1.问题描述
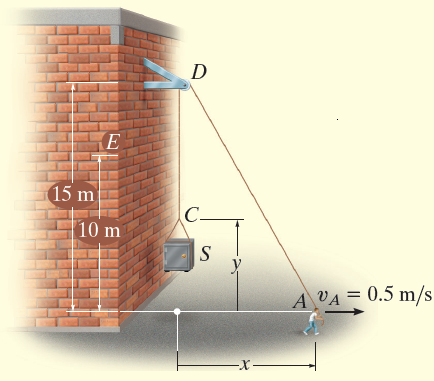
如下图所示,
A
A
A点的人通过向右行走来吊起保险箱
S
S
S,行走速度恒定为
v
A
=
0.5
m
/
s
v_A = 0.5 m/s
vA=0.5m/s。求当保险箱到达10米高度时,保险箱的速度和加速度。绳索长度为30米,绳索经过
D
D
D点的小滑轮。
2.理论解
- 位置-坐标方程。
这个问题与之前的例题不同,因为绳索段 D A DA DA同时改变方向和长度。然而,绳索的两端, A A A点和 C C C点,分别沿着 x x x轴和 y y y轴运动。
由于绳索有固定长度 l = 30 m l = 30 m l=30m,这些坐标可以建立关联,绳长在任何时刻都等于线段 D A DA DA的长度加上 C D CD CD的长度。使用勾股定理来确定 l D A l_{DA} lDA,我们有:
l D A = ( 15 ) 2 + x 2 l_{DA}=\sqrt{(15)^{2}+x^{2}} lDA=(15)2+x2
因此:
l C D = 15 − y l_{CD}=15-y lCD=15−y
{ l = l D A + l C D 30 = ( 15 ) 2 + x 2 + ( 15 − y ) y = 225 + x 2 − 15 \begin{cases} l & =l_{DA}+l_{CD} \\ 30 & =\sqrt{(15)^{2}+x^{2}}+(15-y) \\ y & =\sqrt{225+x^{2}}-15 \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧l30y=lDA+lCD=(15)2+x2+(15−y)=225+x2−15
- 时间导数。
对方程求时间导数,使用链式法则,其中 v S = d y / d t v_S = dy/dt vS=dy/dt 且 v A = d x / d t v_A = dx/dt vA=dx/dt,我们有:
v S = d y d t = [ 1 2 2 x 225 + x 2 ] d x d t = x 225 + x 2 v A \begin{gathered} v_{S}=\frac{dy}{dt}=\left[\frac{1}{2}\frac{2x}{\sqrt{225+x^{2}}}\right]\frac{dx}{dt} \\ =\frac{x}{\sqrt{225+x^2}}v_A \end{gathered} vS=dtdy=[21225+x22x]dtdx=225+x2xvA
v S = 20 225 + ( 20 ) 2 ( 0.5 ) = 0.4 m / s = 400 m m / s ↑ v_S=\frac{20}{\sqrt{225+(20)^2}}(0.5)=0.4\mathrm{m/s}=400\mathrm{mm/s}\uparrow vS=225+(20)220(0.5)=0.4m/s=400mm/s↑
a S = d 2 y d t 2 = [ − x ( d x / d t ) ( 225 + x 2 ) 3 / 2 ] x v A + [ 1 225 + x 2 ] ( d x d t ) v A + [ 1 225 + x 2 ] x d v A d t = 225 v A 2 ( 225 + x 2 ) 3 / 2 a_S=\frac{d^2y}{dt^2}=\left[\frac{-x(dx/dt)}{(225+x^2)^{3/2}}\right]xv_A+\left[\frac{1}{\sqrt{225+x^2}}\right]\left(\frac{dx}{dt}\right)v_A+\left[\frac{1}{\sqrt{225+x^2}}\right]x\frac{dv_A}{dt}=\frac{225v_A^2}{(225+x^2)^{3/2}} aS=dt2d2y=[(225+x2)3/2−x(dx/dt)]xvA+[225+x21](dtdx)vA+[225+x21]xdtdvA=(225+x2)3/2225vA2
a s = 225 ( 0.5 m / s ) 2 [ 225 + ( 20 m ) 2 ] 3 / 2 = 0.00360 m / s 2 = 3.60 m m / s 2 ↑ a_{s} = \frac{225(0.5 \ \mathrm{m/s})^{2}}{[225 + (20 \ \mathrm{m})^{2}]^{3/2}} = 0.00360 \ \mathrm{m/s}^{2} = 3.60 \ \mathrm{mm/s}^{2} \uparrow as=[225+(20 m)2]3/2225(0.5 m/s)2=0.00360 m/s2=3.60 mm/s2↑
3.pinn模拟
- 深的网络结构:从3层增加到4层,每层128个神经元
- 增强的物理约束:
添加了人的加速度为0的约束
从绳长约束直接导出一阶和二阶导数约束
调整了损失权重以更好地学习加速度 - 改进的训练策略:
使用余弦退火学习率调度
增加训练轮数到20000
在关键时刻(t=40s附近)增加采样密度
添加梯度裁剪防止梯度爆炸 - 精确的导数计算:使用自动微分而不是数值微分
- 详细的误差分析和可视化
