01 - 原始版本的 IOC 容器
IOC 容器的作用是自动创建对象,降低系统间的耦合度
core
public interface Resource extends Iterator<Object>{
}
外部的配置信息都当成 Resource (资源)来进行抽象
public class ClassPathXmlResource implements Resource {
Document document;
Element rootElement;
Iterator<Element> elementIterator;
public ClassPathXmlResource(String fileName) {
// 通过类加载器获取资源路径
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(fileName);
try {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
// 读取 xml 文件
document = reader.read(url);
rootElement = document.getRootElement();
elementIterator = rootElement.elementIterator();
} catch (DocumentException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public Object next() {
return elementIterator.next();
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return elementIterator.hasNext();
}
}
从 xml 读取配置信息
beans
public class BeanDefinition {
private String id;
private String className;
}
xml 配置信息在内存种对应的信息
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader {
BeanFactory beanFactory;
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) {
while (resource.hasNext()) {
Element next = (Element) resource.next();
String id = next.attributeValue("id");
String className = next.attributeValue("className");
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(new BeanDefinition(id, className));
}
}
}
解析 xml 里的配置信息,转换为 BeanDefinition
public interface BeanFactory {
Object getBean(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException, ClassNotFoundException;
void registerBeanDefinition(BeanDefinition beanDefinition);
}
bean 工厂,用于创建 bean
public class SimpleBeanFactory implements BeanFactory {
