一、文件IO相关函数
1.read/write cp
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
if(argc<3)
{
fprintf(stderr, "usage:./a.out srcfile dstfile\n");
return 1;
}
int srcfd = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
int dstfd = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666);
if (-1 == srcfd||dstfd==-1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "open error\n");
return 1;
}
while(1)
{
char buf[1024]={0};
ssize_t ret= read(srcfd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if(0==ret)
{
break;
}
write(dstfd, buf, ret);
}
close(srcfd);
close(dstfd);
return 0;
}
2.文件的插入功能(insert_hw.c)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE*fp=fopen("1.txt","r+");
if(NULL==fp)
{
fprintf(stderr, "fopen error\n");
return 1;
}
char data[]="aaa";
int pos=4;
fseek(fp,0,SEEK_END);
long size=ftell(fp);
fseek(fp, pos, SEEK_SET);
char*end = malloc(size-pos);
if(NULL==end)
{
return 1;
}
fread(end, size-pos, 1, fp);
fseek(fp, pos, SEEK_SET);
fputs(data,fp);
fputs(end, fp);
free(end);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
3.查字典
(1)klist.c
#include "./klist.h"
void klist_init(KLIST* head)
{
head->prev = head;
head->next = head;
}
void klist_add(KLIST* newnode,KLIST*prev,KLIST* next)
{
newnode->next =next;
newnode->prev = prev;
prev->next = newnode;
next->prev = newnode;
}
void klist_add_head(KLIST* head,KLIST* newnode)
{
klist_add(newnode,head,head->next);
}
void klist_add_tail(KLIST* head,KLIST* newnode)
{
klist_add(newnode,head->prev,head);
}
void klist_del(KLIST*prev,KLIST*next)
{
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
}
(2)klist.h
#ifndef __KLIST_H__
#define __KLIST_H__
typedef struct __klist
{
struct __klist *next;
struct __klist* prev;
}KLIST;
#define offset(type,mem) ((size_t) &((type*)0)->mem)
/**
* @brief ptr 结构体node的指针
type 结构体 per
* mem node在结构中的变量名
*/
#define containerof(ptr,type,mem) ({ const typeof(((type*)0)->mem) * _mptr = (ptr);\
(type*) ((char*)_mptr- offset(type,mem)); })
#define klist_for_entry(ptr,type,mem) containerof(ptr,type,mem)
/**
* @brief p , 指向结构体的指针
* n, 指向当前结构体的下一个指针
mem, node在结构体中变量的名字
*/
//for(p=klist_for_entry(&(head)->next,typeof(*p),mem),n=klist_for_entry((p)->mem.next,typeof(*p),mem);
#define klist_for_each(p,n,head,mem) \
for(p=klist_for_entry(head->next,typeof(*p),mem),n=klist_for_entry((p)->mem.next,typeof(*p),mem);\
&p->mem != (head); p=n,n=klist_for_entry((n)->mem.next,typeof(*n),mem))
// #define offset(type,mem) ((size_t) &((type*)0)->mem)
// #define containerof(p,type,mem) ({\
// const typeof( ((type*)0)->mem ) * _mptr = (p);\
// (type*)((char*)_mptr - offset(type,mem));})
// #define klist_entry(p,type,mem) containerof(p,type,mem)
// #define klist_for_each(p,n,head,node)\
// for(p=klist_entry((head)->next,typeof(*p),node),\
// n=klist_entry(p->node.next,typeof(*p),node); \
// &p->node != (head);p=n,n=klist_entry(n->node.next,typeof(*n),node))
void klist_init(KLIST* head);
void klist_add_head(KLIST* head,KLIST* newnode);
void klist_add_tail(KLIST* head,KLIST* newnode);
void klist_del(KLIST*prev,KLIST*next);
#endif
(3)main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "klist.h"
typedef struct
{
char word[50];
char mean[512];
KLIST node;
} DATATYPE;
int add_word(char* word, char* mean, KLIST* head)
{
DATATYPE* data = malloc(sizeof(DATATYPE));
if (NULL == data)
{
perror("add_per malloc\n");
return 1;
}
strcpy(data->word, word);
strcpy(data->mean, mean);
klist_add_tail(head, &data->node);
return 0;
}
DATATYPE* find_word(KLIST* head, char* word)
{
DATATYPE *p, *n;
