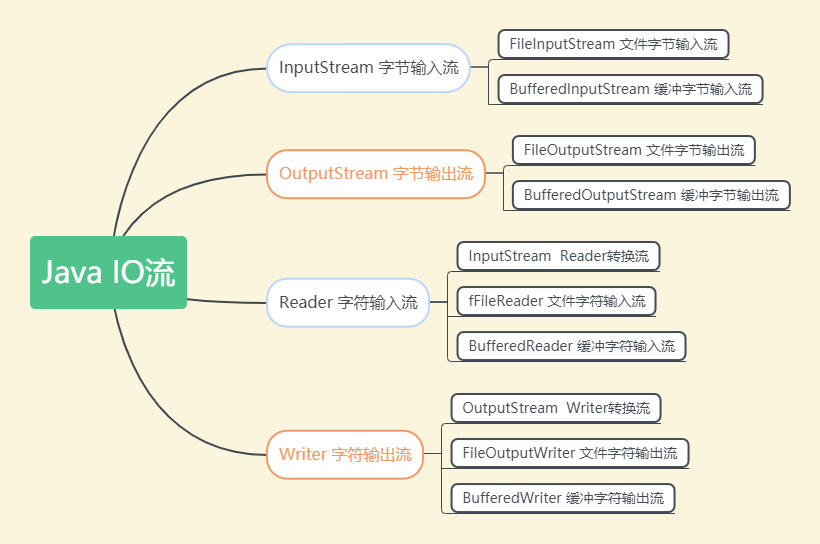
IO流简单使用
输入和输出是相对于程序来说的,读取到程序中叫做输入,写到文件中叫输出.
InputStream 字节输入流
InputStream 字节输入流基类,是字节输入流所有类的超类
// 从输入流中读取数据中下一个字节
abstract int read();
// 读取一定数量的字节,并将其缓冲到 b 数组中
int read(byte[] b);
// 读取最多 len 个字节,并并将其缓冲到 b 数组中
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len);
// 跳过或丢弃数据中 n 个字节
long skip(lone n);
// 关闭流并释放流关系中所有资源
void close();
OutputStream 字节输出流
OutputStream 字节输出流基类,是字节输出流所有类的超类
// 讲指定的字节写入输出流
abstract void write(int b);
// 将 b.length 个字节从 b 中写入输出流中
void write(byte[] b);
// 将 b 数组下标 off(b[off]) 后 len 个字节写入输出流
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
// 刷新输出流并写出所有缓冲的输出字节数据
void flush();
// 关闭输出流,并释放输出流相关的资源
// 关闭之前,使用flush()写出缓冲的字节
void close();
Reader 字符输入流
Reader 字符输入流,是读取字符流的抽象类
// 读取单个字符
int read();
// 将字符读入数组
int read(char[] cbuf);
// 将 len 个字符读到char数组下标 off 后面
abstract int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len);
// 跳过n个字符
long skip(long n);
// 关闭字符流,并释放相关的资源
abstract void close();
Writer 字符输出流
Writer 字符输出流,是写入字符流的抽象类
// 将 char 数组写入字符流
void write(char[] cbuf);
// 将 char 数组下标 off 后 len 个字符写入字符流
abstract void read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len);
// 写入单个字符
void write(int c);
// 写入字符串
void write(Stirng str);
// 写入字符串的某一部分
// 也是将 string 转成 char 然后执行 read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len);
void write(String str, int off, int len);
// 将指定的字符序列附加到此 Wirter
Writer append(CharSequence csq);
// 将指定字符序列的子序列追加到此 Writer
Writer append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end)
// 将指定字符追加到此 Writer
Writer append(char c);
// 刷新流的缓冲
abstract void flush();
// 关闭流,但是要刷新该流,否则关闭时会报错 IOException
abstract void close();
实例
- 实例不全,需自己动手探讨其中的奥秘
- 实例中使用了junit等注解,我在这里贴一。也可以不用,就是吧log换成println多写几个类
<dependencies>
<!--lombok 注解集合 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.12</version>
</dependency>
<!-- logback 记录日志框架-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--Junit 单元测试框架-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author http://cnblogs.com/beixuan
*/
@Slf4j
public class StreamTest {
private static String fileName = "D:/Stream.txt";
private static String fileName1 = "D:/Reader.txt";
private static String fileName2 = "D:/红色高跟鞋.mp3";
@Before
public void getFile(){
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.exists()){
try {
//创建文件
file.createNewFile();
log.debug("创建文件成功:{}", fileName);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
File file1 = new File(fileName1);
if (!file1.exists()){
try {
//创建文件
file1.createNewFile();
log.debug("创建文件成功:{}", fileName1);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 字节输出流
*/
@Test
public void testOutputStream(){
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(fileName);
fos.write("Hello world".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//刷新缓冲区
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.flush();
log.debug("写入数据成功");
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 字节输入流
*/
@Test
public void testInputStream(){
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
int i = 0;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
while ((i = fis.read()) != -1){
// i是字符对应的ASCII码
sb.append((char) i);
}
log.debug("{}:\n{}", fileName, sb.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 字符输出流
*/
@Test
public void testWriter(){
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
try {
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(fileName1));
osw.write("可以输出中文哦!\n\r\t还又'\\n\\r\\t'");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (osw != null){
try {
osw.flush();
osw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 字符输入流
*/
@Test
public void testReader(){
// InputStreamReader 转换流
InputStreamReader isr = null;
try {
isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName2));
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int i;
while ((i = isr.read()) != -1){
sb.append((char)i);
}
log.debug("{}:\n{}", fileName2, sb);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (isr != null){
try {
isr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 高效流对比
*/
@Test
public void IoEquals() throws IOException{
//操作的是一个3.19MB的音频文件 它们之间文件越大,效果就越明显
/***********************************************************************/
FileInputStream fis1 = new FileInputStream(fileName2);
FileOutputStream fos1 = new FileOutputStream(fileName);
int i;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((i = fis1.read()) != -1){
fos1.write(i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.debug("第一种高效流:{}", endTime - startTime);
fos1.close();
fis1.close();
/***********************************************************************/
FileInputStream fis2 = new FileInputStream(fileName2);
FileOutputStream fos2 = new FileOutputStream(fileName);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((i = fis2.read(bytes)) != -1){
fos2.write(bytes, 0, i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.debug("第二种高效流:{}", endTime - startTime);
fos2.close();
fis2.close();
/***********************************************************************/
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(fileName2));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(fileName));
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((i = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){
bos.write(bytes, 0, i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.debug("第三种高效流:{}", endTime - startTime);
bos.close();
bis.close();
/**
* 第一种高效流:20186
* 第三种高效流:30
* 第二种高效流:10
* 这么对比下 BufferedInputStream BufferedOutputStream 是最好的配合
*/
}
}
小结
- 字节流常用于图片、音频、视频文件及PPT、Word文件.
- 字符流常用于处理文本类型的文件如txt、ini文件等
- 字节流也可以处理纯文本文件,但字符流不可以处理图片视频等非纯文本类型的文件





















 143
143

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








