C++ STL-Deque的实现
中控指针数组
- 本质上是一个指向指针的指针
- 它保存的是多个指向内存块(缓冲区/缓冲段)的指针
- 这些内存块每个保存固定数量的元素
缓冲区
- 每个缓冲区用于存放真正的数据。
- 不同缓冲区在内存中不一定连续,因此 deque 可以有效地从两端插入或删除元素
Deque的内部结构采用分段数组,而不是简单的连续数组
deque的内部结构利用了多个缓冲区,有助于提高内存局部性,不同缓冲区在内存中不一定连续,因此 deque 可以有效地从两端插入或删除元素
deque的大小可以动态调整,无需事先分配固定大小的内存
deque 允许在常量时间内对元素进行随机访问,这意味着可以通过索引直接访问deque中的元素,而不会随deque的大小而增加访问时间
1.Deque成员变量定义
private:
T* elements; //数组指针
size_t capacity; //容量
size_t frontIndex; //Deque的头索引
size_t backIndex; //Deque的尾索引
size_t size; //Deque的元素数量
2.Deque构造函数
Deque() : elements(nullptr), capacity(0), frontIndex(0), backIndex(0), size(0) {}
3.Deque析构函数
~Deque()
{
clear(); //clear在后面介绍
delete[] elements;
}
4.从Deque前端清除元素
void pop_front()
{
//判断Deque是否非空
if(size == 0)
{
throw out_of_range("Deque if empty!");
}
//使用%capacity的原因是当 frontIndex 到达数组末尾(最大索引)时,回绕回到数组起点,实现环形行为(循环利用数组空间),防止访问越界,避免未定义行为
frontIndex = (frontIndex + 1) % capacity;
//更新元素数量
--size;
}
5.从Deque后端清除元素
//从Deque后端清除元素
void pop_back()
{
//判断Deque是否非空
if(size == 0)
{
throw out_of_range("Deque if empty!");
}
backIndex = (backIndex - 1 + capacity) % capacity;
//更新元素数量
--size;
}
6.在Deque前端插入新元素
//在Deque前端插入新元素
void push_front(const T& value)
{
//判断元素数量是否已达到容器总量
if(size == capacity)
{
resize();
}
//计算插入的新元素后前端的新的索引值
frontIndex = (frontIndex - 1 + capacity) % capacity;
elements[frontIndex] = value;
//更新元素总数
++size;
}
7.在Deque后端插入元素
//在Deque后端插入元素
void push_back(const T& value)
{
//判断元素数量是否已达到容器总量
if(size == capacity)
{
resize();
}
//直接调用elements[backIndex]的原因是backIndex所指向的是最后一个元素的后面一个位置
elements[backIndex] = value;
backIndex = (backIndex + 1) % capacity;
//更新元素总数
++size;
}
8.清空Deque
//清空Deque
void clear()
{
while(size > 0 )
{
pop_front();
}
}
9.[]运算符重载: 以提供Deque访问能力
//[]运算符重载: 以提供Deque访问能力
T& operator[] (int index)
{
//判断越界行为
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
{
throw out_of_range("Index out of range");
}
return elements[(frontIndex + index) % capacity];
}
10.获取Deque元素数量
//Deque元素总数
size_t getSize() const
{
return size;
}
11.数组扩容:resize
private:
//数组扩容
void resize()
{
//判断是否是0
size_t newCapacity = (capacity == 0) ? 1 : capacity*2;
//创建新的数组用于放置原来的数组元素
T* newELements = new T[newCapacity];
size_t index = frontIndex;
for(size_t i= 0; i < size; ++i)
{
newELements[i] = elements[index];
index = (index + 1) % capacity;
}
//释放原始数组的内存
delete[] elements;
//扩容后的数组成员变量更新
elements = newELements;
capacity = newCapacity;
frontIndex = 0;
backIndex = size;
}
12.打印Deque中的元素
//print Deque中的所有元素
void printElements() const
{
size_t index = frontIndex;
for(size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
cout << elements[index] << " ";
index = (index + 1) % capacity;
}
cout << endl;
}
13.C++完整代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
class Deque
{
private:
T* elements; //数组指针
size_t capacity; //容量
size_t frontIndex; //Deque的头索引
size_t backIndex; //Deque的尾索引
size_t size; //Deque的元素数量
//数组扩容
void resize()
{
//判断是否是0
size_t newCapacity = (capacity == 0) ? 1 : capacity*2;
