对链表的删除操作
从一个动态链表中删去一个结点,并不是真正从内存中把它抹掉,而是把它从链表中分离开来,只要撤销原来的链接关系即可。
随堂练习
题目:写一函数以删除动态链表中指定的结点。
解题思路:
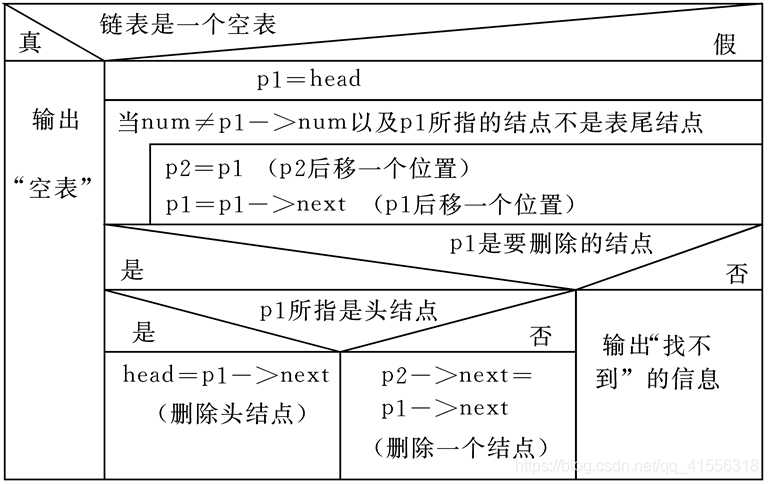
一、从p指向的第一个结点开始,检查该结点中的num值是否等于输入的要求删除的那个学号。
二、如果相等就将该结点删除,如不相等,就将p后移一个结点,再如此进行下去,直到遇到表尾为止。
三、可以设两个指针变量p1和p2,先使p1指向第一个结点 。
四、如果要删除的不是第一个结点,则使p1后移指向下一个结点(将p1->next赋给p1),在此之前应将p1的值赋给p2 ,使p2指向刚才检查过的那个结点。
五、将以上几点我们综合得出算法流程图:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define LEN sizeof(struct student) // student结构的大小
struct student *creat(); //创建链表
struct student *del(struct student *head, int num); //del函数用于删除结点, *head即链表
//的头指针, num是要删除的结点num。
void print(struct student *head); //打印链表
struct student
{
int num;
float score;
struct student *next;
};
int n; //全局变量,用来记录存放了多少数据。
void main()
{
struct student *stu, *p;
int n;
stu = creat();
p = stu;
print(p);
printf("Please enter the num to delete: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
print(del(p, n));
printf("\n\n");
system("pause");
}
struct student *creat()
{
struct student *head;
struct student *p1, *p2;
p1 = p2 = (struct student *)malloc(LEN); // LEN是student结构的大小
printf("Please enter the num :");
scanf("%d", &p1->num);
printf("Please enter the score :");
scanf("%f", &p1->score);
head = NULL;
n = 0;
while (p1->num)
{
n++;
if (1 == n)
{
head = p1;
}
else
{
p2->next = p1;
}
p2 = p1;
p1 = (struct student *)malloc(LEN);
printf("\nPlease enter the num :");
scanf("%d", &p1->num);
printf("Please enter the score :");
scanf("%f", &p1->score);
}
p2->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void print(struct student *head)
{
struct student *p;
printf("\nThere are %d records!\n\n", n);
p = head;
if (head)
{
do
{
printf("学号为 %d 的成绩是: %f\n", p->num, p->score);
p = p->next;
} while (p);
}
}
struct student *del(struct student *head, int num)
{