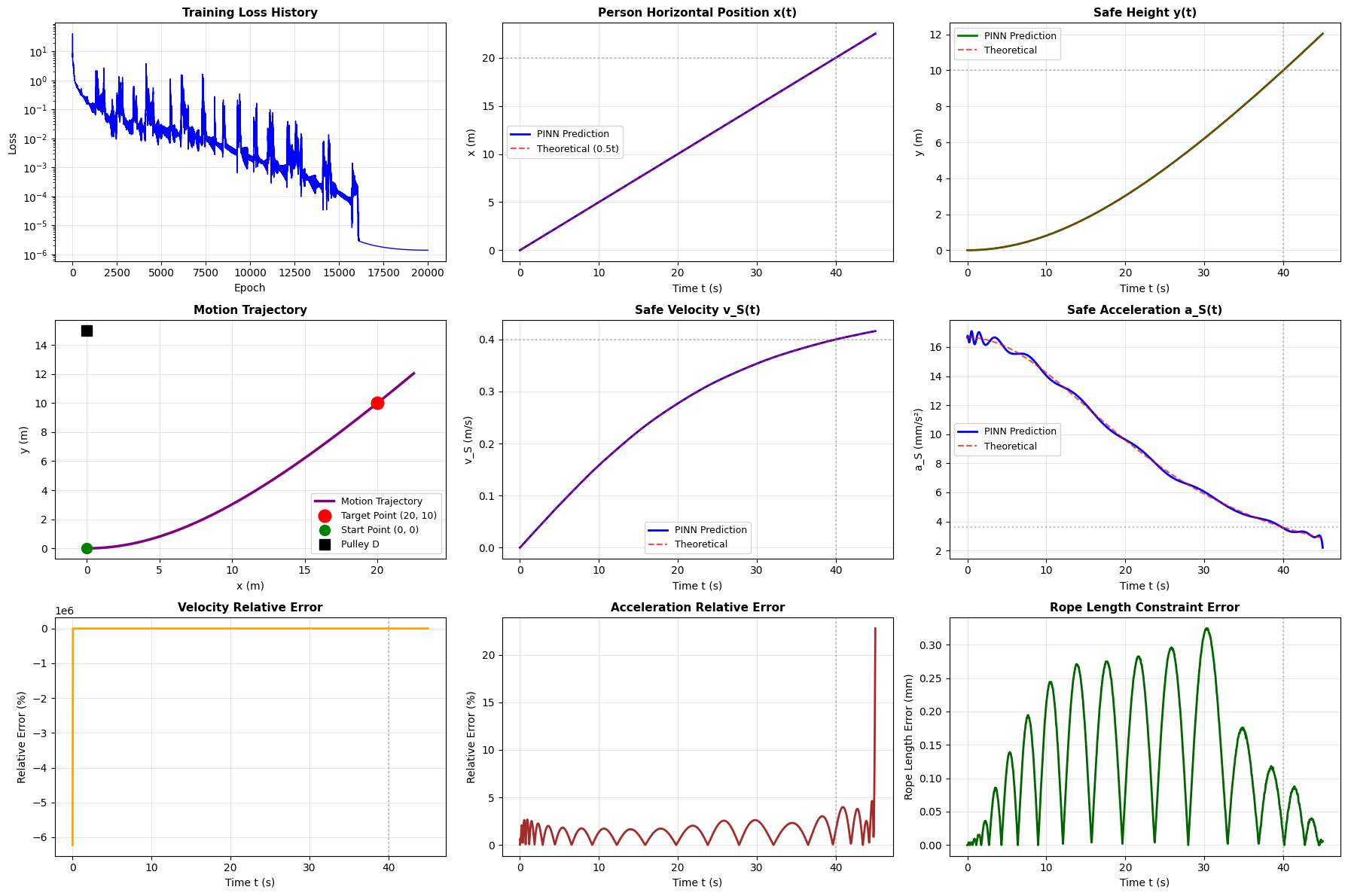
4.部分结果
预测结果 (当保险箱高度接近 10.0 m 时)
时间 t = 40.00 s
人的位置 x = 19.999996 m (理论值: 20.000000 m)
保险箱高度 y = 9.999986 m (理论值: 10.000000 m)
速度分析
PINN预测: v_S = 0.40010089 m/s = 400.10089 mm/s
理论值: v_S = 0.40000000 m/s = 400.00000 mm/s
绝对误差: Δv = 0.00010089 m/s
相对误差: ε_v = 0.0252%
加速度分析
PINN预测: a_S = 0.0035417541 m/s² = 3.5417541 mm/s²
理论值: a_S = 0.0036000000 m/s² = 3.6000000 mm/s²
绝对误差: Δa = 0.0000582459 m/s²
相对误差: ε_a = 1.6179%
约束验证结果
绳长约束 (L = 30 m):
最大误差: 0.3242 mm
平均误差: 0.1288 mm
标准差: 0.0935 mm
5.部分代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置随机种子以保证可重复性
torch.manual_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
class SafeLiftingPINN(nn.Module):
"""
改进的物理信息神经网络模型
使用更深的网络和适当的激活函数
"""
def __init__(self, layers=[1, 128, 128, 128, 128, 2]):
super(SafeLiftingPINN, self).__init__()
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(len(layers) - 1):
self.layers.append(nn.Linear(layers[i], layers[i+1]))
# Xavier初始化
for m in self.layers:
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.xavier_normal_(m.weight)
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
def forward(self, t):
"""前向传播 - 使用tanh激活函数"""
for i, layer in enumerate(self.layers[:-1]):
t = torch.tanh(layer(t))
t = self.layers[-1](t)
return t
def compute_loss(model, t_collocation, device, v_A=0.5):
"""
改进的损失函数 - 增加了更多的物理约束
"""
t_pde = t_collocation.requires_grad_(True)
output = model(t_pde)
x = output[:, 0:1]
y = output[:, 1:2]
# 计算一阶导数 (速度)
dx_dt = torch.autograd.grad(x, t_pde,
grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(x),
create_graph=True)[0]
dy_dt = torch.autograd.grad(y, t_pde,
grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(y),
create_graph=True)[0]
# 计算二阶导数 (加速度)
d2x_dt2 = torch.autograd.grad(dx_dt, t_pde,
grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(dx_dt),
create_graph=True)[0]
d2y_dt2 = torch.autograd.grad(dy_dt, t_pde,
grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(dy_dt),
create_graph=True)[0]
# 损失1: 初始条件 (t=0时,x=0, y=0)
t_ic = torch.zeros(1, 1).to(device).requires_grad_(True)
output_ic = model(t_ic)
loss_ic = torch.mean(output_ic**2)
# 损失2: 人以恒定速度行走 dx/dt = v_A
loss_velocity_x = torch.mean((dx_dt - v_A)**2)
# 损失3: 人的加速度为0 (新增)
loss_acceleration_x = torch.mean(d2x_dt2**2)
