目录
技巧5:laterval view explode()行转列
HQL 与 SQL的区别
| 查询语言 | HQL | SQL |
| 数据存储位置 | HDFS | 块设备或者本地文件 |
| 数据格式 | 用户定义 | 系统决定 |
| 数据更新 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 索引 | 无 | 有 |
| 执行 | mapredurce | executor |
| 执行延迟 | 高 | 低 |
| 可扩展性 | 高 | 低 |
| 数据规模 | 大 | 小 |
分区
如果该表是个分区表,那么需要在where加上分区的限制
如,该表的分区是 date,那么查询某个日期的的数据的时候在where 加上 date=‘日期时间’
专用函数
日期时间
1、from_unixtime(时间戳,日期时间格式)
因时间戳 以秒数存储,所以需要转换成日期时间格式
日期时间格式:
- yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss
- yyyy-MM-dd hh
- yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm
- yyyyMMmdd
2、unix_timestamp(日期时间)
日期时间转时间戳
3、to_date(日期时间)
只保留日期,去掉时间
4、datediff(结束日期,开始日期)
两个日期的天数差
条件函数
5、(一般用于新字段,同样可用于group by)
case when ... then ...else ...end 可用于多少种结果
if(条件, A,B) 一般用于两种结果
字符串函数
6、普通字符串
substr(被截取字段,从第几位开始截取,截取几位)
substr(被截取字段,从第几位开始截取) --截取后面所有结果
7、string、map数据类型的提取 string、map是键值对{key:value}
string类型:get_json_object(主字段名,'$.子字段')
map<string,string>类型:主字段名[‘子字段’]
聚合统计函数(同mysql)
常见错误
- 半角写成全角
- 没有对子查询的表重命名 ()a
- 字段名写错
- 字段之间丢了逗号分隔符(多字段情况下)
表连接
当数据量大且查询结果需要去重时,在表连接前去重的效率会比连接后去重的效率要高;
1、join 交集
2、left join的应用:A left join B
- 求有A行为(属性),但是没有B行为(属性)——注意添加筛选条件:where b.字段 is null
- 求A行为中有关B分类的分布情况:B分类的信息可能收集得不全(null),但是也属于A行为下的一种特殊分类(null),需要统计
注意:hive 不支持在 in中插入子查询 [not] in 、exist (select...)
3、full join
full join 的应用:获取两个表中的所有用户名(有时候full join会出现A、B表用户名为空的情况),需要用到coalesce函数 :按表达式的顺序遍历数值,遇到非空值立即停止并返回值,如果所有表达式为NULL,则最终返回NULL
select coalesce(a.name,b.name) from a full join b on a.id=b.id
4、union (追加行)
- union 去重排序
- union all 不去重不排序 ,配合 用0补位 、group by 实现多字段的拼接 汇总
窗口函数
累计计算
sum(计算字段) over(partition by .. order by ...rows ... between ... and ...)
avg(计算字段) over(partition by .. order by ...rows ... between ... and ...)
- rows between unounded preceding and current now 当前行及前面所有行
- rows between current now and unounded following 当前行及后面所有行
- rows between 3 preceding and current now 当前行及前面三行
- rows between 3 preceding and 1 following 前面三行到后面1行(共5行)
最值计算
max(计算字段) over(partition by .. order by ...rows ... between ... and ...)
min(计算字段) over(partition by .. order by ...rows ... between ... and ...)
排序
rank () over(partition by .. order by ...) ——跳过相同位置
dense_rank () over(partition by .. order by ...) ——不跳过相同位置
row_number () over(partition by .. order by ...) ——不重复排序
分组排序(前百分之多少的数据)
ntile(n) over(partition by .. order by ...) as level
- 用于将分组数据按照顺序切分成n份,返回当前切片值
- 不支持rows ... between ... and ...
