一、什么是graphQL
- GraphQL 是一种用于 API(应用程序编程接口)的查询语言,由 Facebook 在 2012 年开发,并于 2015 年开源。
- GraphQL允许客户端按需获取数据。就像你去自助餐厅,你可以自己决定要哪些食物,而不是服务员决定给你什么。这种方式让前端开发者不用依赖后端的接口设计,他们可以自由地获取他们需要的数据结构。
- 它提供了一种更高效、强大的方式来获取和操作数据
- 与传统的 RESTful API 相比,GraphQL优点 1 具有更高的灵活性和更低的网络负载。2 减少冗余和提高效率 3 简化客户端代码
- 通过 GraphQL,客户端可以精确地请求所需的数据,而服务器则只返回这些数据,从而避免了过度加载或不足加载的问题。
二、如何实现GraphQL?
服务端的角色
定义Type及其Field
服务端需要定义各种数据类型,包括标量类型(基本数据类型)、对象类型(复杂数据类型)、接口类型、联合类型、枚举类型、输入对象类型等。这就像是在自助餐厅中,厨师需要准备各种食材和菜品,以满足顾客的不同需求。
定义Schema
Schema是GraphQL的核心,它定义了客户端可以进行的操作(query、mutation、subscription)以及这些操作如何获取数据。这就像是餐厅的菜单,上面列出了所有可以点的菜,以及它们是怎么做的。
定义Resolve
Resolver是实际处理数据请求的函数。当客户端发起一个请求时,Resolver负责获取数据并返回给客户端。这就像是餐厅里的服务员,根据顾客的订单去厨房取菜。
客户端的角色
构建请求Document
客户端在发送请求时,需要构建一个请求Document,它包括操作和片段。这就像是在自助餐厅中,你填写订单,上面标明你想要哪些菜品。
实战示例
好的,接下来我会给出一个简单的Node.js示例,用于创建一个GraphQL服务。这个服务将允许客户端查询一本书的信息。
首先,我们需要安装一些必要的包:
npm install express express-graphql graphql --save
这里我们使用 express 作为Web服务器,使用 express-graphql 在 Express 中集成 GraphQL,使用 graphql 这个包来实现 GraphQL。
现在我们来编写代码:
const express = require('express');
const { graphqlHTTP } = require('express-graphql');
const { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
// 使用GraphQL schema language构建一个schema
const schema = buildSchema(`
type Query {
book(id: ID!): Book
}
type Book {
id: ID
title: String
author: String
}
`);
// 根提供了每个API端点的Resolve函数
const root = {
book: ({id}) => {
// 这里应该是数据库的查询逻辑,但为了示例简单,我们使用了硬编码的数据
const books = [
{ id: '1', title: 'The Great Gatsby', author: 'F. Scott Fitzgerald' },
{ id: '2', title: '1984', author: 'George Orwell' },
{ id: '3', title: 'The Catcher in the Rye', author: 'J.D. Salinger' },
];
return books.find(book => book.id === id);
},
};
const app = express();
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true, // 开启GraphiQL工具
}));
app.listen(4000, () => console.log('Now browse to localhost:4000/graphql'));在这段代码中,我们首先定义了一个schema,它描述了查询类型Query和一个Book类型。在Query类型中,我们定义了一个book查询,它接受一个必需的id参数,并返回一个Book对象。
接下来,我们定义了一个根解析器root,它包含了一个book函数。这个函数接受一个包含id的参数对象,并返回匹配该id的书籍信息。在真实应用中,这里应该是一个数据库查询操作。
最后,我们使用Express创建了一个应用,通过express-graphql中间件在/graphql路径上提供GraphQL服务,并开启了GraphiQL,这是一个内嵌的Web IDE,用于在浏览器中测试GraphQL查询。
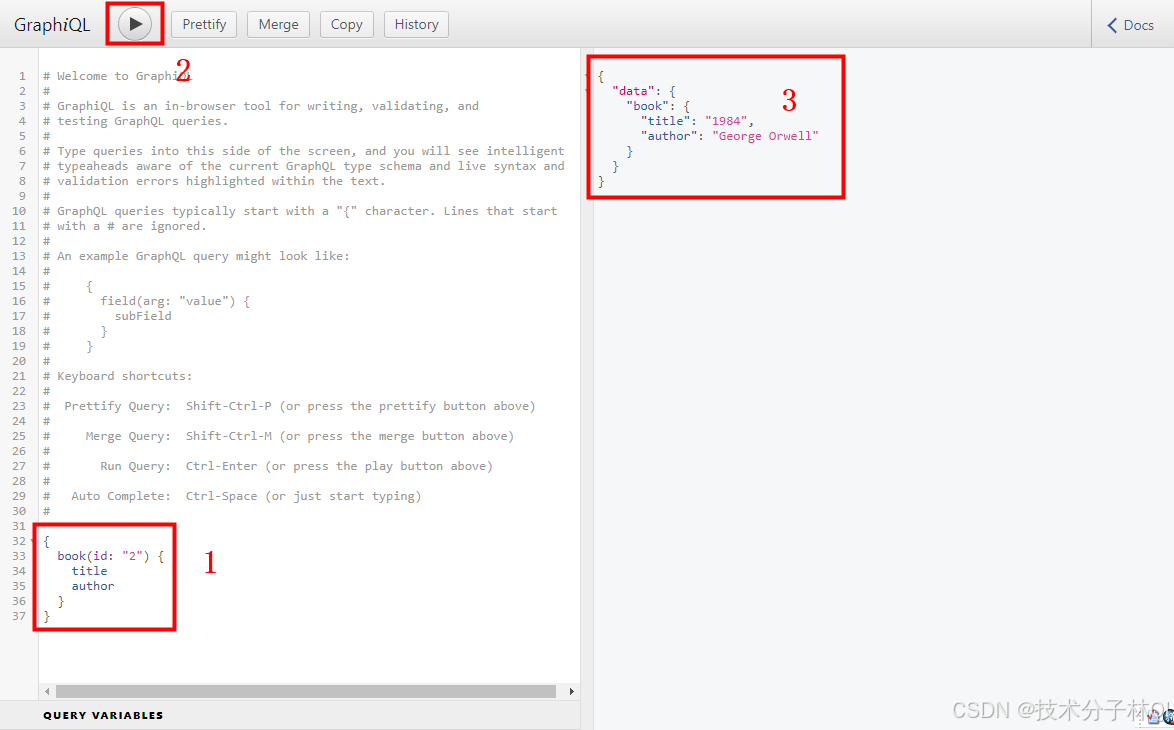
现在,如果你运行这段代码,并在浏览器中打开http://localhost:4000/graphql,你就可以使用GraphiQL工具来执行GraphQL查询了。例如,使用下面的查询:
{
book(id: "2") {
title
author
}
}
演示效果如下,这将返回id为"2"的书的标题和作者信息。
GraphQL 的核心概念
- 类型系统:GraphQL 使用强类型系统定义数据模型。每个字段都有明确的数据类型,如 String、Int、Boolean 等,还可以定义复杂类型如对象类型、枚举类型、输入对象类型等。
- 查询:客户端可以通过发送一个查询语句来请求特定的数据。查询语句是一个树状结构,描述了需要获取的数据字段及其子字段。
- 变更(Mutations):用于执行写操作,如创建、更新或删除数据。变更操作也遵循严格的类型定义。
- 订阅(Subscriptions):允许客户端实时接收数据更新。订阅通常用于实现实时通信功能,如聊天应用中的消息推送。
- 字段解析器(Resolvers):服务器端的逻辑单元,负责处理查询中的每个字段。解析器可以根据请求参数从数据库或其他数据源中获取数据,并将其返回给客户端。
- 模式(Schema):定义了 API 的结构,包括可用的查询、变更和订阅,以及它们的参数和返回类型。模式是 GraphQL API 的核心部分,确保了客户端和服务器之间的契约。
代码讲解
示例说明
为了更好地理解 GraphQL 的工作原理和优势,我们通过一个具体的示例来说明。假设我们正在开发一个社交媒体应用,需要展示用户的个人信息和最近发布的帖子。
定义模式
首先,我们需要定义 GraphQL 模式,描述可用的查询、变更和订阅。以下是一个简单的模式定义:
type User {
id: ID!
name: String!
email: String!
posts: [Post!]!
}
type Post {
id: ID!
title: String!
content: String!
createdAt: String!
author: User!
}
type Query {
user(id: ID!): User
posts(userId: ID!): [Post!]!
}
type Mutation {
createUser(name: String!, email: String!): User
createPost(title: String!, content: String!, userId: ID!): Post
}
type Subscription {
newPost: Post
}
查询示例
假设我们想获取某个用户的详细信息及其最近发布的帖子,可以发送以下查询:
query GetUserWithPosts($userId: ID!) {
user(id: $userId) {
id
name
email
posts {
id
title
content
createdAt
}
}
}
在这个查询中,我们使用了变量 $userId 来指定要查询的用户 ID。服务器将返回该用户的详细信息及其最近发布的帖子。
变更示例
假设我们要创建一个新的用户,可以发送以下变更请求:
mutation CreateUser($name: String!, $email: String!) {
createUser(name: $name, email: $email) {
id
name
email
}
}
在这个变更请求中,我们传递了用户的姓名和电子邮件地址。服务器将创建新的用户并返回其详细信息。
订阅示例
假设我们要实现实时的新帖子通知,可以使用订阅机制:
subscription NewPost {
newPost {
id
title
content
createdAt
author {
id
name
}
}
}
当有新的帖子发布时,服务器会实时推送新帖子的信息到订阅的客户端。
实现细节
服务器端实现
在服务器端,我们需要实现字段解析器来处理查询和变更请求。以下是一个使用 Node.js 和 Express 实现的简单示例:
const express = require('express');
const { ApolloServer, gql } = require('apollo-server-express');
// 模拟数据存储
const users = [
{ id: '1', name: 'Alice', email: 'alice@example.com' },
{ id: '2', name: 'Bob', email: 'bob@example.com' }
];
const posts = [
{ id: '1', title: 'First Post', content: 'This is the first post.', createdAt: '2023-10-01T00:00:00Z', authorId: '1' },
{ id: '2', title: 'Second Post', content: 'This is the second post.', createdAt: '2023-10-02T00:00:00Z', authorId: '2' }
];
// 定义模式
const typeDefs = gql`
type User {
id: ID!
name: String!
email: String!
posts: [Post!]!
