1.Motivation:
现如今,各大主流深度学习框架都有着自己独有的特点与魅力,吸引着广大科研与开发人员,例如:
Caffe2:方便机器学习算法和模型大规模部署在移动设备
PyTorch:PyTorch是一个快速便于实验深度学习框架。但是由于其高度封装,导致部分function不够灵活
TensorFlow:TensorFlow 是一个开放源代码软件库,是很多主流框架的基础或者依赖。几乎能满足所有机器学习开发的功能,但是也有由于其功能代码过于底层,学习成本高,代码冗繁,编程逻辑与常规不同等缺点。
此外还有:Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK),Apache MXNet,Chainer,Apple CoreML,SciKit-Learn,ML.NET
深度学习算法大多通过计算数据流图来完成神经网络的深度学习过程。 一些框架(例如CNTK,Caffe2,Theano和TensorFlow)使用静态图形,而其他框架(例如PyTorch和Chainer)使用动态图形。 但是这些框架都提供了接口,使开发人员可以轻松构建计算图和运行时,以优化的方式处理图。 这些图用作中间表示(IR),捕获开发人员源代码的特定意图,有助于优化和转换在特定设备(CPU,GPU,FPGA等)上运行。
假设一个场景:现在某组织因为主要开发用TensorFlow为基础的框架,现在有一个深度算法,需要将其部署在移动设备上,以观测变现。传统地我们需要用caffe2重新将模型写好,然后再训练参数;试想下这将是一个多么耗时耗力的过程。
此时,ONNX便应运而生,Caffe2,PyTorch,Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit,Apache MXNet等主流框架都对ONNX有着不同程度的支持。这就便于了我们的算法及模型在不同的框架之间的迁移。
2. ONNX :
2.1 ONNX Overview
开放式神经网络交换(ONNX)是迈向开放式生态系统的第一步,它使AI开发人员能够随着项目的发展选择合适的工具。 ONNX为AI模型提供开源格式。 它定义了可扩展的计算图模型,以及内置运算符和标准数据类型的定义。 最初的ONNX专注于推理(评估)所需的功能。 ONNX解释计算图的可移植,它使用graph的序列化格式。 它不一定是框架选择在内部使用和操作计算的形式。 例如,如果在优化过程中操作更有效,则实现可以在存储器中以不同方式表示模型。
ONNX是一个开放式规范,由以下组件组成:
- 可扩展计算图模型的定义
- 标准数据类型的定义
- 内置运算符的定义
2.2 ONNX model:
The top-level ONNX construct is a ‘Model.’
模型结构的主要目的是将元数据(meta data)与图形(graph)相关联,图形包含所有可执行元素。 首先,读取模型文件时使用元数据,为实现提供所需的信息,以确定它是否能够:执行模型,生成日志消息,错误报告等功能。此外元数据对工具很有用,例如IDE和模型库,它需要它来告知用户给定模型的目的和特征。
每个model具有以下组件:
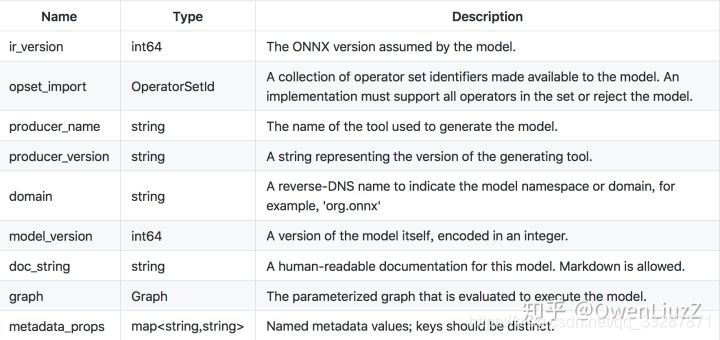
2.2.1 ONNX Operator Sets:
每个模型必须明确命名它依赖于其功能的运算符集。 操作员集定义可用的操作符,其版本和状态。 每个模型按其域定义导入的运算符集。 所有模型都隐式导入默认的ONNX运算符集。
运算符集的属性是:

2.2.2 ONNX Operator
图(graph)中使用的每个运算符必须由模型(model)导入的一个运算符集明确声明。
运算符定义的属性是:

2.3.1 ONNX Graph
序列化图由一组元数据字段(meta data),模型参数列表(a list of model parameters,)和计算节点列表组成(a list of computation nodes)。
每个计算数据流图被构造为拓扑排序的节点列表,这些节点形成图形,其必须没有周期。 每个节点代表对运营商的呼叫。 每个节点具有零个或多个输入以及一个或多个输出。