# 损失4: 绳长恒定约束 sqrt(225 + x^2) + (15 - y) = 30
rope_length = torch.sqrt(225 + x**2) + (15 - y)
loss_rope = torch.mean((rope_length - 30)**2)
# 损失5: 速度关系 dy/dt = x/sqrt(225+x^2) * v_A
v_S_physics = x / torch.sqrt(225 + x**2) * v_A
loss_kinematics = torch.mean((dy_dt - v_S_physics)**2)
# 损失6: 加速度关系 d²y/dt² = 225*v_A²/(225+x²)^(3/2)
a_S_physics = 225 * v_A**2 / (225 + x**2)**(3/2)
loss_acceleration = torch.mean((d2y_dt2 - a_S_physics)**2)
# 损失7: 从绳长约束直接导出的加速度关系 (新增,更强的约束)
# 对绳长约束方程两次求导
sqrt_term = torch.sqrt(225 + x**2)
# 第一次求导: d/dt[sqrt(225+x²) + 15 - y] = 0
# => x*dx/dt/sqrt(225+x²) - dy/dt = 0
constraint_1st = x * dx_dt / sqrt_term - dy_dt
loss_constraint_1st = torch.mean(constraint_1st**2)
# 第二次求导得到加速度约束
# d²y/dt² = d/dt[x*dx/dt/sqrt(225+x²)]
acc_from_constraint = (dx_dt**2 / sqrt_term +
x * d2x_dt2 / sqrt_term -
x**2 * dx_dt**2 / (225 + x**2)**(3/2))
loss_constraint_2nd = torch.mean((d2y_dt2 - acc_from_constraint)**2)
# 总损失(调整权重以更好地学习加速度)
loss = (200.0 * loss_ic +
20.0 * loss_velocity_x +
50.0 * loss_acceleration_x + # 新增
20.0 * loss_rope +
10.0 * loss_kinematics +
10.0 * loss_acceleration + # 增加权重
15.0 * loss_constraint_1st + # 新增
10.0 * loss_constraint_2nd) # 新增
return loss, {
'ic': loss_ic.item(),
'vel_x': loss_velocity_x.item(),
'acc_x': loss_acceleration_x.item(),
'rope': loss_rope.item(),
'kinematics': loss_kinematics.item(),
'acceleration': loss_acceleration.item(),
'const_1st': loss_constraint_1st.item(),
'const_2nd': loss_constraint_2nd.item()
}
def train_pinn(epochs=20000, lr=1e-3, n_collocation=2000):
"""改进的训练函数 - 使用更多的配置点和分阶段训练"""
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(f"使用设备: {device}")
# 创建模型
model = SafeLiftingPINN().to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
# 使用余弦退火学习率
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(
optimizer, T_max=epochs, eta_min=1e-6
)
# 生成配置点 - 使用更密集的采样
v_A = 0.5
t_max = 45.0
# 在关键时刻(t=40s附近)增加采样密度
t_collocation_uniform = torch.linspace(0, t_max, n_collocation // 2)
t_collocation_focus = torch.linspace(35, 45, n_collocation // 2)
t_collocation = torch.cat([t_collocation_uniform, t_collocation_focus]).reshape(-1, 1).to(device)
# 训练历史
loss_history = []
print("\n开始训练...")
print("-" * 90)
for epoch in range(epochs):
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss, loss_dict = compute_loss(model, t_collocation, device, v_A)