private List<BeanDefinition> beanDefinitions = new ArrayList<>();
private List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>();
private Map<String, Object> singletons = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
Object object = singletons.get(beanName);
if (object == null) {
int i = beanNames.indexOf(beanName);
if (i == -1) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException();
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitions.get(i);
try {
object = Class.forName(beanDefinition.getClassName()).newInstance();
singletons.put(beanDefinition.getId(), object);
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return object;
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
beanDefinitions.add(beanDefinition);
beanNames.add(beanDefinition.getId());
}
}
一个简单的 BeanFactoy 实现类
context
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements BeanFactory {
BeanFactory beanFactory;
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String fileName) {
// 抽象为资源
Resource res = new ClassPathXmlResource(fileName);
// bean 工厂
BeanFactory bf = new SimpleBeanFactory();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(bf);
// 解析资源
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(res);
this.beanFactory = bf;
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException, ClassNotFoundException {
return beanFactory.getBean(beanName);
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
this.beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanDefinition);
}
}
02 - 扩展 Bean
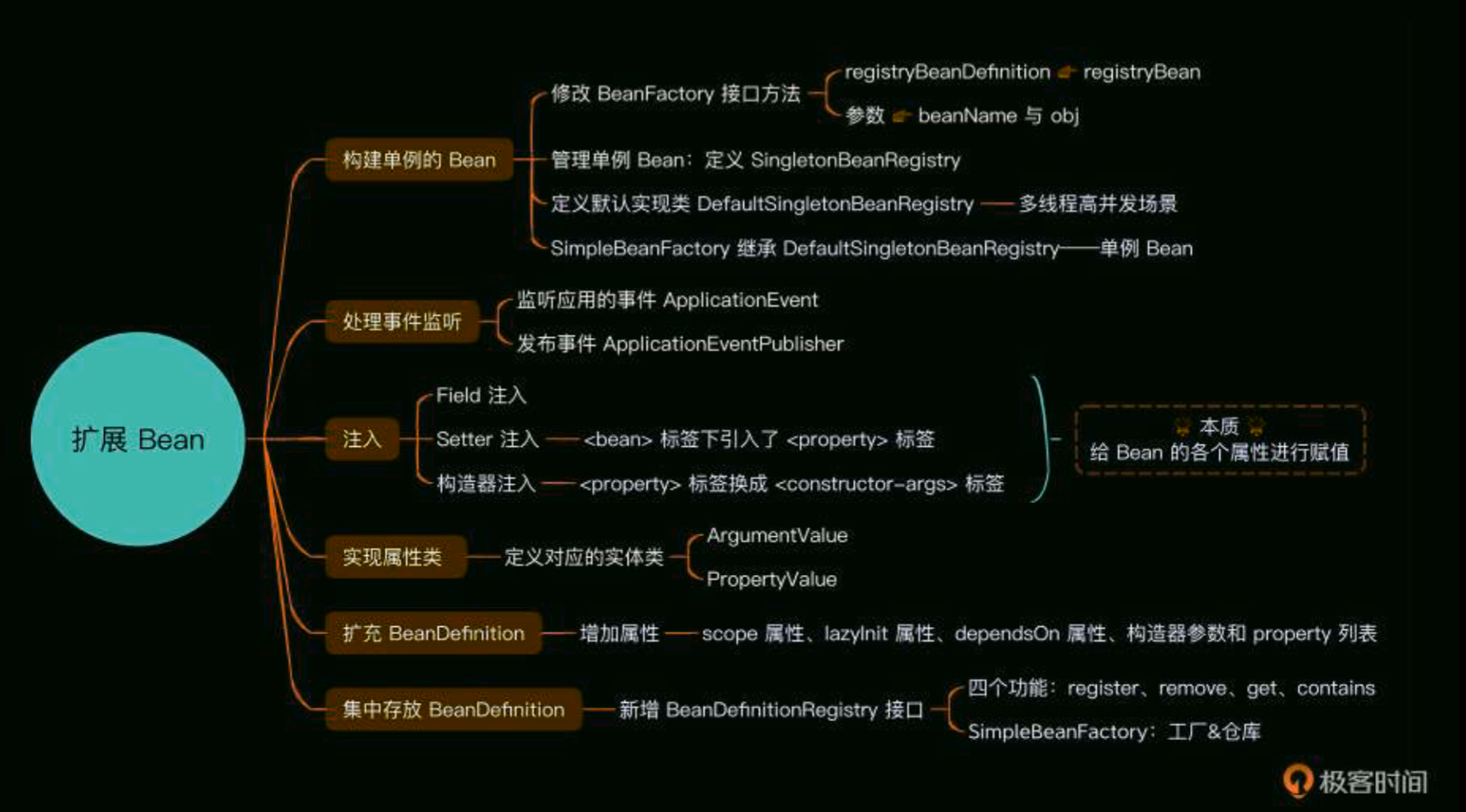
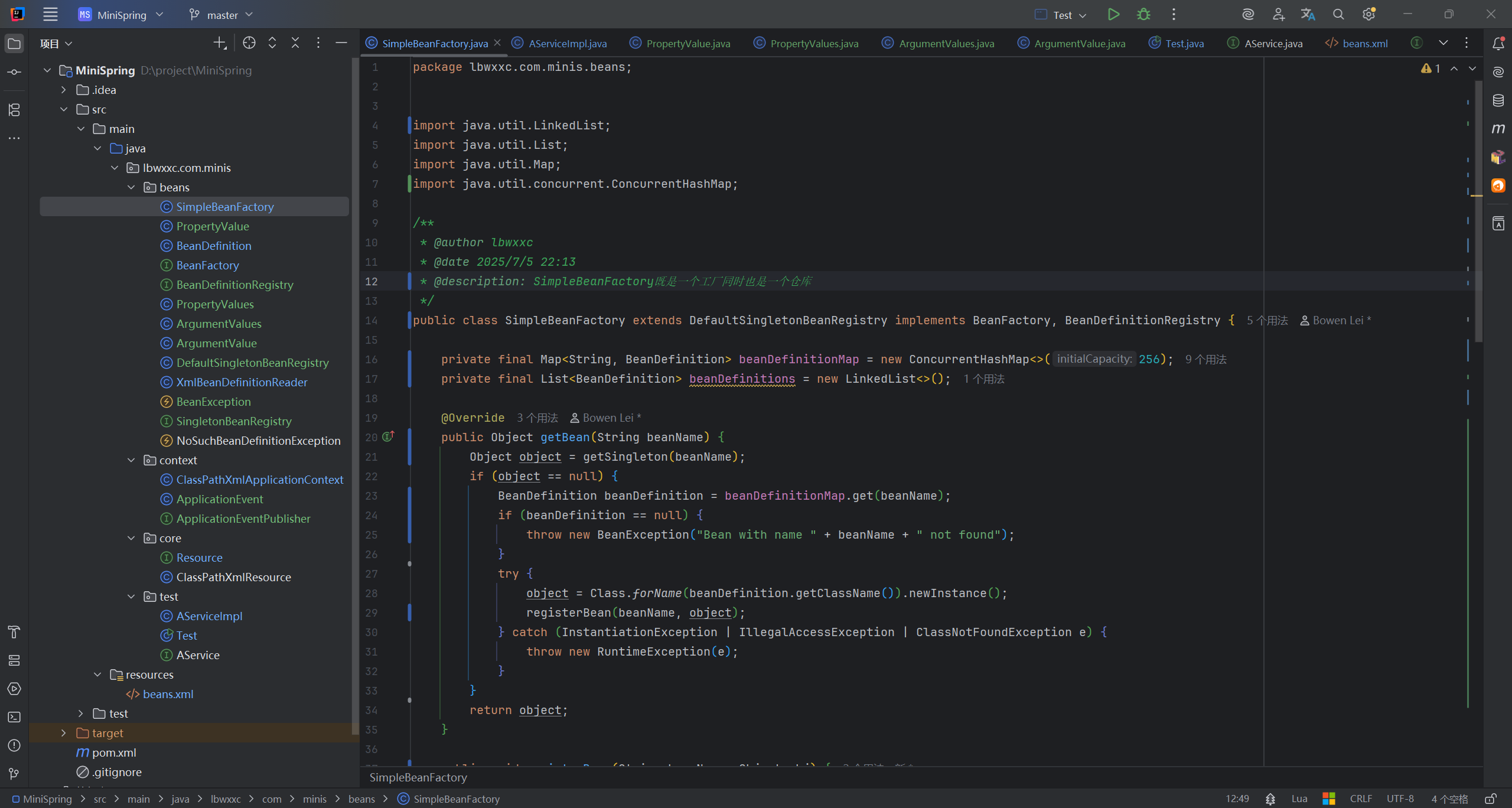
03 - 依赖注入:如何给Bean注入值并解决循环依赖问题?