}
type Post {
id: ID!
title: String!
content: String!
createdAt: String!
author: User!
}
type Query {
user(id: ID!): User
posts(userId: ID!): [Post!]!
}
type Mutation {
createUser(name: String!, email: String!): User
createPost(title: String!, content: String!, userId: ID!): Post
}
type Subscription {
newPost: Post
}
`;
// 定义解析器
const resolvers = {
Query: {
user: (parent, { id }) => users.find(user => user.id === id),
posts: (parent, { userId }) => posts.filter(post => post.authorId === userId)
},
Mutation: {
createUser: (parent, { name, email }) => {
const newUser = { id: users.length + 1, name, email };
users.push(newUser);
return newUser;
},
createPost: (parent, { title, content, userId }) => {
const newPost = { id: posts.length + 1, title, content, createdAt: new Date().toISOString(), authorId: userId };
posts.push(newPost);
return newPost;
}
},
Subscription: {
newPost: {
subscribe: () => pubsub.asyncIterator('NEW_POST')
}
},
User: {
posts: (parent) => posts.filter(post => post.authorId === parent.id)
},
Post: {
author: (parent) => users.find(user => user.id === parent.authorId)
}
};
// 创建 Apollo Server
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });
// 应用中间件
const app = express();
server.applyMiddleware({ app, path: '/graphql' });
// 启动服务器
app.listen({ port: 4000 }, () => {
console.log(`🚀 Server ready at http://localhost:4000${server.graphqlPath}`);
});客户端实现
在客户端,我们可以使用 Apollo Client 来发送查询和变更请求。以下是一个使用 React 和 Apollo Client 的示例:
import React from 'react';
import { ApolloProvider, useQuery, gql } from '@apollo/client';
// 配置 Apollo Client
const client = new ApolloClient({
uri: 'http://localhost:4000/graphql'
});
const GET_USER_WITH_POSTS = gql`
query GetUserWithPosts($userId: ID!) {
user(id: $userId) {
id
name
email
posts {
id
title
content
createdAt
}
}
}
`;
function App() {
const { loading, error, data } = useQuery(GET_USER_WITH_POSTS, {
variables: { userId: '1' }
});
if (loading) return <p>Loading...</p>;
if (error) return <p>Error: {error.message}</p>;
return (
<div>
<h1>User: {data.user.name}</h1>
<p>Email: {data.user.email}</p>
<h2>Posts</h2>
<ul>
{data.user.posts.map(post => (
<li key={post.id}>
<h3>{post.title}</h3>
<p>{post.content}</p>
<p>Created At: {post.createdAt}</p>
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
function Root() {
return (
<ApolloProvider client={client}>
<App />
</ApolloProvider>
);
}
export default Root;好文章啊:什么是graphQL-CSDN博客
GraphQL的局限性
现有基础设施的兼容性
许多公司已经投入了大量资源建立起基于REST的服务架构,要迁移到GraphQL,需要重构现有的API和后端服务。这种转变涉及到时间和成本的投入,对于那些已经运行良好的服务来说,这样的投资可能难以说服管理者,这个事就干不成,即使有前端同学愿意用爱发电,还得说服后端一起发电才行,难度可想而知。
不适用的场景
虽然GraphQL强大,但它并不适用于所有场景。例如,对于一些简单的项目,只有几个API,使用GraphQL可能有点大材小用,而且还需要学习新的查询语言。就像是为了买一瓶水而去开一辆卡车,有些不必要。
还有GraphQL不适合传输二进制数据。
单一端点的缓存问题
由于GraphQL通常只使用一个端点,这使得基于URL的缓存变得困难。这就像是自助餐厅中,所有的食物都在一个窗口领取,导致排队等待的时间变长。
安全性和性能问题
GraphQL的灵活性虽然是一个优点,但也带来了潜在的安全风险。它主要关注数据检索,但忽略了其他重要的 API 方面,如身份验证、授权和错误处理。还有恶意用户可能通过复杂的查询来对服务器进行攻击(例如,深度查询和循环查询)。此外,由于GraphQL允许客户端制定查询,这可能导致非预期的数据库性能问题。




















 1052
1052

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