loss.backward()
# 梯度裁剪防止梯度爆炸
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0)
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
loss_history.append(loss.item())
if epoch % 1000 == 0:
lr_current = optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr']
print(f'Epoch {epoch:5d} | Loss: {loss.item():.6f} | '
f'IC: {loss_dict["ic"]:.2e} | '
f'Rope: {loss_dict["rope"]:.2e} | '
f'Acc: {loss_dict["acceleration"]:.2e} | '
f'C2nd: {loss_dict["const_2nd"]:.2e} | '
f'LR: {lr_current:.2e}')
print("-" * 90)
print("训练完成!\n")
return model, loss_history
def predict_at_height(model, target_y=10.0, v_A=0.5):
"""
使用自动微分精确计算速度和加速度
"""
device = next(model.parameters()).device
x_target = 20.0
t_target = x_target / v_A
t_tensor = torch.tensor([[t_target]], device=device, requires_grad=True)
output = model(t_tensor)
x = output[:, 0:1]
y = output[:, 1:2]
# 计算速度
dy_dt = torch.autograd.grad(y, t_tensor,
grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(y),
create_graph=True)[0]
# 计算加速度
d2y_dt2 = torch.autograd.grad(dy_dt, t_tensor,
grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(dy_dt))[0]
# 理论值
v_theory = 0.4
a_theory = 0.0036
print(f"{'='*90}")
print(f"预测结果 (当保险箱高度接近 {target_y} m 时)")
print(f"{'='*90}")
print(f"时间 t = {t_target:.2f} s")
print(f"人的位置 x = {x.item():.6f} m (理论值: 20.000000 m)")
print(f"保险箱高度 y = {y.item():.6f} m (理论值: 10.000000 m)")
print(f"\n{'速度分析':^90}")
print(f"{'-'*90}")
print(f"PINN预测: v_S = {dy_dt.item():.8f} m/s = {dy_dt.item()*1000:.5f} mm/s")
print(f"理论值: v_S = {v_theory:.8f} m/s = {v_theory*1000:.5f} mm/s")
print(f"绝对误差: Δv = {abs(dy_dt.item() - v_theory):.8f} m/s")
print(f"相对误差: ε_v = {abs(dy_dt.item() - v_theory)/v_theory * 100:.4f}%")
print(f"\n{'加速度分析':^90}")
print(f"{'-'*90}")
print(f"PINN预测: a_S = {d2y_dt2.item():.10f} m/s² = {d2y_dt2.item()*1000:.7f} mm/s²")
print(f"理论值: a_S = {a_theory:.10f} m/s² = {a_theory*1000:.7f} mm/s²")
print(f"绝对误差: Δa = {abs(d2y_dt2.item() - a_theory):.10f} m/s²")
print(f"相对误差: ε_a = {abs(d2y_dt2.item() - a_theory)/a_theory * 100:.4f}%")
print(f"{'='*90}\n")
return x.item(), y.item(), dy_dt.item(), d2y_dt2.item()
def visualize_results(model, loss_history):
"""增强的可视化"""
device = next(model.parameters()).device
# 生成测试数据
t_test = torch.linspace(0, 45, 1000).reshape(-1, 1).to(device)