struct student *p1, *p2;
if (NULL == head)
{
printf("\nThis list is null!\n");
goto end;
}
p1 = head;
while (p1->num != num && p1->next != NULL)
{
p2 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
if (num == p1->num)
{
if (p1 == head)
{
head = p1->next;
}
else
{
p2->next = p1->next;
}
printf("Delete No: %d succeed!\n", num);
n = n - 1;
}
else
{
printf("%d not been found!\n", num);
}
end:
return head;
}对链表的插入操作
对链表的插入是指将一个结点插入到一个已有的链表中。
为了能做到正确插入,必须解决两个问题:
① 怎样找到插入的位置;
② 怎样实现插入。
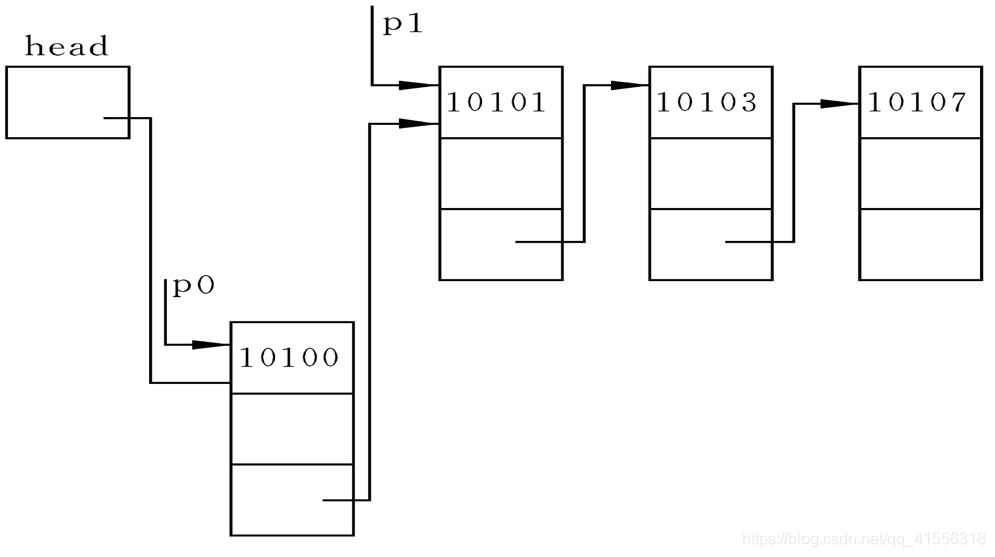
我们可以先用指针变量p0指向待插入的结点,p1指向第一个结点。将p0->num与p1->num相比较,如果p0->num>p1-> num ,此时将p1后移,并使p2指向刚才p1所指的结点。
情形1:插入位置在链表头
情形2:插入位置在链表尾
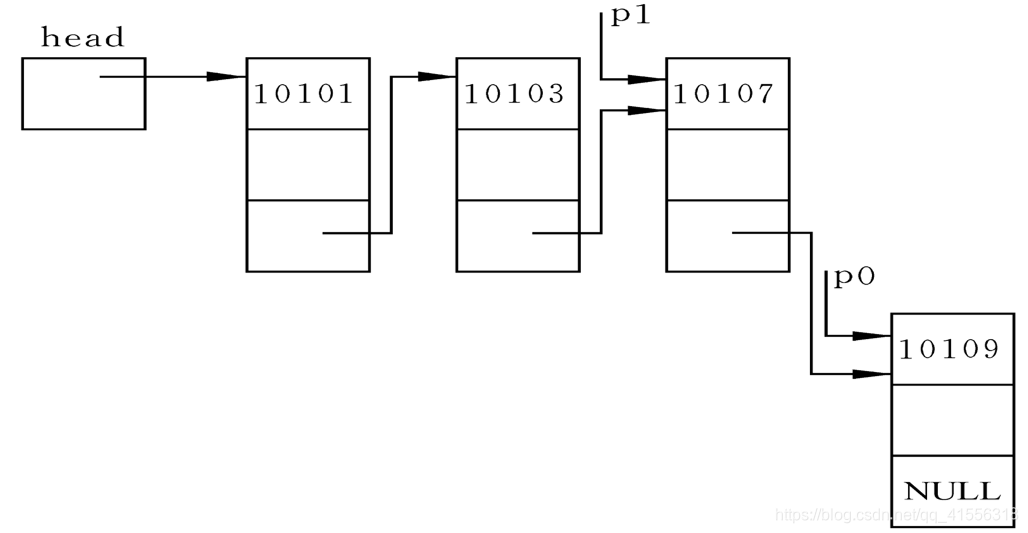
情形3:插入位置属于中部

流程图如下:
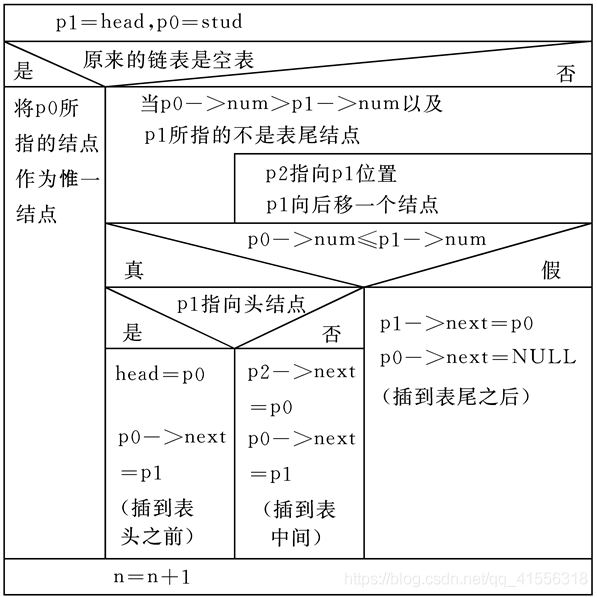
源程序如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define LEN sizeof(struct student) // student结构的大小
struct student *creat(); //创建链表
struct student *del(struct student *head, int num); //del函数用于删除结点, *head即链表
//的头指针, num是要删除的结点num。
struct student *insert(struct student *head, struct student *stu_2); // 第一个参数需要被插入的链表
// 第二个参数待插入的结构的地址
void print(struct student *head); //打印链表
struct student
{
int num;
float score;
struct student *next;
};
int n; //全局变量,用来记录存放了多少数据。
void main()
{
struct student *stu, *p, stu_2;
int n;
stu = creat();
p = stu;
print(p);
printf("\nPlease input the num to delete: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
print(del(p, n));
printf("\nPlease input the num to insert: ");
scanf("%d", &stu_2.num);
printf("Please input the score: ");
scanf("%f", &stu_2.score);
p = insert(stu, &stu_2);
print(p);
printf("\n\n");
system("pause");
}
struct student *creat()
{
struct student *head;
struct student *p1, *p2;
p1 = p2 = (struct student *)malloc(LEN); // LEN是student结构的大小
