# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
多元分类:逻辑回归分类器 并绘制pcolormesh伪彩图
sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression(
solver='liblinear',
C=正则强度)
'''
# pcolormesh(x, y, c=d, cmap='jet') cmap:渐变色映射
plt.pcolormesh(...):
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([-1, -2, -3, -4])
a.shape, b.shape
Out[55]: ((3,), (4,))
c = np.meshgrid(a, b); c # c is a 'list', not 'numpy.array'
Out[57]: # c[0]:沿行(axis=0)广播, 每一行元素跟上一行相同
[array([[1, 2, 3], # c[1]:沿列(axis=1)广播, 每一列元素跟上一列相同
[1, 2, 3], # (c[0],c[1])组成的坐标点(x,y)将覆盖并形成(1<=x<=3,-4<=y<=-1)区间组成的2*3的矩形
[1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3]]),
array([[-1, -1, -1],
[-2, -2, -2],
[-3, -3, -3],
[-4, -4, -4]])]
c[0].shape, c[1].shape
Out[61]: ((4, 3), (4, 3))
plt.pcolormesh(c[0], c[1], c=...) # c[0]表示点横坐标,c[1]表示纵坐标
对样本(c[0], c[1])周围(包括样本所在坐标)的四个坐标点进行着色,C代表着色方案
# 点(c[0], c[1])所有坐标点如下:
'''
^
|---1------2------3---->
|
-1 (1,-1) (2,-1) (3,-1)
|
-2 (1,-2) (2,-2) (3,-2)
|
-3 (1,-3) (2,-3) (3,-3)
|
-4 (1,-4) (2,-4) (3,-4)
|
'''
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Jul 31 16:12:18 2018
@author: Administrator
"""
'''
多元分类:逻辑回归分类器
sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression(
solver='liblinear',
C=正则强度)
'''
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn.linear_model as lm
# train_set
x = np.array([
[4, 7],
[3.5, 8],
[3.1, 6.2],
[0.5, 1],
[1, 2],
[1.2, 1.9],
[4, 2],
[5.7, 1.5],
[5.4, 2.2]]) # 散点[x,y]
y = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2]) # 多元分类 3类
# 逻辑回归分类器
model = lm.LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear', C=50) # C
model.fit(x, y)
plt.figure('Logistic Classification', facecolor='lightgray')
plt.title('Logistic Classification', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('x', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('y', fontsize=14)
plt.tick_params(labelsize=10)
'''
pcolormesh参数设置:
'''
l, r, h = x[:, 0].min() - 1, x[:, 0].max() + 1, 0.005 # 左边界,右边界,水平方向点间距
b, t, v = x[:, 1].min() - 1, x[:, 1].max() + 1, 0.005 # 下边界,上边界,垂直方向点间距
#print(np.arange(l, r, h).shape, np.arange(b, t, v).shape) # (1440,) (1800,),shape不同,不能直接作为输入,转为
grid_x = np.meshgrid(np.arange(l, r, h), np.arange(b, t, v)) # (m-array,n-array)--> list(mat(m,n), mat(m,n))
print(grid_x[0]) # x[i, j] (1800, 1440) <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
print(grid_x[1]) # y[i, j] (1800, 1440) <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
#print(grid_x[1].shape) # (1800, 1440) <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
flat_x = np.c_[grid_x[0].ravel(), grid_x[1].ravel()] # 保证输入散点的坐标点横纵坐标个数一样
flat_y = model.predict(flat_x) # 输入栅格点阵坐标,模型预测输出的分类
grid_y = flat_y.reshape(grid_x[0].shape) # 分类标签:用做pcolormesh栅格着色的依据
print(grid_y)