图表具有以下属性:
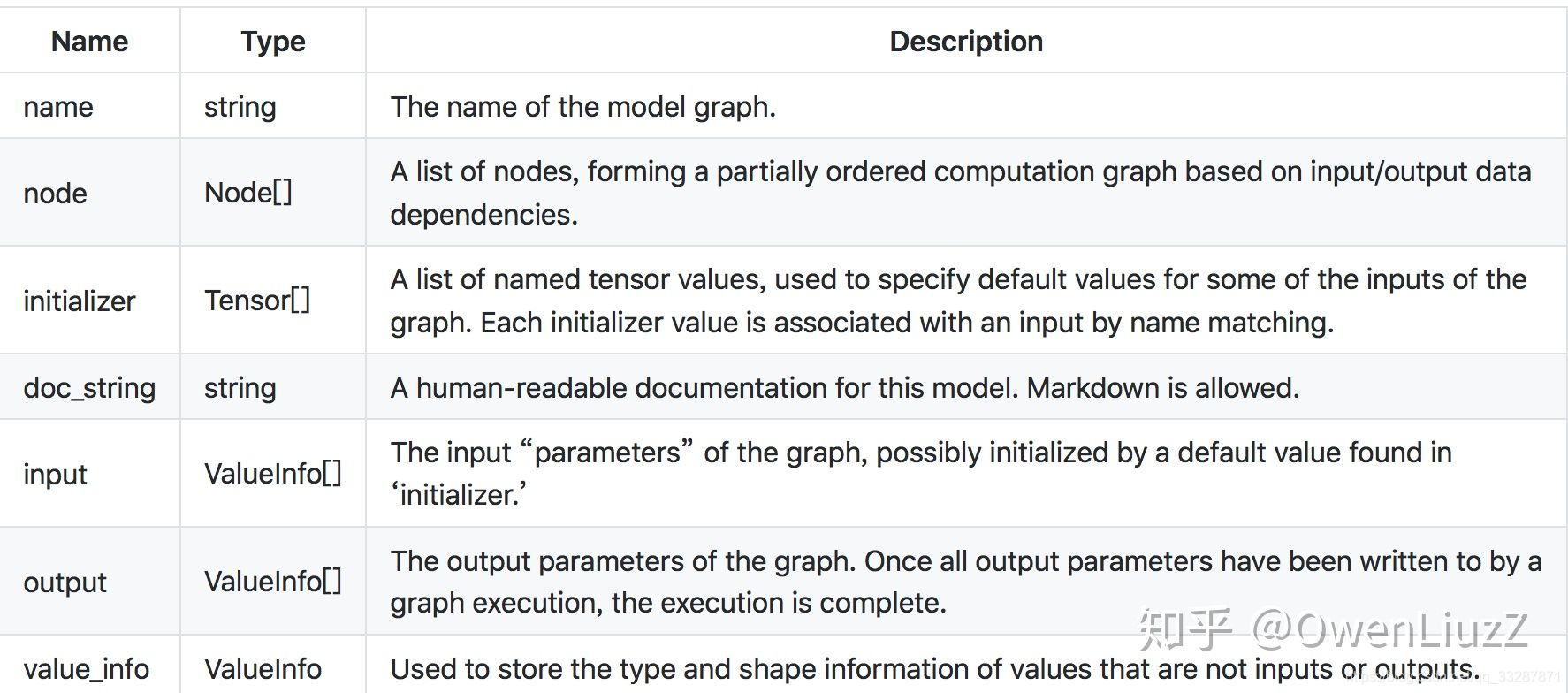
每个图都必须定义其输入和输出的名称和类型,并指定为“值信息”结构,并具有以下属性:
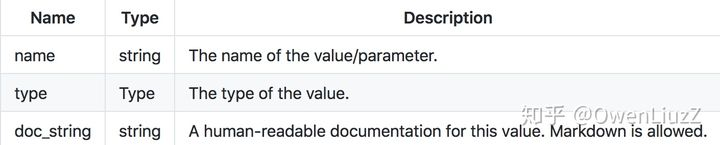
2.3.2 图的名称
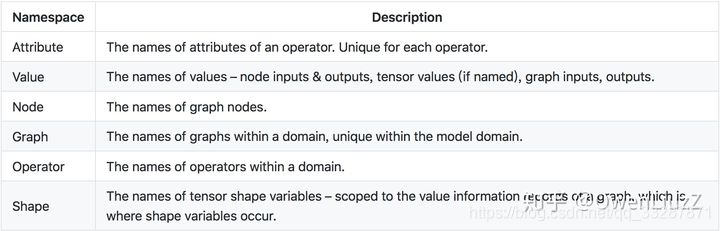
所有名称必须遵守C标识符语法规则。
节点,输入,输出,初始化器和属性的名称被组织到多个名称空间中。 在命名空间内,每个给定图形的每个名称必须是唯一的。
命名空间是:
2.3.3 Node
计算节点由名称,它调用的运算符的名称,命名输入列表,命名输出列表和属性列表组成。输入和输出在位置上与operator输入和输出相关联。 属性按名称与运算符属性相关联。
它们具有以下属性:
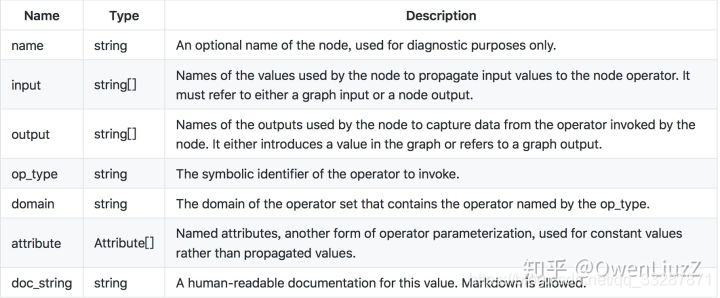
计算图中的边缘由后续节点的输入中由名称引用的一个节点的输出建立。
给定节点的输出将新名称引入图中。 节点输出的值由节点的运算符计算。 节点输入可以指定节点输出,图形输入和图形初始化。 当节点输出的名称与图形输出的名称一致时,图形输出的值是该节点计算的相应输出值。
3. ONNX Python API
- Loading an ONNX Model
- Saving an ONNX Model
- ManipulatingTensorProtoandNumpyArray
- Creating an ONNX Model Using HelperFunctions
- Checking an ONNX Model
- Optimizing an ONNX Model
- Running Shape Inference on an ONNX Model
- UtilityFunctions
3.1 Loading an ONNX Model
import onnx
onnx_model = onnx.load('path/to/the/model.onnx')
# `onnx_model` is a ModelProto struct
3.2 Saving an ONNX Model
import onnx
onnx_model = ... # Your model in memory as ModelProto
# Save the ONNX model
onnx.save(onnx_model, 'path/to/the/model.onnx')
3.3 ManipulatingTensorProtoandNumpyArray
import numpy
import onnx
from onnx import numpy_helper
# Preprocessing: create a Numpy array
numpy_array = numpy.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]], dtype=float)
print('Original Numpy array:\n{}\n'.format(numpy_array))
# Convert the Numpy array to a TensorProto
tensor = numpy_helper.from_array(numpy_array)
print('TensorProto:\n{}'.format(tensor))
# Convert the TensorProto to a Numpy array
new_array = numpy_helper.to_array(tensor)
print('After round trip, Numpy array:\n{}\n'.format(numpy_array))
# Save the TensorProto
with open('tensor.pb', 'wb') as f:
f.write(tensor.SerializeToString())
