-
6 10 5 2 2 2 4 4
-
4 0 5 2 6 6
描述
Little Hi is studying on memory allocating algorithms this summer. He starts his experiments with a very simple algorithm. By this algorithm memory is considered as a sequence of M consecutive storage units, numbered from 0 to M-1.
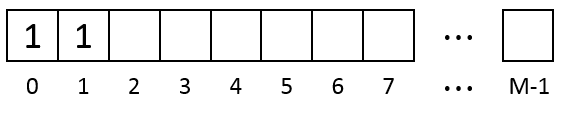
Whenever a piece of data is written to the memory the algorithm finds from 0 to M-1 the first segment of consecutive empty units which is large enough and save the data there. For example if the data size is 2 after saving it the memory look as below. Units are marked as 1 because they contain the 1st data we write.
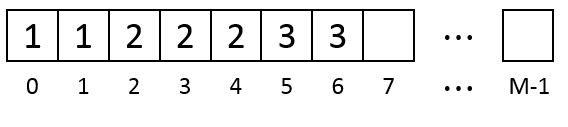
If we continue to write two pieces of data of size 3 and 2 the memory looks like below. Units 2-4 contain the 2nd data and Units 5 and 6 contain the 3rd data.
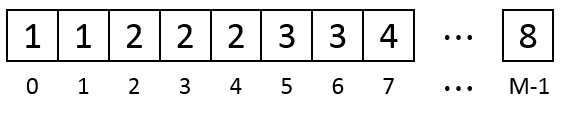
If there is not enough consecutive empty units for the coming data the algorithm will keep removing the earliest data until the coming data can be saved. Assume the memory if full after we write the 8th data:
And we need to write the 9th data of size 4. The algorithm removes the 1st data:
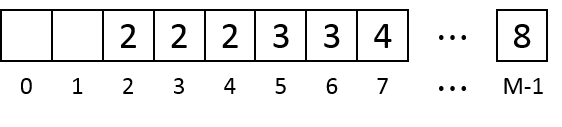
There is still not enough consecutive empty units so the 2nd data is also removed. Then the 9th data is saved at Units 0-3:
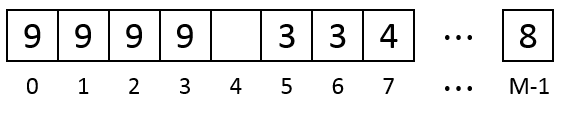
Remember if there are multiple possible segments to save the coming data the algorithm always choose the segment which is started at the unit of the smallest number.
After writing N data of different sizes Little Hi wants to know what the memory looks like.
输入
Line 1: N and M, the number of data and the size of the memory.
Line 2: N integers, K1, K2 …, KN. Ki is the size of the ith data.
For 60% of the data 1≤N≤200,10≤M≤100,1≤Ki≤5
For 100% of the data 1≤N≤2,000,10≤M≤109,1≤Ki≤M
输出
For each data which is still in the memory at last output one line of two integers id and s: the number of the data and its starting position in the memory. Output them in increasing order of id.
样例提示
The memory looks after saving each data:
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 2 2 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 0
4 4 0 0 0 2 2 3 3 0
4 4 5 5 5 5 0 3 3 0
4 4 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6
样例输出
题目类似于模拟内存分配,输入的第一行是操作的次数和内存大小。
然后内存分配的规则是从左开始寻找,如果有某一段内存刚好可以分配,然后就把新的数据分配到这块内存,如果没有找到,则需要释放内存,并且以后释放内存从前面释放之后的位置开始。
The memory looks after saving each data:
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 2 2 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 0
4 4 0 0 0 2 2 3 3 0
4 4 5 5 5 5 0 3 3 0
4 4 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6
从这里很容易看出内存操作。
至于实现,可以采用数组模拟(不是类似于桶的模拟),或者采用双端队列,其中插入可以插入到任何一个位置,当然也可以用链表啦!链表每一个节点代表当前区域的大小和ID,我们可以设定ID为0代表当前区域是空的,也就是可以被直接分配的。
AC代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <queue>
#include<iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct ds
{
int v;
int s;
int e;
};
bool cmp(ds a,ds b)
{
return a.v<b.v;
}
int main()
{
int n, m,ans;
cin>>n>>m;
deque<ds>que;
bool f = true;
for (int k = 1; k <= n; ++k)
{
if(f)cin>>ans;
if (que.empty())que.push_back({k,0,ans-1});
else
{
bool flag = false;
int mk = n+1,idx = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)que.size(); ++i)
{
if (mk > que[i].v)mk = que[i].v,idx = i;
if (i == 0)
{
if (ans - 1 < que[i].s)
{
que.push_front({k,0,ans-1});
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if (i == (int)que.size() - 1)
{
if (que[i].e + ans < m)
{
que.push_back({k,que[i].e+1,que[i].e+ans});
flag = true;
break;
}
}
else
{
if (que[i + 1].s-que[i].e-1>=ans)
{
que.insert(que.begin()+i+1, {k,que[i].e+1,que[i].e+ans});
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (!flag)
{
que.erase(que.begin()+idx);
k--;
f = false;
}
else f = true;
}
}
sort(que.begin(), que.end(),cmp);
for (deque<ds>::iterator i=que.begin(); i!=que.end(); i++)
cout<<(*i).v<<" "<<(*i).s<<endl;
return 0;
}























 161
161











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