- 如果切片不均匀,默认增加到第一个切片
- 筛选时 添加 where level = n
偏移分析
lag(exp_str,offset,defval) over(partition by .. order by ...) ——往前
lead(exp_str,offset,defval) over(partition by .. order by ...) ——往后
- exp_str,为字段名
- offset,为偏移量,默认1
- defval,当偏移中超出范围时,指定默认值为返回值,默认NULL
- 应用:配合减法,计算特定的差量
常用技巧
技巧1:去重
group by 优于 distinct(原因:group by分担给多台机器,distinct只在一台机器上计算)
改良版
求去重的用户
select user_id from user group by user_id;
求去重的用户数
select count(1)
from (select user_id from user group by user_id)a;
原版
求去重的用户
select distinct user_id from user;
求去重的用户数
select count(distinct user_id) from user;技巧2:聚合
1、GROUPING SETS()
应用场景:用户画像(同时查询多个不同用户属性特征的分布)
(null表示没有汇总)
1、单个汇聚合
每个性别、城市、年龄的分布情况
select sex,city,age,count(user_id)
group by (sex,city,age)
grouping sets(sex,city,age);
2、多重聚合
每个性别、性别城市的分布情况
select sex,city,count(user_id)
group by (sex,city)
grouping sets(sex,(sex,city));效果,等价于 先分别group by不同属性count数量 ,之后用0占位符和union all 拼接
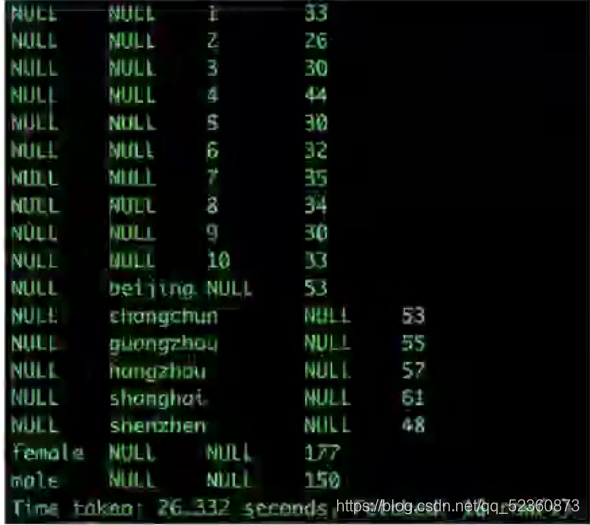
2、WITH CUBE()
根据group by 的维度,进行所有组合的聚合; (null表示没有汇总)
可以将结果迁移到excel中进行筛选
select sex,city,age,count(user_id)
group by (sex,city,age)
with cube;2、WITH ROLLUP()
以最左侧的维度为主,进行层级聚合,是cube的子集
应用:时间层级的统计(年 > 年-月 > 年-月-日 ...)
select year(dt), month(dt), dt, sum(amout)
from user_trade where dt>0
group by year(dt),month(dt),dt
with rollup技巧3:换个思路解题
举例:求在2017和2018年有购买的用户
方法一:常规思路 join
select a.user_id
from (select distinct user_id
from user_trade
where year(dt)=2017)a
join (select distinct user_id
from user_trade
where year(dt)=2018) b
on a.user_id=b.user_id;方法二:求 2017-2018范围内的年购买频次,筛选 2次
select a.user_id
from
(select user_id , count(distinct year(dt)) year_num
from user_trade
where year(dt) in (2017,2018)
group by user_id )a
where a.year_num =2 ;技巧4:union all 并发执行
参数设置:hive> set hive exec: parallel=true
可并行的任务较多时,可以开启并发执行,提高执行效率
比如:union (all)可以并行
技巧5:laterval view explode()行转列
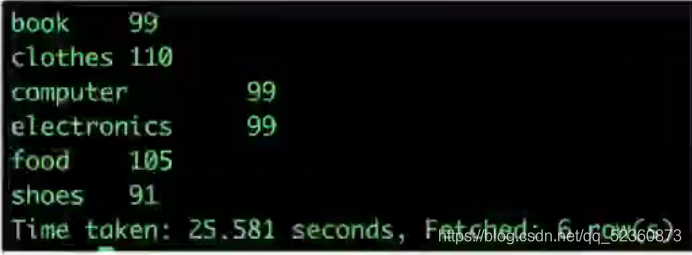
需求:求出每个品类有多少人购买?