# Load a TensorProto
new_tensor = onnx.TensorProto()
with open('tensor.pb', 'rb') as f:
new_tensor.ParseFromString(f.read())
print('After saving and loading, new TensorProto:\n{}'.format(new_tensor))
3.4 Creating an ONNX Model Using HelperFunctions
import onnx
from onnx import helper
from onnx import AttributeProto, TensorProto, GraphProto
# The protobuf definition can be found here:
# https://github.com/onnx/onnx/blob/master/onnx/onnx.proto
# Create one input (ValueInfoProto)
X = helper.make_tensor_value_info('X', TensorProto.FLOAT, [1, 2])
# Create one output (ValueInfoProto)
Y = helper.make_tensor_value_info('Y', TensorProto.FLOAT, [1, 4])
# Create a node (NodeProto)
node_def = helper.make_node(
'Pad', # node name
['X'], # inputs
['Y'], # outputs
mode='constant', # attributes
value=1.5,
pads=[0, 1, 0, 1],
)
# Create the graph (GraphProto)
graph_def = helper.make_graph(
[node_def],
'test-model',
[X],
[Y],
)
# Create the model (ModelProto)
model_def = helper.make_model(graph_def, producer_name='onnx-example')
print('The model is:\n{}'.format(model_def))
onnx.checker.check_model(model_def)
print('The model is checked!')
3.5 Checking an ONNX Model
import onnx
# Preprocessing: load the ONNX model
model_path = 'path/to/the/model.onnx'
onnx_model = onnx.load(model_path)
print('The model is:\n{}'.format(onnx_model))
# Check the model
onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model)
print('The model is checked!')
3.6 Optimizing an ONNX Model
import onnx
from onnx import optimizer
# Preprocessing: load the model to be optimized.
model_path = 'path/to/the/model.onnx'
original_model = onnx.load(model_path)
print('The model before optimization:\n{}'.format(original_model))
