简介
本篇博客介绍一种点云分割通过形态学滤波的方法,该算法来自于 A Progressive Morphological Filter for Removing Nonground Measurements from Airborne LIDAR Data论文,主要是解决航空摄影测量时候,如何有效的分割出地平面的点云。关于该算法具体流程参见该博客传送门,讲解该算法过程还是比较清晰的。下面我们就简单跑一下Demo并且对比一下Approximate的方式与原始的性能差异。
Demo代码
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/progressive_morphological_filter.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/approximate_progressive_morphological_filter.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
pcl::PointIndicesPtr ground(new pcl::PointIndices);
// Fill in the cloud data
pcl::PCDReader reader;
// Replace the path below with the path where you saved your file
reader.read<pcl::PointXYZI>("apollo.pcd", *cloud);
std::cerr << "Cloud before filtering: " << cloud->points.size() << std::endl;
auto startTime = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
// Create the filtering object
// pcl::ProgressiveMorphologicalFilter<pcl::PointXYZI> pmf;
pcl::ApproximateProgressiveMorphologicalFilter<pcl::PointXYZI> pmf;
pmf.setInputCloud(cloud);
pmf.setMaxWindowSize(20); // set window size
pmf.setSlope(1.0f); // slope
pmf.setInitialDistance(0.5f);
pmf.setMaxDistance(1.5f);
pmf.extract(ground->indices);
// Create the filtering object
pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZI> extract;
extract.setInputCloud(cloud);
extract.setIndices(ground);
extract.filter(*cloud_filtered);
std::cerr << "Ground cloud after filtering: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << *cloud_filtered << std::endl;
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write<pcl::PointXYZI> ("apollo-utm_ground.pcd", *cloud_filtered, false);
// Extract non-ground returns
extract.setNegative(true);
extract.filter(*cloud_filtered);
auto endTime = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto ellapsedTime = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(endTime - startTime);
std::cout << "Ellapse-Time: " << ellapsedTime.count() << " milliseconds." << std::endl;
std::cerr << "Object cloud after filtering: " << cloud_filtered->points.size() << std::endl;
writer.write<pcl::PointXYZI>("apollo-utm_object.pcd", *cloud_filtered, false);
return 0;
}
实验结果
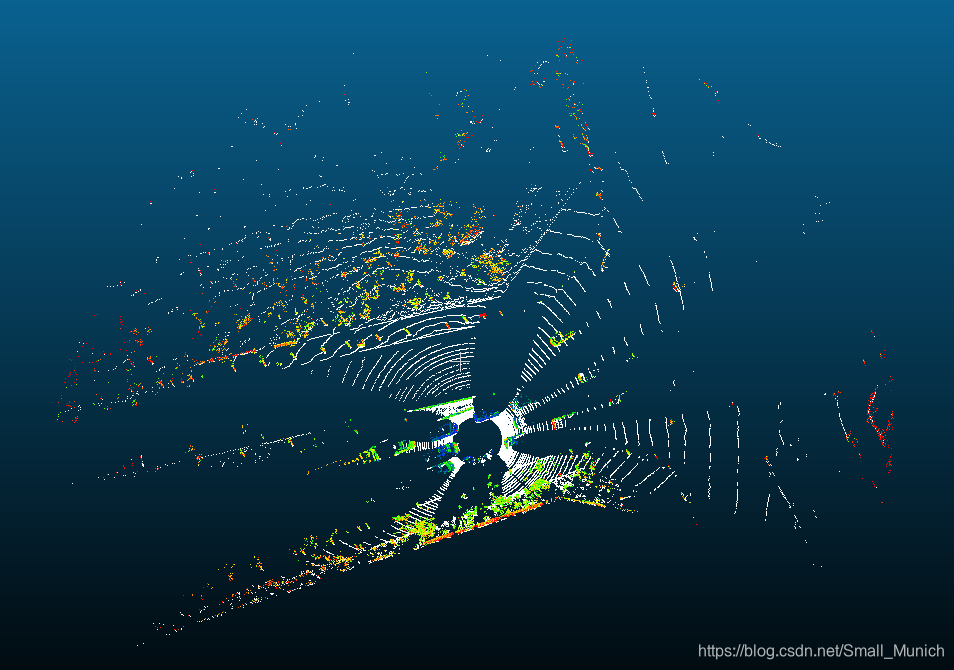

