接口 Java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService 表述了异步执行的机制,并且可以让任务在后台执行。壹個 ExecutorService 实例因此特别像壹個线程池。事实上,在 java.util.concurrent 包中的 ExecutorService 的实现就是壹個线程池的实现。
ExecutorService 样例
这里有壹個简单的使用Java 实现的 ExectorService 样例:
- ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
-
- executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
- public void run() {
- System.out.println("Asynchronous task");
- }
- });
-
- executorService.shutdown();
首先使用 newFixedThreadPool() 工厂方法创建壹個 ExecutorService ,上述代码创建了壹個可以容纳10個线程任务的线程池。其次,向 execute() 方法中传递壹個异步的 Runnable 接口的实现,这样做会让 ExecutorService 中的某個线程执行这個 Runnable 线程。
任务的委托(Task Delegation)
下方展示了一个线程的把任务委托异步执行的ExecutorService的示意图。
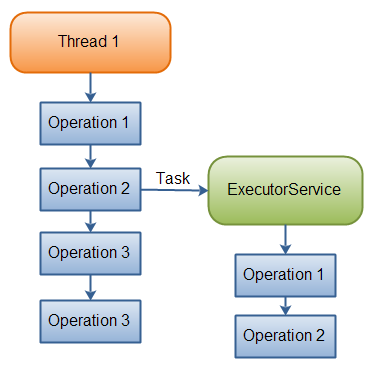
壹旦线程把任务委托给 ExecutorService,该线程就会继续执行与运行任务无关的其它任务。
ExecutorService 的实现
由于 ExecutorService 只是壹個接口,你壹量需要使用它,那麽就需要提供壹個该接口的实现。ExecutorService 接口在 java.util.concurrent 包中有如下实现类:
创建壹個 ExecutorService
你可以根据自己的需要来创建壹個 ExecutorService ,也可以使用 Executors 工厂方法来创建壹個 ExecutorService 实例。这里有几個创建 ExecutorService 的例子:
- ExecutorService executorService1 = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
- ExecutorService executorService2 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
- ExecutorService executorService3 = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10);
ExecutorService 使用方法
这里有几种不同的方式让你将任务委托给壹個 ExecutorService:
- execute(Runnable)
- submit(Runnable)
- submit(Callable)
- invokeAny(...)
- invokeAll(...)
我会在接下来的内容里把每個方法都看壹遍。
execute(Runnable)
方法 execute(Runnable) 接收壹個 java.lang.Runnable 对象作为参数,并且以异步的方式执行它。如下是壹個使用 ExecutorService 执行 Runnable 的例子:
- ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
-
- executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
- public void run() {
- System.out.println("Asynchronous task");
- }
- });
-
- executorService.shutdown();
使用这种方式没有办法获取执行 Runnable 之后的结果,如果你希望获取运行之后的返回值,就必须使用 接收 Callable 参数的 execute() 方法,后者将会在下文中提到。
submit(Runnable)
方法 submit(Runnable) 同样接收壹個 Runnable 的实现作为参数,但是会返回壹個 Future 对象。这個 Future 对象可以用于判断 Runnable 是否结束执行。如下是壹個 ExecutorService 的 submit() 方法的例子:
- Future future = executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
- public void run() {
- System.out.println("Asynchronous task");
- }
- });
-
- System.out.println("future.get()=" + future.get());
submit(Callable)
方法 submit(Callable) 和方法 submit(Runnable) 比较类似,但是区别则在于它们接收不同的参数类型。Callable 的实例与 Runnable 的实例很类似,但是 Callable 的 call() 方法可以返回壹個结果。方法 Runnable.run() 则不能返回结果。
Callable 的返回值可以从方法 submit(Callable) 返回的 Future 对象中获取。如下是壹個 ExecutorService Callable 的样例:
- Future future = executorService.submit(new Callable(){
- public Object call() throws Exception {
- System.out.println("Asynchronous Callable");
- return "Callable Result";
- }
- });
-
- System.out.println("future.get() = " + future.get());
上述样例代码会输出如下结果:
- ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
-
- Set<Callable<String>> callables = new HashSet<Callable<String>>();
-
- callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 1";
- }
- });
- callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 2";
- }
- });
- callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 3";
- }
- });
-
- String result = executorService.invokeAny(callables);
-
- System.out.println("result = " + result);
-
- executorService.shutdown();
inVokeAny()
方法 invokeAny() 接收壹個包含 Callable 对象的集合作为参数。调用该方法不会返回 Future 对象,而是返回集合中某壹個 Callable 对象的结果,而且无法保证调用之后返回的结果是哪壹個 Callable,只知道它是这些 Callable 中壹個执行结束的 Callable 对象。
如果壹個任务运行完毕或者抛出异常,方法会取消其它的 Callable 的执行。
以下是壹個样例:
- ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
-
- Set<Callable<String>> callables = new HashSet<Callable<String>>();
-
- callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 1";
- }
- });
- callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 2";
- }
- });
- callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 3";
- }
- });
-
- String result = executorService.invokeAny(callables);
-
- System.out.println("result = " + result);
-
- executorService.shutdown();
以上样例代码会打印出在给定的集合中的某壹個 Callable 的返回结果。我尝试运行了几次,结果都在改变。有时候返回结果是"Task 1",有时候是"Task 2",等等。
invokeAll()
方法 invokeAll() 会调用存在于参数集合中的所有 Callable 对象,并且返回壹個包含 Future 对象的集合,你可以通过这個返回的集合来管理每個 Callable 的执行结果。
需要注意的是,任务有可能因为异常而导致运行结束,所以它可能并不是真的成功运行了。但是我们没有办法通过 Future 对象来了解到这個差异。
以下是壹個代码样例:
- ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
-
- Set<Callable<String>> callables = new HashSet<Callable<String>>();
-
- callables.add(new Callable<String>() {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 1";
- }
- }); <li style="border-top: none; border-right: none; border-bottom: none; border-left: 3px solid rgb(108, 226, 108); border-image: initial;





















 898
898











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








