在使用spring 的 BeanUtils.copyProperties()进行对象赋值时,只能拷贝单一字段的值,如果对象是复合对象,比如成员变量中有对象,链表等时,BeanUtils.copyProperties()拷贝的还是复杂成员变量的引用,如下代码:
List<Particle> particleList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Particle particle : particles.getParticles()) {
Particle temp = new Particle();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(particle, temp);
//Particle temp = CommonUtil.deepCloneObject(particle);
particleList.add(temp);
}用BeanUtils.copyProperties()将particle拷贝到temp时,由于path是一个链表,此时并不会拷贝值,而是一个引用,本质上path还是一个对象,这在运算中可能是致命的。
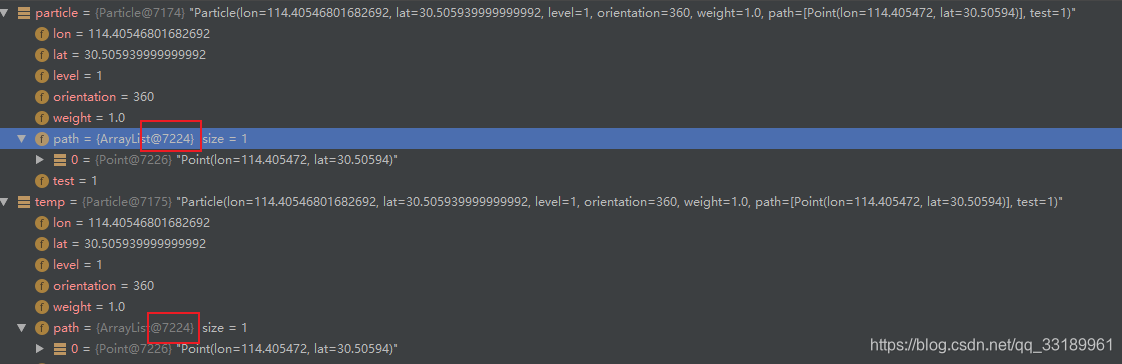
而java本身是不支持深拷贝的,可以 利用序列化和反序列化的方式进行深拷贝(致谢这位大佬),方法直接拿过去用,代码如下:
/**
* 对象的深度克隆,此处的对象涉及Collection接口和Map接口下对象的深度克隆
* 利用序列化和反序列化的方式进行深度克隆对象
*
* @param <T> 待克隆对象的数据类型
* @param object 待克隆的对象
* @return 已经深度克隆过的对象
*/
public static <T extends Serializable> T deepCloneObject(Particle object) {
T deepClone = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
ByteArrayInputStream bais = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
oos.writeObject(object);
bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos
.toByteArray());
ois = new ObjectInputStream(bais);
deepClone = (T)ois.readObject();
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(baos != null) {
baos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(oos != null) {
oos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try{
if(bais != null) {
bais.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try{
if(ois != null) {
ois.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return deepClone;
}使用一下:
List<Particle> particleList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Particle particle : particles.getParticles()) {
Particle temp = CommonUtil.deepCloneObject(particle);
particleList.add(temp);
}可以看到path是一个新对象:
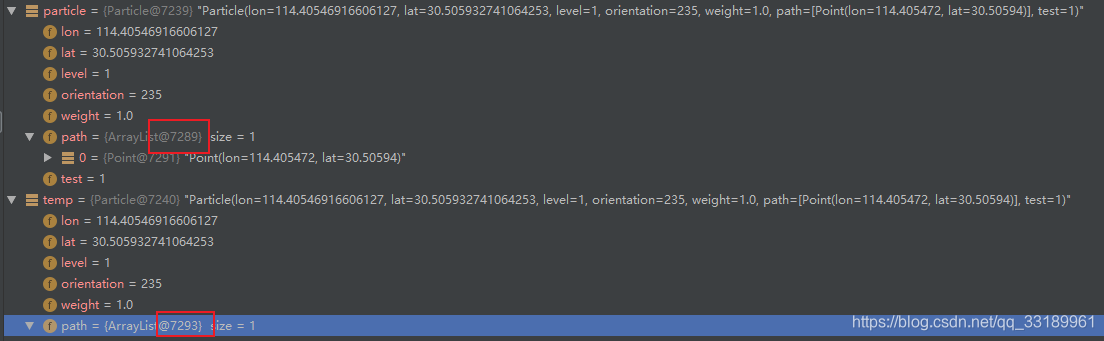
注意事项,实体类要 implements Serializable接口,比如我用的实体是Particle:
@Data
@Repository
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Particle implements Serializable {
private double lon; //经度
private double lat; //纬度
private int level; //楼层
private int orientation; //方向
private float weight = 1; //权重
private List<Point> path = new ArrayList<>(); //粒子走过的路径
private int test = 1; //测试字段
}





 博客指出使用Spring的BeanUtils.copyProperties()进行对象赋值时,对复合对象只能拷贝引用,可能导致运算问题。由于Java本身不支持深拷贝,可利用序列化和反序列化方式实现深拷贝,同时提醒实体类需实现Serializable接口。
博客指出使用Spring的BeanUtils.copyProperties()进行对象赋值时,对复合对象只能拷贝引用,可能导致运算问题。由于Java本身不支持深拷贝,可利用序列化和反序列化方式实现深拷贝,同时提醒实体类需实现Serializable接口。
















 1365
1365

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








