SpringBoot 源码深度解析
第八章 内嵌Tomcat原理前言
内嵌Tomcat原理
Spring Boot默认支持Tomcat,Jetty,和Undertow作为底层容器。
而Spring Boot默认使用Tomcat,一旦引入spring-boot-starter-web模块,就默认使用Tomcat容器。
内嵌Tomcat自动配置原理
那些看似简单的事物,其实并不简单。我们之所以觉得他简单,是因为复杂性都被隐藏了,大概率可以提出以下几个疑问
SpringBoot是如何启动内置tomcat的SpringBoot为什么可以响应请求,他是如何配置的SpringMvc
SpringBoot启动内置tomcat流程
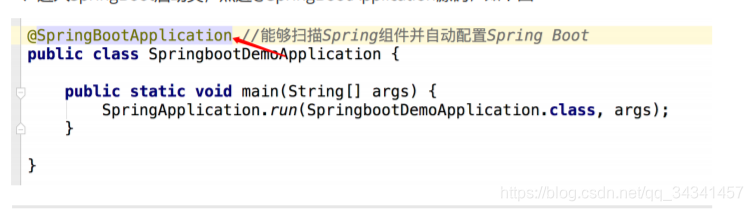
进入SpringBoot启动类,点进@SpringBootApplication源码
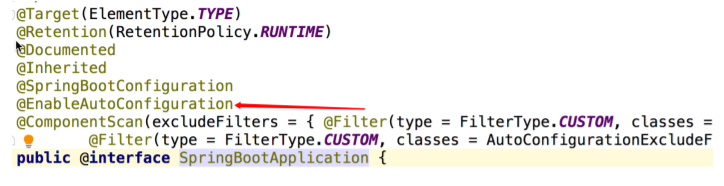
继续点进@EnableAutoConfiguration进入该注解
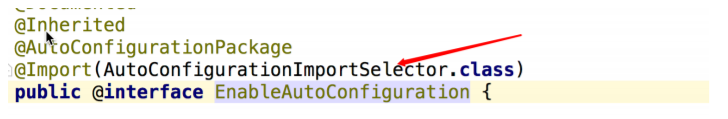
@AutoConfigurationPackage主要实现自动配置包,会扫描@SpringbootApplication标注的类所在包名及其子包,将创建的组件添加到容器中;而@Import则是导入了AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class,实现查找classpath上所有jar包中的ETA-INF/spring.factories,找出其中的自动配置类并导入到容器中,其中Web容器所对应的自动配置类为ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration。
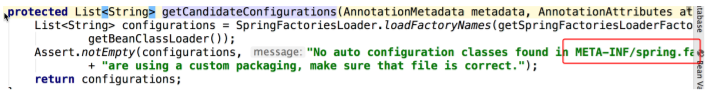
这个spring.factories配置文件是加载的spring-boot-autoconfigure的配置文件
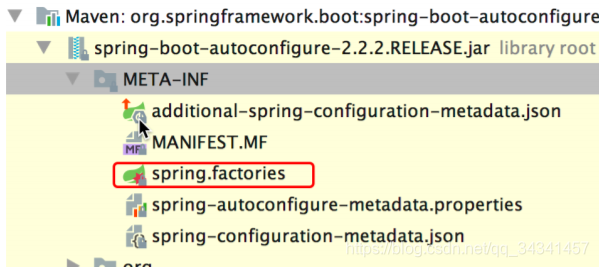
继续打开spring.factories配置文件,找到tomcat所在的类,tomcat加载在ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration配置类中
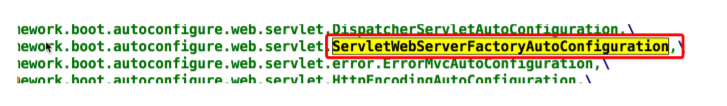
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration中支持好几种web容器,比如Tomcat、Jetty和Undertow。
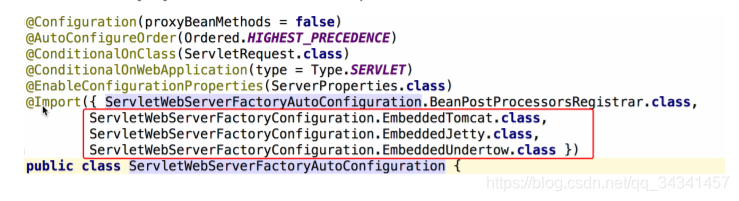
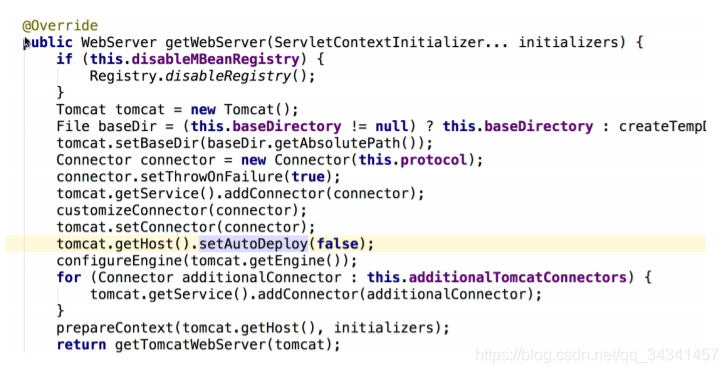
对于EmbeddedTomcat,它本身是一个就是一个FactoryBean,是用来实例化TomcatServletWebServerFactory的。此时TomcatServletWebServerFactory中就包含了创建和启动Tomcat的方法getWebServer()。
我们点击进入EmbeddedTomcat中,查看下的getWebServer()方法:
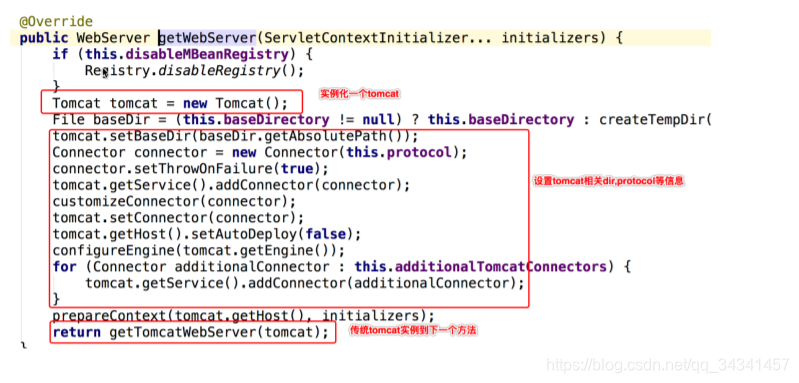
这段代码的作用就是处理Tomcat容器对象的创建、环境配置和启动。