// p 代表当前节点 n 是当前节点的下一个 head 链表的头指针 node
// ,自定义结构体中,节点变量的名字
klist_for_each(p, n, head, node)
{
// printf("%d %s\n",p->id,p->name);
if (0 == strcmp(p->word, word))
{
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
FILE* fp = fopen("/home/linux/dict.txt", "r");
if (NULL == fp)
{
return 1;
}
KLIST head;
klist_init(&head);
while (1)
{
char buf[1024] = {0};
if (NULL == fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), fp))
{
break;
}
char* word = strtok(buf, " ");
char* mean = strtok(NULL, "\r");
add_word(word, mean, &head);
}
while (1)
{
char want_word[50] = {0};
printf("input word:");
fgets(want_word, sizeof(want_word), stdin); // zoo\n #quit
want_word[strlen(want_word) - 1] = '\0';
if(0==strcmp(want_word,"#quit"))
{
break;
}
DATATYPE* tmp = find_word(&head, want_word);
if (NULL == tmp)
{
printf("can't find, %s\n", want_word);
}
else
{
printf("%s %s\n", tmp->word, tmp->mean);
}
}
// system("pause");
return 0;
}
4.lseek
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
功能:定位光标的位置
参数:fd:文件描述符;offset:偏移量;正:向后偏移;负:向前偏移;零:不偏移
whence:SEEK_SET;SEEK_CUR;SEEK_END
返回值:成功返回偏移量;失败返回-1
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd = open("1.txt", O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666);
if(-1==fd)
{
fprintf(stderr, "open error");
return 1;
}
off_t offset = lseek(fd, 1024, SEEK_SET);
printf("%ld\n",offset);
write(fd, "a", 2);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
5.fopen与open 对应权限问题
fopen open
w O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC
w+ O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC
r O_RDONLY
r+ O_RDWR
a O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND
a+ O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_APPEND
6.fileno
转换: FILE* fp -> int fd fgets(,);
int fileno(FILE *stream);
功能:获得一个文件流指针中的文件描述符
参数:stream:文件流指针
返回值:成功返回文件描述符;失败返回-1
#include<stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE*fp = fopen("2.txt", "w");
if(NULL==fp)
{
return 1;
}
int fd = fileno(fp);
write(fd, "hello", 5);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
7.fdopen
转换:int fd -> FILE *fp
FILE *fdopen(int fd, const char *mode);
功能:将文件描述符转化为文件流指针
参数:fd:已经打开的文件描述符
mode:"r" "r+" "w" "w+" "a" "a+"
返回值:成功返回文件流指针;失败返回NULL
#include<stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd = open("2.txt", O_RDONLY);
if(-1==fd)
{
return 1;
}
FILE*fp = fdopen(fd, "r");
if(NULL==fp)
{
return 1;
}
char buf[512]={0};
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),fp);
printf("%s",buf);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
8.perror 系统错误警告
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE*fp = fopen("5.txt", "r");
if(NULL==fp)
{
printf("error %d\n",errno);
perror("fopen main.c:10");
}
return 0;
}
二、目录操作
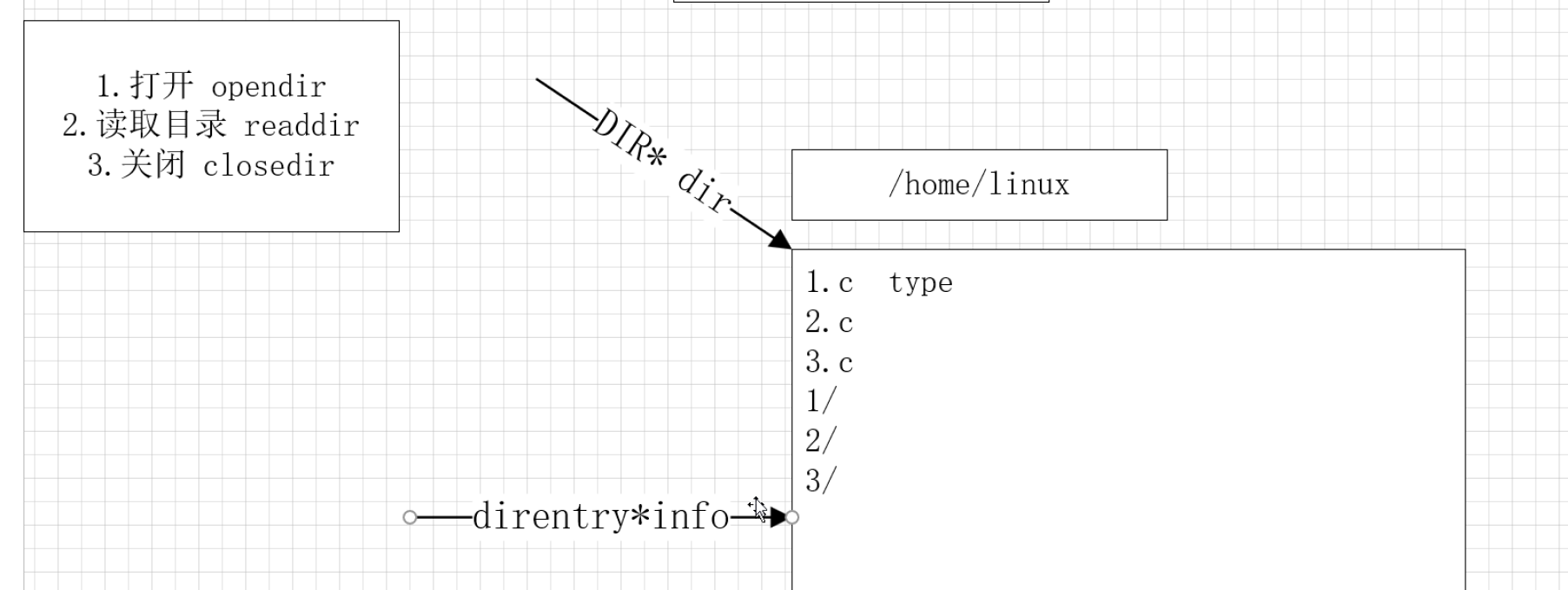
1.步骤
- 打开目标目录
- 读取目录
- 关闭目录
2. 目录的遍历-ls
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
DIR*dir=opendir("../");
if(NULL==dir)
{
perror("opendir");
return 1;
}
while (1)
{
struct dirent*info= readdir(dir);
if(NULL==info)
{
break;
}
printf("%s\n",info->d_name);
}
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
3.time
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
time_t tm;
tm =time(NULL);
printf("%ld\n",tm);
struct tm*tminfo = localtime(&tm);
printf("%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d\n",tminfo->tm_year+1900,tminfo->tm_mon+1,tminfo->tm_mday
,tminfo->tm_hour,tminfo->tm_min,tminfo->tm_sec);
return 0;
}




















 343
343

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