#[[1 1 1 ... 2 2 2] # 0, 1, 2 分别代表三种不同颜色
# [1 1 1 ... 2 2 2]
# [1 1 1 ... 2 2 2]
# ...
# [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
# [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
# [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]
# pcolormesh: 伪彩图 pcolormesh(X, Y, C)
# X,Y均为2-D array,如果为1-D 会自动广播,X和Y构成网格点阵
# X,Y对应位置元素x[i,j]和y[i,j]组成一个坐标点(x[i,j],y[i,j]),对样本周围(包括样本所在坐标)的四
#个坐标点进行着色,C代表着色方案
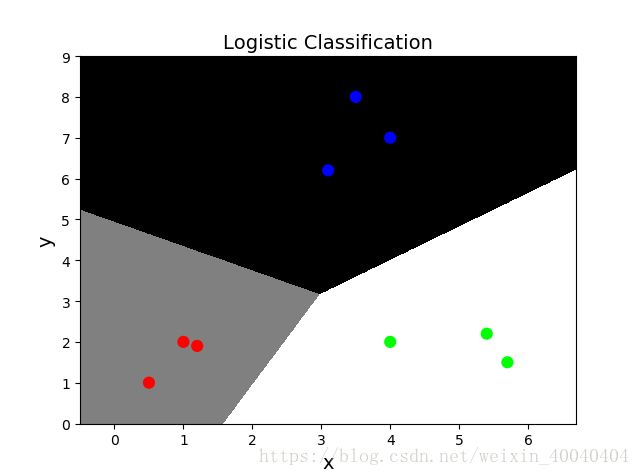
plt.pcolormesh(grid_x[0], grid_x[1], grid_y, cmap='gray') # gray_r 与gray的色带相反
plt.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], c=y, cmap='brg', s=60) # 颜色映射
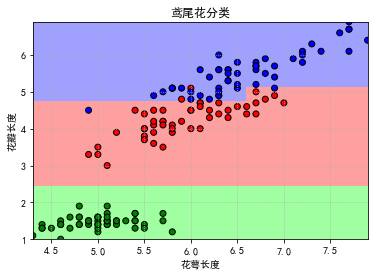
接下来主要介绍如何利用plt.pcolormesh来绘制如下的分类图
plt.pcolormesh的作用在于能够直观表现出分类边界。如果只是单纯的绘制散点图,效果如下:
那么我们就看不出分类的边界。
下面将以鸢尾花数据集为例说明如何使用plt.pcolormesh,该数据集一共包含3类鸢尾花的数据
首先引入必要的库
-
import numpy as np -
import pandas as pd -
import matplotlib as mpl -
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt -
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
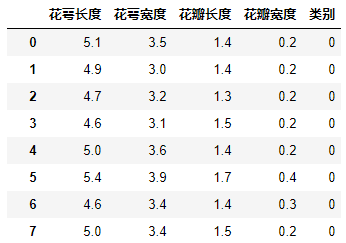
然后读取鸢尾花数据集,并对数据做一定的处理
-
iris_feature = u'花萼长度', u'花萼宽度', u'花瓣长度', u'花瓣宽度',u'类别' -
path = 'iris.data' # 数据文件路径 -
data = pd.read_csv(path, header=None) -
data.columns=iris_feature -
data['类别']=pd.Categorical(data['类别']).codes
处理完成后,一共有150组数据,数据长下面这样子
取花萼长度和花瓣长度做为特征,训练决策树模型
-
x_train = data[['花萼长度','花瓣长度']] -
y_train = data['类别'] -
model = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy', min_samples_leaf=3) -
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
训练完模型后,现在需要画出分类边界,首先需要在横纵坐标各取500点,一共组成2500个点,然后把这2500个点送进决策树,来算出所属的种类,代码如下:
-
N, M = 500, 500 # 横纵各采样多少个值 -
x1_min, x2_min = x_train.min(axis=0) -
x1_max, x2_max = x_train.max(axis=0) -
t1 = np.linspace(x1_min, x1_max, N) -
t2 = np.linspace(x2_min, x2_max, M) -
x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(t1, t2) # 生成网格采样点 -
x_show = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1) # 测试点 -
y_predict=model.predict(x_show)
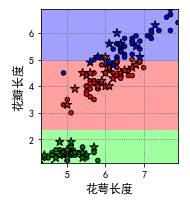
接着就可以绘制出分类图了。由于该数据集中一共有三种鸢尾花,所以绘制图片的时候需要三种颜色
-
cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['#A0FFA0', '#FFA0A0', '#A0A0FF']) -
cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['g', 'r', 'b'])
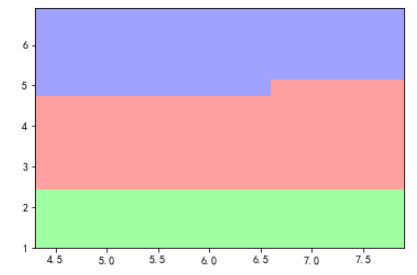
接着使用plt.pcolormesh来绘制分类图
-
plt.pcolormesh(x1, x2, y_predict.reshape(x1.shape), cmap=cm_light) -
plt.show()
plt.pcolormesh()会根据y_predict的结果自动在cmap里选择颜色
结果如下图
接着再把散点图也画上就大功告成了,结果如下:
完整代码如下
-
import numpy as np -
import pandas as pd -
import matplotlib as mpl -
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt -
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier -
iris_feature = u'花萼长度', u'花萼宽度', u'花瓣长度', u'花瓣宽度',u'类别' -
path = 'iris.data' # 数据文件路径 -
data = pd.read_csv(path, header=None) -
data.columns=iris_feature -
data['类别']=pd.Categorical(data['类别']).codes -
x_train = data[['花萼长度','花瓣长度']] -
y_train = data['类别'] -
model = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy', min_samples_leaf=3) -
model.fit(x_train, y_train) -
N, M = 500, 500 # 横纵各采样多少个值 -
x1_min, x2_min = x_train.min(axis=0) -
x1_max, x2_max = x_train.max(axis=0) -
t1 = np.linspace(x1_min, x1_max, N) -
t2 = np.linspace(x2_min, x2_max, M) -
x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(t1, t2) # 生成网格采样点 -
x_show = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1) # 测试点 -
y_predict=model.predict(x_show) -
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] -
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False -
cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['#A0FFA0', '#FFA0A0', '#A0A0FF']) -
cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['g', 'r', 'b']) -
plt.xlim(x1_min, x1_max) -
plt.ylim(x2_min, x2_max) -
plt.pcolormesh(x1, x2, y_predict.reshape(x1.shape), cmap=cm_light) -
plt.scatter(x_train['花萼长度'],x_train['花瓣长度'],c=y_train,cmap=cm_dark,marker='o',edgecolors='k') -
plt.xlabel('花萼长度') -
plt.ylabel('花瓣长度') -
plt.title('鸢尾花分类') -
plt.grid(True,ls=':') -
plt.show()























 2964
2964











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