继续进入getTomcatWebServer()等方法,一直往下跟到tomcat初始化方法,调用tomcat.start()方法,tomcat就正式开启运行:
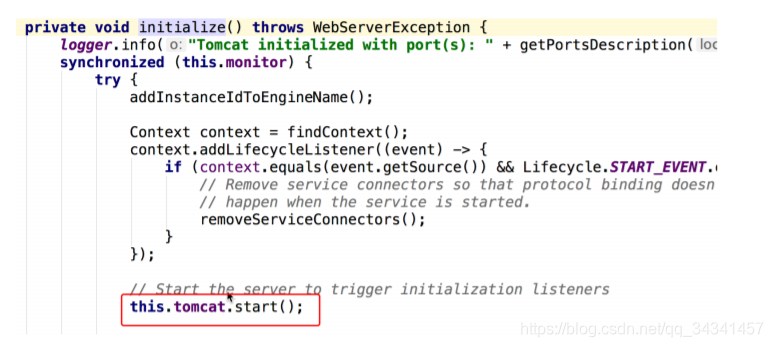
getWebServer()的调用
首先进入SpringBoot启动类的run方法:
SpringApplication.run(HppaApplication.class, args);
然后进入run方法:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//StopWatch主要是用来统计每项任务执行时长,例如Spring Boot启动占用总时长。
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
//第一步:获取并启动监听器 通过加载META-INF/spring.factories 完成了SpringApplicationRunListener实例化工作
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//实际上是调用了EventPublishingRunListener类的starting()方法
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new
DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//第二步:构造容器环境,简而言之就是加载系统变量,环境变量,配置文件
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
//设置需要忽略的bean
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//打印banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//第三步:创建容器
context = createApplicationContext();
//第四步:实例化SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,用来支持报告关于启动的错误
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class },
context);
//第五步:准备容器 这一步主要是在容器刷新之前的准备动作。包含一个非常关键的操作:
将启动类注入容器,为后续开启自动化配置奠定基础。
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners,applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//第六步:刷新容器 springBoot相关的处理工作已经结束,接下的工作就交给了spring。 内部会调用spring的refresh方法,
// refresh方法在spring整个源码体系中举足轻重,是实现 ioc 和 aop的关键。
refreshContext(context);
//第七步:刷新容器后的扩展接口 设计模式中的模板方法,默认为空实现。如果有自定义需求,可以重写该方法。比如打印一些启动结束log,或者一些其它后置处理。
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(),
stopWatch);
}
//发布应用已经启动的事件
listeners.started(context);
/*