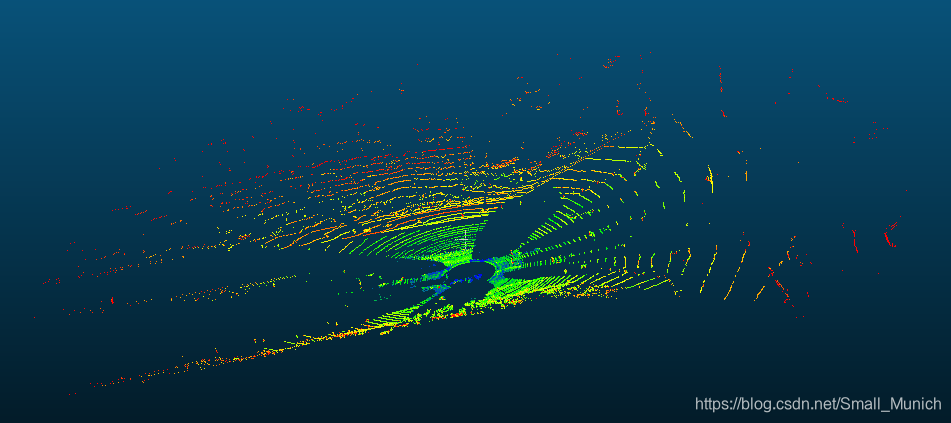
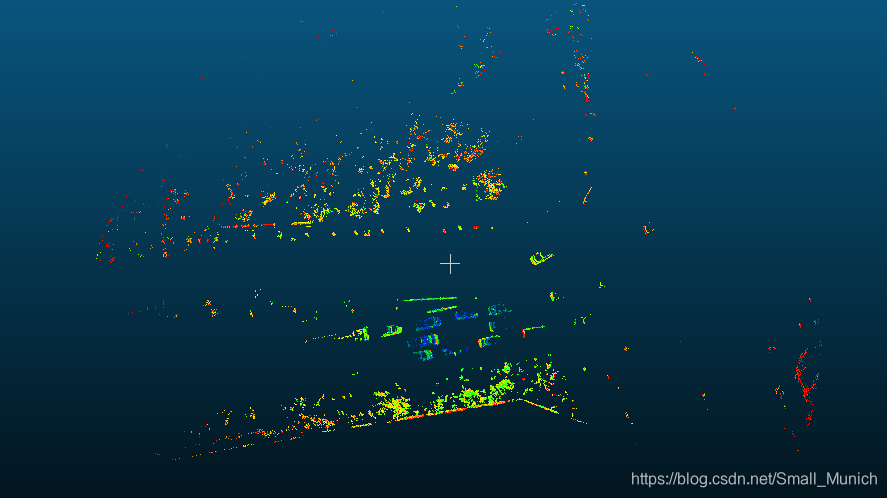
算法耗时对比:
| 算法 | 原始点云个数 | 滤波后点云个数 | 算法耗时/milliseconds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Approximate-PMF | 76053 | 43338 | 91 |
| PMF | 76053 | 42147 | 39318 |
很好奇为什么Approximate-PMF比原始PMF耗时降低这么多,它是怎么做的呢?
阅读pcl的ApproximateProgressiveMorphologicalFilter源码可以发现,该部分较原始的ProgressiveMorphologicalFilter增加多线程处理方式进行加速,通过使用OpenMP的并行编程思路来进行加速多核CPU处理方式。其中80%的代码几乎一致,只是在extract()函数里面使用并行加速的方式。
小结
上述近似Approximate-PMF算法的效果与耗时要远远低于原版本的PMF算法,当然效果上面要略逊色与原版PMF算法。对于离线处理对性能指标要求更高的遥感影像来说,PMF是首选。但是,针对实时性要求较高的无人驾驶来说,这个明显就不符合实际应用。就是Approximate-PMF的算法耗时都有些吃紧,希望还能出现更多的算法来加速场景落地。
参考
https://pcl-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/progressive_morphological_filtering.html#progressive-morphological-filtering
http://users.cis.fiu.edu/~chens/PDF/TGRS.pdf
https://blog.csdn.net/ambitiousruraldog/article/details/80268920





















 74
74











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