printf("Please enter the num :");
scanf("%d", &p1->num);
printf("Please enter the score :");
scanf("%f", &p1->score);
head = NULL;
n = 0;
while (p1->num)
{
n++;
if (1 == n)
{
head = p1;
}
else
{
p2->next = p1;
}
p2 = p1;
p1 = (struct student *)malloc(LEN);
printf("\nPlease enter the num :");
scanf("%d", &p1->num);
printf("Please enter the score :");
scanf("%f", &p1->score);
}
p2->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void print(struct student *head)
{
struct student *p;
printf("\nThere are %d records!\n\n", n);
p = head;
if (head)
{
do
{
printf("学号为 %d 的成绩是: %f\n", p->num, p->score);
p = p->next;
} while (p);
}
}
struct student *del(struct student *head, int num)
{
struct student *p1, *p2;
if (NULL == head)
{
printf("\nThis list is null!\n");
goto end;
}
p1 = head;
while (p1->num != num && p1->next != NULL)
{
p2 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
if (num == p1->num)
{
if (p1 == head)
{
head = p1->next;
}
else
{
p2->next = p1->next;
}
printf("Delete No: %d succeed!\n", num);
n = n - 1;
}
else
{
printf("%d not been found!\n", num);
}
end:
return head;
}
struct student *insert(struct student *head, struct student *stu_2)
{
struct student *p0, *p1, *p2;
p1 = head;
p0 = stu_2;
if (NULL == head)
{
head = p0;
p0->next = NULL;
}
else
{
while ((p0->num > p1->num) && (p1->next != NULL)) //两种情况推出while,一:
{
p2 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
if (p0->num <= p1->num)
{
if (head == p1) // p1是头结点,插入头部
{
head = p0;
}
else // 普通情况,插入中间
{
p2->next = p0;
}
p0->next = p1;
}
else // p0的num最大,插入到末尾
{
p1->next = p0;
p0->next = NULL;
}
}
n = n + 1; // 由于插入了,所以增加了一位数据成员进入链表中。
return head;
}但是这个程序有些问题需要大家齐心协力来发掘并研究方法解决!
欢迎大家评论并修正。





















 1193
1193











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