* 遍历所有注册的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner,并执行其run()方法。
* 我们可以实现自己的ApplicationRunner或者CommandLineRunner,来对SpringBoot的启动过程进行扩展。
*/
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
//应用已经启动完成的监听事件
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
其中refreshContext(context)主要负责容器的刷新;点击进入:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context
initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
一直点击refresh()方法``onRefresh()会调用到ServletWebServerApplicationContext中的createWebServer()
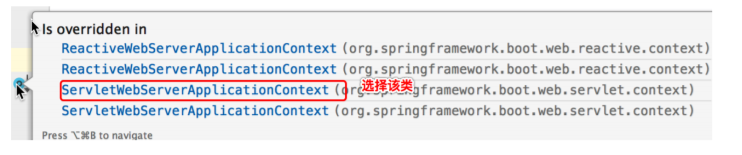
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
} else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
} catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
createWebServer()就是启动web服务,但是还没有真正启动Tomcat,既然webServer是通过ServletWebServerFactory来获取的,那就来看看这个工厂。
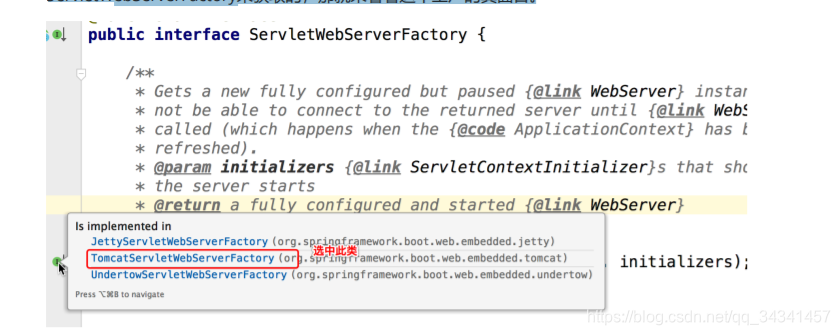
点击进入getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer… initializers).方法








 本文详细探讨了SpringBoot如何内嵌Tomcat作为默认Web服务器,从自动配置原理到启动流程,揭示了SpringBoot启动内置Tomcat的细节。通过分析@SpringBootApplication源码,了解了@EnableAutoConfiguration的工作方式,以及如何通过spring.factories加载自动配置类。在启动流程中,重点讲解了从SpringApplication.run到refreshContext的过程,最后深入到createWebServer方法,展示了Tomcat的实例化和启动步骤。
本文详细探讨了SpringBoot如何内嵌Tomcat作为默认Web服务器,从自动配置原理到启动流程,揭示了SpringBoot启动内置Tomcat的细节。通过分析@SpringBootApplication源码,了解了@EnableAutoConfiguration的工作方式,以及如何通过spring.factories加载自动配置类。在启动流程中,重点讲解了从SpringApplication.run到refreshContext的过程,最后深入到createWebServer方法,展示了Tomcat的实例化和启动步骤。
















 1028
1028

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