# 使用自动微分计算导数
t_test_grad = t_test.clone().requires_grad_(True)
output = model(t_test_grad)
x_pred = output[:, 0:1]
y_pred = output[:, 1:2]
# 计算速度
dy_dt = torch.autograd.grad(y_pred, t_test_grad,
grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(y_pred),
create_graph=True)[0]
# 计算加速度
d2y_dt2 = torch.autograd.grad(dy_dt, t_test_grad,
grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(dy_dt))[0]
# 转换为numpy
t_np = t_test.cpu().detach().numpy().flatten()
x_np = x_pred.cpu().detach().numpy().flatten()
y_np = y_pred.cpu().detach().numpy().flatten()
vy_np = dy_dt.cpu().detach().numpy().flatten()
ay_np = d2y_dt2.cpu().detach().numpy().flatten()
# 计算理论值
v_theory = x_np / np.sqrt(225 + x_np**2) * 0.5
a_theory = 225 * 0.5**2 / (225 + x_np**2)**(3/2)
# 创建图形
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(18, 12))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('pinn_safe_lifting_improved.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
print("详细结果图已保存为 'pinn_safe_lifting_improved.png'")
plt.show()
def verify_constraints(model, v_A=0.5):
"""详细的约束验证"""
device = next(model.parameters()).device
t_test = torch.linspace(0, 45, 200).reshape(-1, 1).to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(t_test)
x = output[:, 0].cpu().numpy()
y = output[:, 1].cpu().numpy()
# 检查绳长约束
rope_length = np.sqrt(225 + x**2) + (15 - y)
rope_error = np.abs(rope_length - 30)
print(f"{'='*90}")
print(f"约束验证结果")
print(f"{'='*90}")
print(f"绳长约束 (L = 30 m):")
print(f" 最大误差: {np.max(rope_error)*1000:.4f} mm")
print(f" 平均误差: {np.mean(rope_error)*1000:.4f} mm")
print(f" 标准差: {np.std(rope_error)*1000:.4f} mm")
print(f"{'='*90}\n")
def main():
"""主函数"""
print("\n" + "="*90)
print("改进的PINN求解保险箱吊装问题")
print("="*90 + "\n")
# 训练模型 - 使用更多epochs和配置点
model, loss_history = train_pinn(epochs=20000, lr=1e-3, n_collocation=2000)
# 在目标高度预测
predict_at_height(model, target_y=10.0, v_A=0.5)
# 验证约束
verify_constraints(model, v_A=0.5)
# 可视化结果
visualize_results(model, loss_history)
# 保存模型
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'safe_lifting_pinn_improved.pth')
print("\n模型已保存为 'safe_lifting_pinn_improved.pth'\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()




















 823
823

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