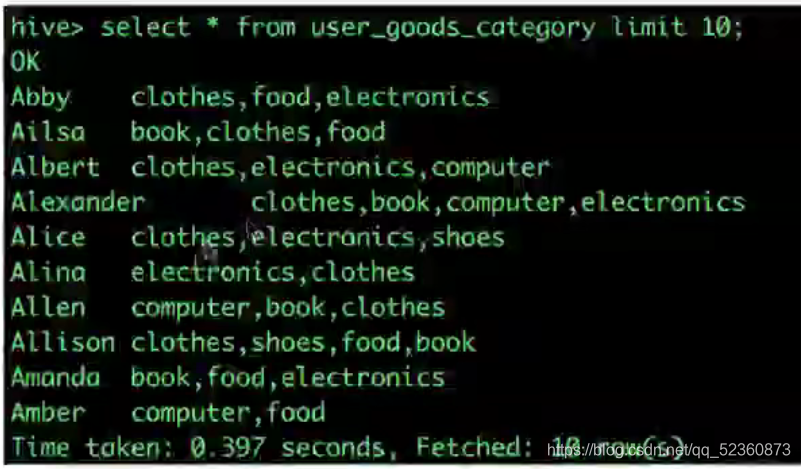
步骤:(放置在from 之后,起修饰表的作用)
1、split(category_detail,',') 分割品类
2、explode( split(category_detail,',') ) b 将品类行转列 记得为之命名
3、laterval view explode( split(category_detail,',') ) b as category 将user_id赋予到每个购买过的品类中(laterval 为横向的意思)
语句:
select b.category , count(distnct a.user_id)
from user_good_category a
laterval view explode( split(category_detail,',') ) b as category
group by b.category;结果:
技巧6:表连接优化(锦上添花)
- 小表在前,大表在后 (join)
- hive假定查询中最后的一个表是大表,会在查询小表的同事将其缓存起来;当扫描好小表后,扫描已经换缓存起来的大表就会快很多
- 使用相同的连接键
- 对多表join连接时,即使有多个唯一键值,也要使用相同的连接键,因为只会产生一个mapredurce job,(如id\name,都是唯一键,需要统一连接键)、
- 尽早的过滤数据
- 减少每个阶段的数据量;对于区分表要加区分限制;同时选择需要用到的字段而不是*
- 逻辑过于复杂的时候,使用中间表
技巧7:解决数据倾斜
表现:当执行进度在99%或100%中停滞不前,查看任务监控页面,发现只有少量redurce子任务未完成,因为其处理的数据量远超其他redurce
- 控制产生的数据倾斜
- 解决::尽量在连接前,先去除连接键的NULL值,因为计算机无法将A表的null匹配给B表的某个null
- 例子:on a.user_id=b.user_id and a.user_id is not null
- 大小表连接中(数据量差异极大)
- 解决:将小表放到内存中,在map端做join
- 例子:select /* +mapjoin(a)*/, b.* from a join b on a.*=b.*
- 两个表连接条件的字段数据类型不一致(少见、适用于量大)
- 解决:两个表连接条件的字段数据类型转换成一致
- 例子:on a.user_id = cast(b.user_id as string)
技巧8:如何计算按月累计去重
需求:2017、2018按月计算累计去重用户数
方法一、(推荐)
步骤:
- 查询每个用户每年最先出现在的月份
- 基于1.聚合计算每年每月的首次在当年当月出现的用户数
- 基于2.累计计算每年每月累计的用户数
select b.year,b.min_month,sum(b.user_num) over(partition by b.year order by b.month)
from (select a.year,a.min_month,count(distinct a.user_id) user_num
from(select year(dt) as year , user_id, min(month(dt)) min_month
from user_trade
where year(dt) in (2017,2018)
group by year(dt), user_id)a
group by a.year,a.min_month)b
order by b.year,b.month;方法二、cross join (不推荐)
步骤:
将交易用户表与年月表生成笛卡尔积,并加上限制条件 where 年月表的月份大于等于交易用户表,且年份相等
select b.month, --这里是写b表的month,易出错
count(distinct a.user_id)
from
(select substr(dt,1,7) as month, user_id from user_trade where year(dt) in (2017,2018) group by ubstr(dt,1,7) , user_id ) a
cross join
(select month from dim_month)b
where b.month>=a.month and substr(b.month,1,4)=substr(a.month,1,4) --难点在于写条件
group by b.month; Hive SQL 进阶指南:分区与窗口函数实战
Hive SQL 进阶指南:分区与窗口函数实战





 本文深入探讨了Hive SQL与SQL的区别,强调了分区的重要性和使用方法。文章还详细介绍了Hive的专用函数,包括日期时间、条件、字符串和聚合函数。特别讨论了窗口函数在累计计算、最值、排序和分组排序等场景的应用,以及解决数据倾斜的策略。此外,还分享了实用的Hive SQL技巧,如去重、聚合、并发执行和行转列等。
本文深入探讨了Hive SQL与SQL的区别,强调了分区的重要性和使用方法。文章还详细介绍了Hive的专用函数,包括日期时间、条件、字符串和聚合函数。特别讨论了窗口函数在累计计算、最值、排序和分组排序等场景的应用,以及解决数据倾斜的策略。此外,还分享了实用的Hive SQL技巧,如去重、聚合、并发执行和行转列等。
















 3564
3564

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








