MVP
View和Model的交互都由Persenter完成(View和Model的接口都只在Personter中被调用)
- View 对应于Activity,负责View的绘制以及与用户交互
- Model 依然是业务逻辑和实体模型
- Presenter 负责完成View于Model间的交互
MVP 与 MVC 区别
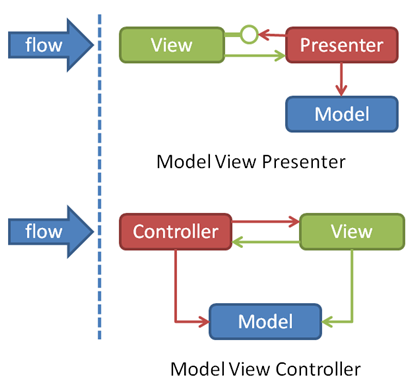
MVC: View允许与View进行交互
MVP: Model与View之间的交互由Presenter完成,Presenter与View之间的交互是通过接口的
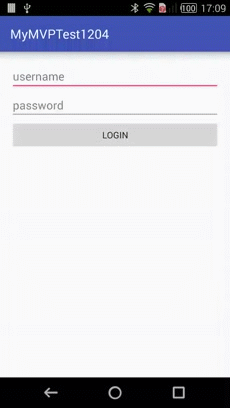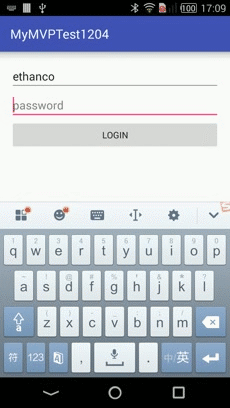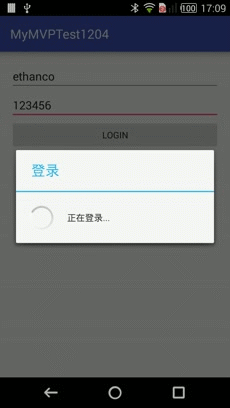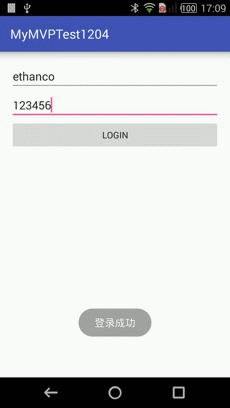
效果
先来创建Bean对象
public class User {
public User(String username, String password) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
private String username;
private String password;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
创建View和Model的接口
先写接口,后写实现
Model的登录接口
public interface IUserMode {
/**
* 登录
*
* @param user
* @return 约定返回"true"为登录成功,其他为登录失败的错误信息
*/
String login(User user);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
View的登录接口
public interface IUserView {
/**
* 登录成功
*/
void onLoginSuccess();
/**
* 登录失败
*
* @param error
*/
void onLoginFailed(String error);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
创建Presenter
public class UserPresenter {
private final IUserView userView;
private final UserMode userMode;
public UserPresenter(IUserView userView) {
this.userView = userView;
this.userMode = new UserMode();
}
/**
* 登录
*
* @param user
*/
public void login(final User user) {
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
final String res = userMode.login(user);
new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if ("true".equals(res)) {
userView.onLoginSuccess();
} else {
userView.onLoginFailed(res);
}
}
});
}
}.start();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
其中,login方法虽然实现了登录操作,并且通过new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper())使IUserView的回调运行在主线程,但是这显然代码太臃肿了,如果使用JAVA8的Lambda表达式,就会简洁很多,在Android Studio中使用Lambda,请参考这里
创建View和Model的实现类
Model的登录实现类
public class UserMode implements IUserMode {
@Override
public String login(User user) {
boolean networkError = false; //网络是否异常
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);//模拟网络连接
if (networkError) {
return "网络异常";
} else if ("ethanco".equals(user.getUsername()) && "123456".equals(user.getPassword())) {
return "true";
} else {
return "账号或密码错误";
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return e.getMessage();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
View的登录实现 - Activity
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements IUserView, View.OnClickListener {
private UserPresenter userPresenter;
private EditText etUserName;
private EditText etPassword;
private ProgressDialog loginProgreess;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
etUserName = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_userName);
etPassword = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_password);
findViewById(R.id.btn_login).setOnClickListener(this);
userPresenter = new UserPresenter(this);
}
@Override
public void onLoginSuccess() {
loginProgreess.dismiss();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "登录成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public void onLoginFailed(String error) {
loginProgreess.dismiss();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "登录失败:" + error, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String username = etUserName.getText().toString().trim();
String password = etPassword.getText().toString().trim();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(username) || TextUtils.isEmpty(password)) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "账号或密码不能为空", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}
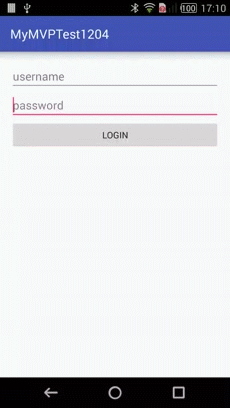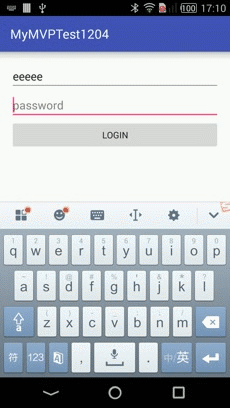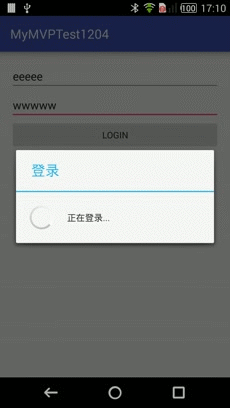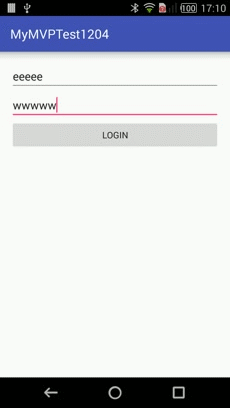
loginProgreess = ProgressDialog.show(this, "登录", "正在登录...");
userPresenter.login(new User(username, password));
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
参考文章
http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/46596109
http://blog.csdn.net/knxw0001/article/details/39637273























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








