1. 问题
图的m着色问题。给定无向连通图G和m种颜色,用这些颜色给图的顶点着色,每个顶点一种颜色。如果要求G的每条边的两个顶点着不同颜色。给出所有可能的着色方案;如果不存在,则回答“NO”。
2. 解析
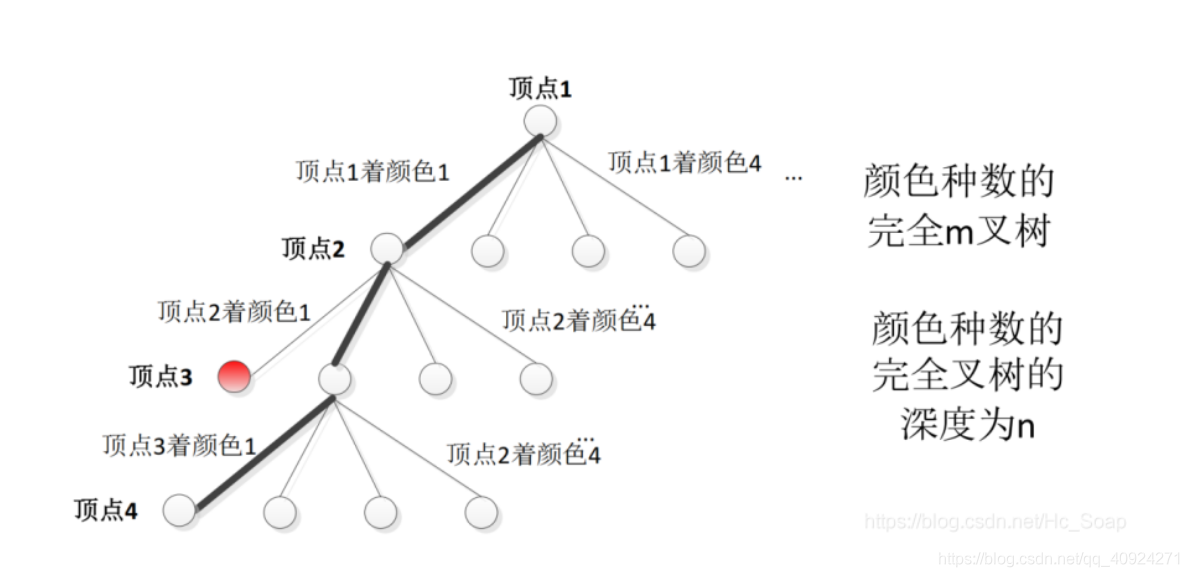
设 G 有 n 个顶点,将顶点编号为 1,2,…,n,则搜索空间为深度n的m叉完全树,将颜色编号为1,2,…,m,结点<x1,x2,…,xn>(x1,x2,…,xk∈{1,…,m},1<=k<=n)表示顶点 1 的颜色x1,顶点2的颜色 ,…, 顶点 k的颜色xk
3. 设计
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<cctype>
#include<iomanip>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include<stdexcept>
#include<fstream>
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define debug() puts("what the fuck!")
#define debug(a) cout<<#a<<"="<<a<<endl;
#define speed {ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); };
#define ll long long
#define mod 998244353
using namespace std;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const int maxn = 1e3 + 10;
const int N = 1e2 + 10;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double esp_0 = 1e-6;
ll gcd(ll x, ll y) {
return y ? gcd(y, x % y) : x;
}
ll lcm(ll x, ll y) {
return x * y / gcd(x, y);
}
ll extends_gcd(ll a, ll b, ll& x, ll& y) {
if (b == 0) {
x = 1;
y = 0;
return a;
}
ll gcdd = extends_gcd(b, a % b, x, y);
ll temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp - (a / b) * y;
return gcdd;
}
int m, n, k;
int G[N][N];
int color[N];
int res;
void dfs(int x) {
if (x == n + 1) {
res++;
return;
}
else {
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
bool flag = false;
for (int y = 1; y <= x; y++) {
if (G[x][y] == 1 && color[y] == i) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if (flag == true)
continue;
color[x] = i;
dfs(x + 1);
color[x] = 0;
}
}
}
char mp[N][N];
int main() {
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k); // n个点m条边k种颜色
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x, y;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
G[x][y] = 1;
G[y][x] = 1;
}
dfs(1);
if (res == 0)
puts("NO");
else
printf("%d", res);
return 0;
}
4. 分析

5. 源码
color




 本文讨论了如何用给定的m种颜色对无向连通图G进行着色,确保每条边的两端颜色不同。通过深度优先搜索策略,生成所有可能的着色方案,如果不存在着色方案则输出'NO'。
本文讨论了如何用给定的m种颜色对无向连通图G进行着色,确保每条边的两端颜色不同。通过深度优先搜索策略,生成所有可能的着色方案,如果不存在着色方案则输出'NO'。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