# A full list of supported optimization passes can be found here:
# https://github.com/onnx/onnx/blob/master/onnx/optimizer.py#L27
passes = ['fuse_consecutive_transposes']
# Apply the optimization on the original model
optimized_model = optimizer.optimize(original_model, passes)
print('The model after optimization:\n{}'.format(optimized_model))
# One can also apply the default passes on the (serialized) model
# Check the default passes here: https://github.com/onnx/onnx/blob/master/onnx/optimizer.py#L41
optimized_model = optimizer.optimize(original_model)
3.7 Running Shape Inference on an ONNX Model
import onnx
from onnx import helper, shape_inference
from onnx import TensorProto
# Preprocessing: create a model with two nodes, Y's shape is unknown
node1 = helper.make_node('Transpose', ['X'], ['Y'], perm=[1, 0, 2])
node2 = helper.make_node('Transpose', ['Y'], ['Z'], perm=[1, 0, 2])
graph = helper.make_graph(
[node1, node2],
'two-transposes',
[helper.make_tensor_value_info('X', TensorProto.FLOAT, (2, 3, 4))],
[helper.make_tensor_value_info('Z', TensorProto.FLOAT, (2, 3, 4))],
)
original_model = helper.make_model(graph, producer_name='onnx-examples')
# Check the model and print Y's shape information
onnx.checker.check_model(original_model)
print('Before shape inference, the shape info of Y is:\n{}'.format(original_model.graph.value_info))
# Apply shape inference on the model
inferred_model = shape_inference.infer_shapes(original_model)
# Check the model and print Y's shape information
onnx.checker.check_model(inferred_model)
print('After shape inference, the shape info of Y is:\n{}'.format(inferred_model.graph.value_info))
3.8 UtilityFunctions
import onnx
import onnx.utils
model = onnx.load('path/to/the/model.onnx')
polished_model = onnx.utils.polish_model(model)





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








