apple推荐category的使用场景
- 给现有的类添加方法
- 可以把类的实现分开在几个不同的文件里面。这样做有几个显而易见的好处
- 可以减少单个文件的体积
- 可以把不同的功能组织到不同的category里
- 可以由多个开发者共同完成一个类
- 可以按需加载想要的category等等
- 声明私有方法
声明私有方法是指,在原类的.m文件中定义category,且category在implement之前,这时在category中声明的方法就是私有方法。
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface ASuper : NSObject
- (void)methodA;
@end
#import "ASuper.h"
@interface ASuper (PrivateMethod)
- (void)myAddPrivateMethod;
@end
@implementation ASuper
- (void)methodA
{
[self myAddPrivateMethod];
NSLog(@"123123");
}
- (void)myAddPrivateMethod
{
NSLog(@"4343434");
}
@end其他使用场景
- 模拟多继承
- 把framework的私有方法公开
category和extension对比
extension在编译期决议,它是类的一部分,在编译期和头文件里的@interface以及实现文件中的@implement一起形成一个完整的类,它伴随类的产生而产生,亦随之一起消亡。extension一般用来隐藏类的私有信息,你必须有一个类的源码才能为一个类添加extension,所以你无法为系统的类比如NSString添加extension。
category在运行期决议。
根据决议期不同,可以看出extension可以添加实例变量,而category是无法添加实例变量的,因为在运行期,对象的内存布局已经确定,如果添加实例变量就会破坏类的内部布局,这对编译型语言来说是灾难性。
#import "MySuper.h"
@interface MySuper (Category1)
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *attrOne;
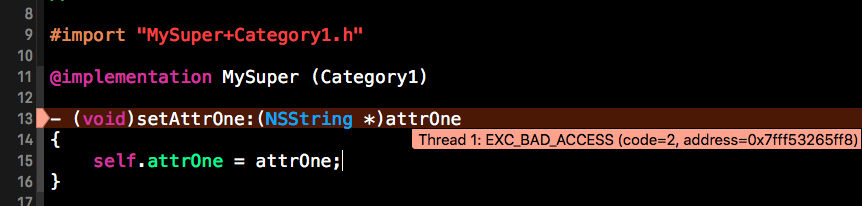
@end直接使用实例变量会报报错
#import "MySuper+Category1.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation MySuper (Category1)
- (void)setAttrOne:(NSString *)attrOne
{
self.attrOne = attrOne;
}
- (NSString *)attrOne
{
return self.attrOne;
}
@end报错截图
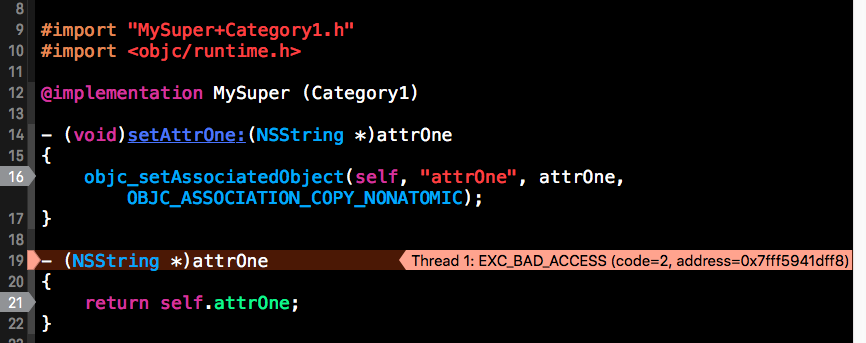
这里只能使用关联对象来进行set和get了。
#import "MySuper+Category1.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation MySuper (Category1)
- (void)setAttrOne:(NSString *)attrOne
{
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, "attrOne", attrOne, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC);
}
- (NSString *)attrOne
{
NSString *attr = objc_getAssociatedObject(self, "attrOne");
return attr;
}
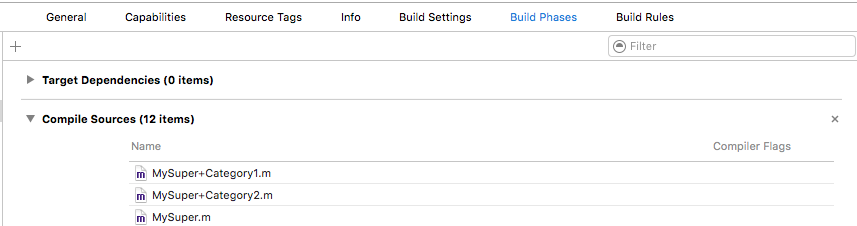
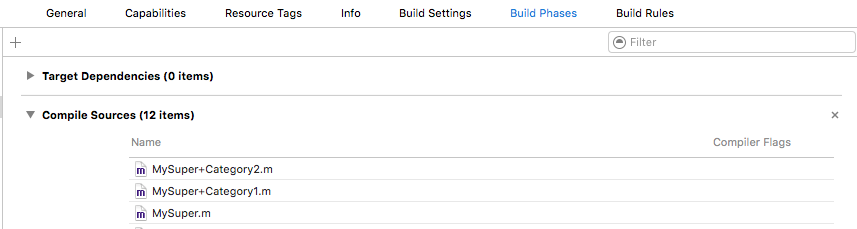
@end同类的多个category中有相同方法时的调用顺序
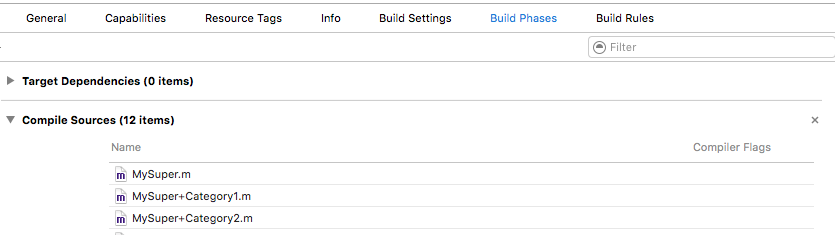
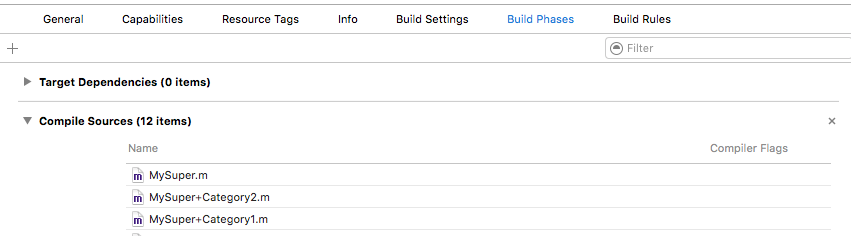
一个类建立多个category,并且在每个category中添加相同的方法(printABC),在其他类调用这个方法时,是调用Compile Sources中排在最后一个category中的printABC方法。如果有和原类相同的方法,原类中的方法会被覆盖,因为category的优先级更高。
注:Category 有一个非常容易误用的场景,那就是用 Category 来覆写父类或主类的方法。虽然目前 Objective-C 是允许这么做的,但是这种使用场景是非常不推荐的。使用 Category 来覆写方法有很多缺点,比如不能覆写 Category 中的方法、无法调用主类中的原始实现等,且很容易造成无法预估的行为。
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface MySuper : NSObject
- (void)printABC;
@end
#import "MySuper.h"
@implementation MySuper
- (void)printABC
{
NSLog(@"123123");
}
@end
//Category1
#import "MySuper.h"
@interface MySuper (Category1)
- (void)printABC;
- (void)printDEF;
@end
#import "MySuper+Category1.h"
@implementation MySuper (Category1)
- (void)printABC
{
NSLog(@"456456");
}
- (void)printDEF
