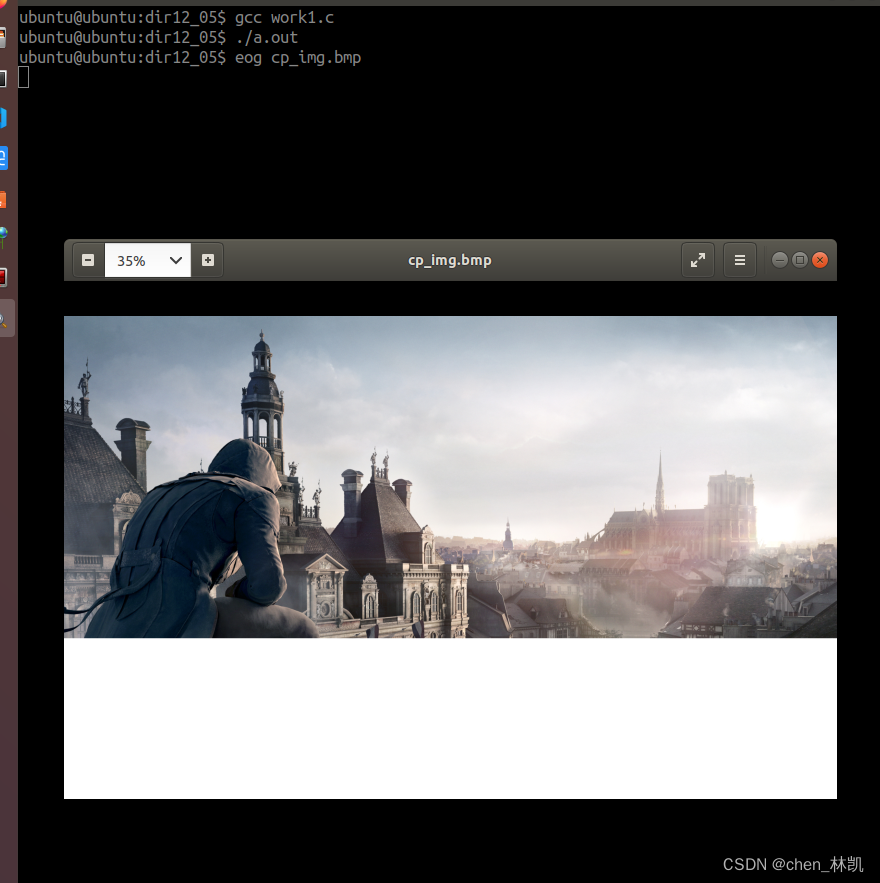
使用文件IO对图像进行读写操作
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int fd = -1;
fd = open("./img.bmp", O_RDONLY);
if(fd == -1){
perror("open ./img.bmp error");
return -1;
}
int cp_fd = -1;
cp_fd = open("./cp_img.bmp", O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664);
if(cp_fd == -1){
perror("open ./cp_img.bmp error");
return -1;
}
char buf[10];
int res;
while((res = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf))) > 0){
write(cp_fd, buf, res);
}
lseek(cp_fd, 18, SEEK_SET);
unsigned int weight;
unsigned int high;
read(cp_fd, &weight, sizeof(weight));
read(cp_fd, &high, sizeof(high));
lseek(cp_fd, 54, SEEK_SET);
unsigned char pix[3] = {255, 255, 255};
int i=0, j=0;
for(i=0; i<(high)/3; i++){
for(j=0; j<weight; j++){
write(cp_fd, pix, sizeof(pix));
}
}
close(fd);
close(cp_fd);
return 0;
}
使用stat函数实现 ls -l 指令功能
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
void print_filetype(struct stat fstat);
void print_privilege(struct stat fstat);
void print_user_name(struct stat fstat);
void print_group_name(struct stat fstat);
void print_time(struct stat fstat);
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 2){
printf("参数输入错误");
return -1;
}
DIR *dp = NULL;
dp = opendir(argv[1]);
if(dp == NULL){
perror("opendir error");
return -1;
}
struct dirent *fp = NULL;
char filepath[128];
struct stat fstat;
while((fp = readdir(dp)) != NULL){
if(fp->d_name[0] == '.'){
continue;
}
int res = snprintf(filepath, sizeof(filepath), "%s%s", argv[1], fp->d_name);
stat(filepath, &fstat);
print_filetype(fstat);
print_privilege(fstat);
printf(" %ld", fstat.st_nlink);
print_user_name(fstat);
print_group_name(fstat);
printf(" %ld", fstat.st_size);
print_time(fstat);
printf(" %s", fp->d_name);
putchar(10);
}
return 0;
}
void print_filetype(struct stat fstat){
switch(fstat.st_mode & S_IFMT){
case S_IFSOCK:
printf("s");
break;
case S_IFLNK:
printf("l");
break;
case S_IFREG:
printf("-");
break;
case S_IFBLK:
printf("b");
break;
case S_IFDIR:
printf("d");
break;
case S_IFCHR:
printf("c");
break;
case S_IFIFO:
printf("p");
break;
}
}
void print_privilege(struct stat fstat){
int n = 8;
while(n>=0){
if(fstat.st_mode & 1<<n){
switch(n%3){
case 2:
printf("%c", 'r');
break;
case 1:
printf("%c", 'w');
break;
case 0:
printf("%c", 'x');
}
}else{
printf("%c", '-');
}
n--;
}
}
void print_user_name(struct stat fstat){
printf(" %s", getpwuid(fstat.st_uid)->pw_name);
}
void print_group_name(struct stat fstat){
printf(" %s", getgrgid(fstat.st_gid)->gr_name);
}
void print_time(struct stat fstat){
struct tm *tp = NULL;
tp = localtime(&fstat.st_ctime);
switch(tp->tm_mon + 1){
case 1:
printf(" 一");
break;
case 2:
printf(" 二");
break;
case 3:
printf(" 三");
break;
case 4:
printf(" 四");
break;
case 5:
printf(" 五");
break;
case 6:
printf(" 六");
break;
case 7:
printf(" 七");
break;
case 8:
printf(" 八");
break;
case 9:
printf(" 九");
break;
case 10:
printf(" 十");
break;
case 11:
printf(" 十一");
break;
case 12:
printf(" 十二");
}
printf(" %2d %2d:%-2d", tp->tm_mday, tp->tm_hour, tp->tm_min);
}







 文章详细介绍了如何使用C语言中的文件I/O操作进行图像读写,以及如何模仿`ls-l`命令的功能,包括文件类型、权限、链接数、用户和组名等信息的处理。
文章详细介绍了如何使用C语言中的文件I/O操作进行图像读写,以及如何模仿`ls-l`命令的功能,包括文件类型、权限、链接数、用户和组名等信息的处理。
















 1033
1033

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








