Thread start() 方法 ,是一个线程开始的方法
Thread run() 方法 ,就是一个普通的方法,可以理解为main方法里面的一个普通的方法
下面写一个demo 理解下
Thread thread = new Thread("other"){
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Log.e("------hxm","threadName = " + threadName + ", id = " + id);
}
};
thread.start();
Thread start() 打印的结果为:------hxm: threadName = other, id = 1286
Thread thread = new Thread("other"){
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Log.e("------hxm","threadName = " + threadName + ", id = " + id);
}
};
thread.run();
Thread run() 打印的结果为:------hxm: threadName = main, id = 2
上面的对比不难发现 Thread start() 的线程为自己创建的other 它的run方法在other线程,Thread run() 则是main 它的run方法在主线程(Thread.currentThread().getName() 是获取当前线程的名字)
如果想更多的了解可以看下源码,这里我看的是android 里面的源码,可能存在修改
start() 方法
public synchronized void start() {
/**
* This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
*
* A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
*/
// Android-changed: Replace unused threadStatus field with started field.
// The threadStatus field is unused on Android.
if (started)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads
* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
// Android-changed: Use field instead of local variable.
// It is necessary to remember the state of this across calls to this method so that it
// can throw an IllegalThreadStateException if this method is called on an already
// started thread.
started = false;
try {
// Android-changed: Use Android specific nativeCreate() method to create/start thread.
// start0();
nativeCreate(this, stackSize, daemon);
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
// Android-changed: Use Android specific nativeCreate() method to create/start thread. // start0(); nativeCreate(this, stackSize, daemon);
看了下nativeCreate 方法里面也是run方法,不过nativeCreate作用了,说了就是创建或者开启一个线程的.
android 对这个地方有所修改,就是使用特有的nativeCreate() 方法,创建或者开启线程. 在往下看就是native 了,这个没有看,
run() 方法

直接调用的run 方法
在看target 是 什么
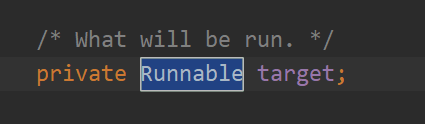
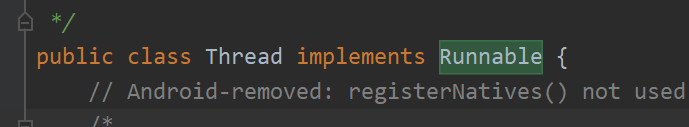
可以看出target 就是Runnable 对象本身.





 本文介绍了Java中Thread.start()和Thread.run()的区别。start()方法用于启动线程,使run()方法在新的线程中执行,而直接调用run()方法则会使其在当前线程(通常是主线程)中执行。通过示例代码展示了两者不同的运行结果,并简单分析了start()方法的源码,揭示了线程的创建过程。
本文介绍了Java中Thread.start()和Thread.run()的区别。start()方法用于启动线程,使run()方法在新的线程中执行,而直接调用run()方法则会使其在当前线程(通常是主线程)中执行。通过示例代码展示了两者不同的运行结果,并简单分析了start()方法的源码,揭示了线程的创建过程。
















 344
344

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