{
NSLog(@"00000");
}
@end
//Category2
#import "MySuper.h"
@interface MySuper (Category2)
- (void)printABC;
- (void)printDEF;
@end
#import "MySuper+Category2.h"
@implementation MySuper (Category2)
- (void)printABC
{
NSLog(@"789789");
}
- (void)printDEF
{
NSLog(@"11111");
}
@end打印结果:789789
打印结果:11111打印结果:456456
打印结果:00000打印结果:789789
打印结果:11111打印结果:456456
打印结果:00000如果是系统类,在category中重写系统类中的方法,在调用该方法时,不会产生覆盖。 这里举例的方法比较特别,Framework中的其它方法照样可以覆盖。
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface NSString (AStr)
- (unichar)characterAtIndex:(NSUInteger)index;
@end
#import "NSString+AStr.h"
@implementation NSString (AStr)
- (unichar)characterAtIndex:(NSUInteger)index
{
NSLog(@"123123123");
return 'a';
}
@end
NSString *oneStr = @"123123123";
char ch = [oneStr characterAtIndex:1];
NSLog(@"%c",ch);
这里的结果为:2,而不是’a’。
模拟多继承
http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20130528/6295.html
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface ASuper : NSObject
- (void)methodA;
@end
#import "ASuper.h"
@implementation ASuper
- (void)methodA
{
NSLog(@"123123");
}
@end
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface BSuper : NSObject
- (void)methodB;
@end
#import "BSuper.h"
@implementation BSuper
- (void)methodB
{
NSLog(@"456456");
}
@end
#import "ASuper.h"
@interface ASuper (BSuperInheritance)
@end
#import "ASuper+BSuperInheritance.h"
#import "BSuper.h"
@implementation ASuper (BSuperInheritance)
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
BSuper *bSuperInstance = [[BSuper alloc] init];
if ([bSuperInstance respondsToSelector:@selector(methodB)]) {
return bSuperInstance;
}
return nil;
}
@end调用methodB,有两种方式:
在类别中加入BSuper类型的方法名
@interface ASuper (BSuperInheritance) - (void)methodB; @end这样就可以在ASuper的对象中直接调用methodB,而通过category中的消息转发就能成功调用methodB。
ASuper *aSuper = [ASuper new]; [aSuper methodB];在调用methodB的地方,引入BSuper类,把ASuper对象强转成BSuper类型来调用methodB。
#import "BSuper.h" ASuper *aSuper = [ASuper new]; [(BSuper *)aSuper methodB];
把framework的私有方法公开
以UIDevice的私有方法setOrientation:为例
@interface UIDevice (Test)
- (void)setOrientation:(UIInterfaceOrientation)orientation;
@end
@implementation UIDevice (Test)
@end这样在引用该category中的类中,就可以通过UIDevice直接调用了。
if ([[UIDevice currentDevice] respondsToSelector:@selector(setOrientation:)]) {
[[UIDevice currentDevice] setOrientation:UIInterfaceOrientationLandscapeRight];
}参考
http://tech.meituan.com/DiveIntoCategory.html
http://blog.csdn.net/yiyaaixuexi/article/details/8970734
https://developer.apple.com/library/ios/documentation/General/Conceptual/DevPedia-CocoaCore/Category.html






















 313
313











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