//创建新的数组用于放置原来的数组元素
T* newELements = new T[newCapacity];
size_t index = frontIndex;
for(size_t i= 0; i < size; ++i)
{
newELements[i] = elements[index];
index = (index + 1) % capacity;
}
//释放原始数组的内存
delete[] elements;
//扩容后的数组成员变量更新
elements = newELements;
capacity = newCapacity;
frontIndex = 0;
backIndex = size;
}
public:
//Deque构造函数
Deque() : elements(nullptr), capacity(0), frontIndex(0), backIndex(0), size(0) {}
//析构函数
~Deque()
{
clear();
delete[] elements;
}
//从Deque前端清除元素
void pop_front()
{
//判断Deque是否非空
if(size == 0)
{
throw out_of_range("Deque if empty!");
}
//使用%capacity的原因是当 frontIndex 到达数组末尾(最大索引)时,回绕回到数组起点,实现环形行为(循环利用数组空间),防止访问越界,避免未定义行为
frontIndex = (frontIndex + 1) % capacity;
//更新元素数量
--size;
}
//从Deque后端清除元素
void pop_back()
{
//判断Deque是否非空
if(size == 0)
{
throw out_of_range("Deque if empty!");
}
backIndex = (backIndex - 1 + capacity) % capacity;
//更新元素数量
--size;
}
//在Deque前端插入新元素
void push_front(const T& value)
{
//判断元素数量是否已达到容器总量
if(size == capacity)
{
resize();
}
//计算插入的新元素后前端的新的索引值
frontIndex = (frontIndex - 1 + capacity) % capacity;
elements[frontIndex] = value;
//更新元素总数
++size;
}
//在Deque后端插入元素
void push_back(const T& value)
{
//判断元素数量是否已达到容器总量
if(size == capacity)
{
resize();
}
//直接调用elements[backIndex]的原因是backIndex所指向的是最后一个元素的后面一个位置
elements[backIndex] = value;
backIndex = (backIndex + 1) % capacity;
//更新元素总数
++size;
}
//[]运算符重载: 以提供Deque访问能力
T& operator[] (int index)
{
//判断越界行为
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
{
throw out_of_range("Index out of range");
}
return elements[(frontIndex + index) % capacity];
}
//Deque元素总数
size_t getSize() const
{
return size;
}
//清空Deque
void clear()
{
while(size > 0 )
{
pop_front();
}
}
//print Deque中的所有元素
void printElements() const
{
size_t index = frontIndex;
for(size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
cout << elements[index] << " ";
index = (index + 1) % capacity;
}
cout << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Deque<int> myDeque;
//总共几条命令
int N;
cin >> N;
getchar();
string line;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
getline(cin,line);
istringstream iss(line);
string command;
iss >> command;
int value;
if(command == "push_back")
{
iss >> value;
myDeque.push_back(value);
}
if(command == "push_front")
{
iss >> value;
myDeque.push_front(value);
}
if (command == "pop_back")
{
if (myDeque.getSize() == 0)
{
continue;
}
myDeque.pop_back();
}
if (command == "pop_front")
{
if (myDeque.getSize() == 0)
{
continue;
}
myDeque.pop_front();
}
if (command == "clear")
{
myDeque.clear();
}
if (command == "size")
{
cout << myDeque.getSize() << endl;
}
if (command == "get")
{
iss >> value;
cout << myDeque[value] << endl;
}
if (command == "print")
{
if (myDeque.getSize() == 0)
{
cout << "empty" << endl;
}
else
{
myDeque.printElements();
}
}
}
return 0;
}
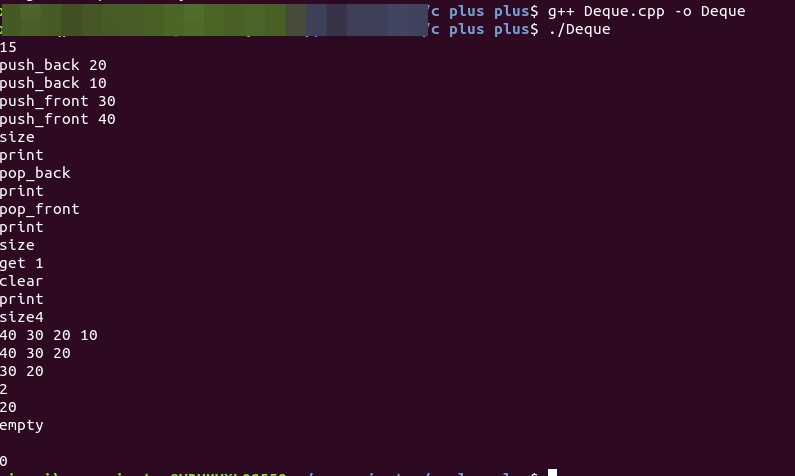
14.运行结果




















 2043
2043

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








