容是不尽相同的,但是大体上的框架,以及常用的一些函数比如转码,校验等等都是相似甚至一样的。所以我感觉设计一个通用的通信协议,可以在之后的开发中进行移植实现高效率的开发是很有必要的。另外,本协议结合我自己所了解的通信知识尽可能的提升了可靠性和移植性,可处理类似粘包这样的问题。对于本文中可能存在的问题,欢迎各位大神多多指点。
报文设计
本报文的字段结构分为Hex编码和BCD(8421)编码两种。由于BCD编码的取值范围其实是Hex编码的真子集,也就是所谓的16进制编码中的“ABCDEF”这六个字母对应的数值是在BCD编码中无法取值的。所以我利用这个特点,将报文中的用于标识的不含实际数据的抽象字段用Hex编码,且取值范围在A~F之间。将反应实际数据的字段用BCD编码。这样,具有标识作用的字段与实际数据字段的取值是互不交叉的。这无形中就避免了很多出现的问题,增强了报文的可靠性。例如:我使用”0xFFFF”代表报文起始符,这个取值是不会在任何一个数据字段中出现的,应为它们是BCD编码。也就是是说,字节流缓冲区中只要出现”0xFFFF”我们就可以判断这个是一个数据包的开头(我在实现在缓冲区中找寻数据包算法时还做了另外的控制,进行双重保障)。
对于正文部分,我设计成了“标识符|数据”成对出现的形式。每个标识符用来指示后面出现的数据的含义,数据字段用于传输真实的数据。这种对的形式,增强了报文的移植性,在新的一次开发到来时,我们只要按需求定义好正文部分的“标识符|数据”对即可。另外,这种设计还增强了发送报文方的灵活性。标识符的存在使得各项数据可以按照任意的顺序发送,没有的数据也可以不发。
基于以上的这些考虑,我把报文设计成了如下形式:
通用报文协议
| 序号 | 名称 | 编码说明 |
| 1 | 报文起始符 | 2字节Hex编码 0xFFFF |
| 2 | 功能码(报文类型) | 2字节Hex编码 0xD1D1 |
| 3 | 密码 | 4字节BCD编码 00 00 00 01 |
| 4 | 长度 | 2字节BCD编码 正文实际长度 |
| 5 | 标识符1 | 2字节Hex编码 自定义数据标识符 0xA001 |
| 6 | 数据1 | N字节BCD编码 N根据实际情况自定义 |
| 7 | 标识符2 | 2字节Hex编码 自定义数据标识符 0xA002 |
| 8 | 数据2 | N字节BCD编码 N根据实际情况自定义 |
| ... | … | |
| | 报文终止符 | 2字节Hex编码 0xEEEE |
| | 校验码 | 校验码前所有字节的CRC校验,生成多项式:X16+X15+X2+1,高位字节在前,低位字节在后。 |
报文示例:
示例背景:发送报文通知远程服务器第1号设备开关的当前状态为开启
需自定义正文部分,含两个字段,设备编号和开关状态
发送的字节数组:255 255 | 209209 | 0 0 0 1 | 0 6 | 160 1 | 1 | 160 2| 0 | 238 238 | 245 40 |
对应含义解释: 起始符FFFF | 功能码D1D1 | 密码00 00 00 01 | 长度(正文)00 06| 标识符A001 | 数据 1 | 标识符A002 | 数据 0 | 报文终止符 EEEE | 校验结果 |
粘包问题的解决
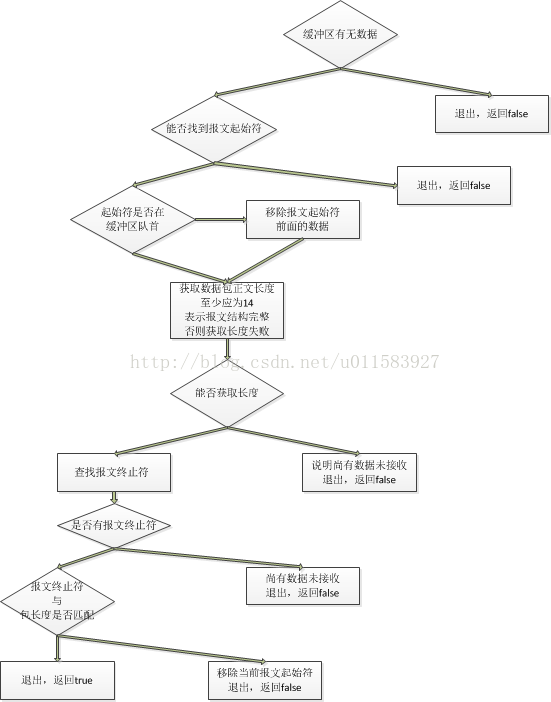
针对我的协议,我设计了一个缓冲区中找寻数据包算法,这两者的配合完美的实现了防止粘包,过滤噪声数据等类似的各种令人头疼的问题。此算法思路来自博文点击打开链接
算法流程图如下:
算法C#代码具体实现:
调用示例:
- private void receive()
- {
- while (true)
- {
- int len = Server.Available;
- if (len > 0)
- {
- byte[] temp = new byte[len];
- Server.Receive(temp,len,SocketFlags.None);
- buffer.Enqueue(temp);
- while (buffer.Find()!=0)
- {
- int length = buffer.GetLength();
- byte[] readBuffer = new byte[len];
- buffer.Dequeue(readBuffer, 0, length);
-
-
- DataPacketEx da = Statute.UnPackMessage(readBuffer);
- ComFun.receiveList.Add(da);
- }
-
- }
-
- Thread.Sleep(100);
- }
- }
其中DataPacketEx是封装数据包正文部分的类,其中的属性记录了要发送的数据
使用时只需开启一个线程,不断的将收到的字节流数据加入缓冲区中。调用Find()方法找寻下一个数据包,如果该方法返回0,说明当前缓冲区中不存在数据包(数据尚未完整接收/存在错误数据,该方法可自行进行处理),如果返回一个正数n,则当前缓冲区中索引0-(n-1)的数据即为一个收到的完整的数据包。对其进行处理即可。
协议的实现
在实现协议前,首先我在自定义的TransCoding类中实现了几个静态方法用于Hex、BCD、string等之间的转换。
-
-
-
-
-
- public static byte[] BCDStrToByte(string str)
- {
- #region 原方法
-
-
- if (str.Length % 2 != 0)
- {
- str = '0' + str;
- }
-
- byte[] bcd = new byte[str.Length / 2];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < str.Length / 2; i++)
- {
- int index = i * 2;
-
-
- byte high = (byte)(str[index] - 48);
- high = (byte)(high << 4);
- byte low = (byte)(str[index + 1] - 48);
-
- bcd[i] = (byte)(high | low);
- }
-
- return bcd;
-
- #endregion
-
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public static string ByteToHexStr(byte[] hex, int index)
- {
- string hexStr = "";
- if (index >= hex.Length || index < 0)
- throw new Exception("索引超出界限");
- for (int i = index; i < hex.Length; i++)
- {
- if (Convert.ToInt16(hex[i]) >= 16)
- {
- hexStr += Convert.ToString(hex[i], 16).ToUpper();
- }
- else
- {
- hexStr += "0" + Convert.ToString(hex[i], 16).ToUpper();
- }
- }
- return hexStr;
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public static byte[] HexStrToByte(string hexStr)
- {
- if (hexStr.Trim().Length % 2 != 0)
- {
- hexStr = "0" + hexStr;
- }
- byte[] hexByte = new byte[hexStr.Length / 2];
- for (int i = 0; i < hexByte.Length; i++)
- {
- string hex = hexStr[i * 2].ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture) + hexStr[i * 2 + 1].ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
- hexByte[i] = byte.Parse(hex, NumberStyles.AllowHexSpecifier);
- }
- return hexByte;
-
- #region 使用Convert.ToByte转换
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- #endregion
- }
以下是协议的实现的两个核心方法,装包和解包
装包方法将已有的具体的不同数据类型的数据转换成byte字节流,以便进行socket通信
解包方法将socket接收到的完整数据包字节流解析成封装数据包的类DataPacketEx
-
-
-
-
-
- public byte[] BuildMessage(DataPacketEx data)
- {
- List<byte> msg = new List<byte>();
-
-
- byte[] tempS = TransCoding.HexStrToByte("FFFF");
- ComFun.bytePaste(msg, tempS);
-
-
- tempS = TransCoding.HexStrToByte("D1D1");
- ComFun.bytePaste(msg, tempS);
-
-
- tempS = TransCoding.BCDStrToByte("00000001");
- ComFun.bytePaste(msg, tempS);
-
-
- tempS = TransCoding.BCDStrToByte("0006");
- ComFun.bytePaste(msg, tempS);
-
-
- tempS = TransCoding.HexStrToByte("A001");
- ComFun.bytePaste(msg, tempS);
-
-
- tempS = TransCoding.BCDStrToByte(data.ObjectID);
- ComFun.bytePaste(msg, tempS);
-
-
- tempS = TransCoding.HexStrToByte("A002");
- ComFun.bytePaste(msg, tempS);
-
-
- tempS = TransCoding.BCDStrToByte(data.IsOpen);
- ComFun.bytePaste(msg, tempS);
-
-
- tempS = TransCoding.HexStrToByte("EEEE");
- ComFun.bytePaste(msg, tempS);
-
-
- byte[] message = new byte[msg.Count];
- for (int i = 0; i < msg.Count; i++)
- {
- message[i] = msg[i];
- }
- byte[] crc = new byte[2];
- Checksum.CalculateCrc16(message, out crc[0], out crc[1]);
-
- message = new byte[msg.Count + 2];
- for (int i = 0; i < msg.Count; i++)
- {
- message[i] = msg[i];
- }
- message[message.Length - 2] = crc[0];
- message[message.Length - 1] = crc[1];
-
- return message;
-
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public DataPacketEx UnPackMessage(byte[] message)
- {
-
- if (!CheckRespose(message))
- return null;
-
-
- byte[] temp = new byte[4];
- temp[0] = message[4];
- temp[1] = message[5];
- temp[2] = message[6];
- temp[3] = message[7];
- if (TransCoding.ByteToHexStr(temp, 0) != "00000001")
- return null;
-
- DataPacketEx DataPacket = new DataPacketEx("", "", "");
-
-
- byte[] funType = new byte[2] { message[2], message[3] };
- string functionStr = TransCoding.ByteToHexStr(funType, 0);
-
- #region 具体解包过程,需根据实际情况修改
-
- int index = 10;
- string tempStr="";
-
- switch (functionStr)
- {
- case "D1D1":
- temp = new byte[2] { message[index], message[index + 1] };
- index = index + 2;
- tempStr = TransCoding.ByteToHexStr(temp, 0);
- while (tempStr != "EEEE")
- {
- switch (tempStr)
- {
-
- case "A001":
-
- temp = new byte[1] { message[index] };
- index = index + 1;
- tempStr = TransCoding.ByteToHexStr(temp, 0);
- DataPacket.ObjectID = tempStr;
- break;
- case "A002":
-
- temp = new byte[1] { message[index] };
- index = index + 1;
- tempStr = TransCoding.ByteToHexStr(temp, 0);
- DataPacket.IsOpen = tempStr;
- break;
-
-
-
- }
- temp = new byte[2] { message[index], message[index + 1] };
- index = index + 2;
- tempStr = TransCoding.ByteToHexStr(temp, 0);
- }
- break;
-
-
-
-
- }
-
- #endregion
-
- return DataPacket;
- }
对于通信可靠性的验证
对此,我制作了两个简单的demo,一个服务器端,一个客户端。
客户端可想服务器端循环发送数据,其中以0.5的概率夹杂着随机长度随机取值的干扰数据,以此来判断本协议在实际应用中的可行性。
服务器端负责循环接收并处理显示收到的数据
最终的运行结果如下图:
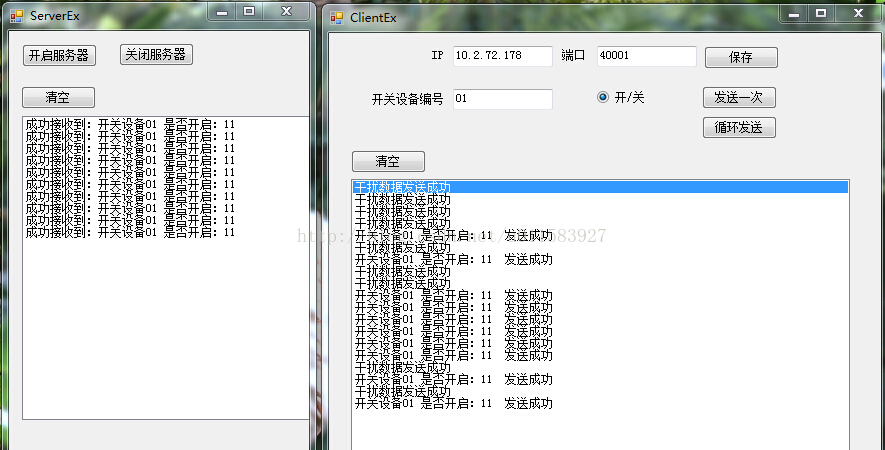
由运行结果可以看出,服务器端完美屏蔽掉了客户端发出的错误数据,全部解析出了客户端发送的实际数据。证明本协议可以解决类似粘包,传错等等类似的通讯中的棘手问题。当然,协议中如果有不完美的地方,希望各位大神指教。另外,上面的demo只是为了验证协议所做,还存在一些零零碎碎的小bug。
亲测以上代码可以正常使用,下面的连接是作者提供的:http://download.csdn.net/detail/u011583927/8653701
























 3212
3212

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