给 Bean 注入属性
<bean id="aservice" className="lbwxxc.com.minis.test.AServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg type="String" name="name" value="abc"/>
<constructor-arg type="Integer" name="level" value="3"/>
<property type="String" name="property1" value="Someone says"/>
<property type="String" name="property2" value="Hello World!"/>
<property type="lbwxxc.com.minis.test.BaseService" name="ref1" ref="baseservice"/>
</bean>
设置 Bean
public class PropertyValue {
private final String type;
private final String name;
private final Object value;
private final boolean isRef;
public PropertyValue(String type, String name, Object value, boolean isRef) {
this.type = type;
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
this.isRef = isRef;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
public boolean isRef() {
return isRef;
}
}
属于对应 Java 的 实体类
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) {
while (resource.hasNext()) {
Element element = (Element) resource.next();
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
String className = element.attributeValue("className");
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition(id, className);
List<Element> property = element.elements("property");
ArrayList<String> refs = new ArrayList<>();
PropertyValues PVS = new PropertyValues();
for (Element propertyElement : property) {
String pType = propertyElement.attributeValue("type");
String pName = propertyElement.attributeValue("name");
String pValue = propertyElement.attributeValue("value");
// 属性是否为其它 Bean
String ref = propertyElement.attributeValue("ref");
String pV = "";
boolean isRef = false;
if (ref != null && !ref.isEmpty()) {
pV = ref;
isRef = true;
refs.add(ref);
} else {
pV = pValue;
}
PVS.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(pType, pName, pV, isRef));
}
beanDefinition.setPropertyValues(PVS);
// 依赖
beanDefinition.setDependsOn(refs.toArray(new String[0]));
List<Element> constructorArg = element.elements("constructor-arg");
ArgumentValues AVS = new ArgumentValues();
for (Element constructorArgElement : constructorArg) {
String pType = constructorArgElement.attributeValue("type");
String pName = constructorArgElement.attributeValue("name");
String pValue = constructorArgElement.attributeValue("value");
AVS.addArgumentValue(new ArgumentValue(pType, pName, pValue));
}
beanDefinition.setConstructorArgumentValues(AVS);
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanDefinition);
}
}
// 设置属性
private void handleProperties(BeanDefinition bd, Class<?> clz, Object obj) {
// 设置属性
PropertyValues propertyValues = bd.getPropertyValues();
if (!propertyValues.isEmpty()) {
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : propertyValues.getPropertyValues()) {
String pType = propertyValue.getType();
String pName = propertyValue.getName();
Object pValue = propertyValue.getValue();
boolean ref = propertyValue.isRef();
Class<?>[] paraTypes = new Class[1];
Object[] paraValues = new Object[1];
if (!ref) {
if (pType.equals("String")) {
paraTypes[0] = String.class;
} else if (pType.equals("int")) {
paraTypes[0] = int.class;
} else if (pType.equals("Integer")) {
paraTypes[0] = Integer.class;
} else {
continue;
}
paraValues[0] = pValue;
} else {
try {
paraTypes[0] = Class.forName(pType);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
paraValues[0] = getBean((String) pValue);
}
String methodName = "set" + pName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + pName.substring(1);
try {
Method method = clz.getMethod(methodName, paraTypes);
method.invoke(obj, paraValues);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException | InvocationTargetException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
直接反射进行硬编码设置属性
解决循环依赖

<bean id="basebaseservice" className="lbwxxc.com.minis.test.BaseBaseService">
<property type="lbwxxc.com.minis.test.AServiceImpl" name="as" ref="aservice" />
</bean>
<bean id="aservice" className="lbwxxc.com.minis.test.AServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg type="String" name="name" value="abc"/>
<constructor-arg type="Integer" name="level" value="3"/>
<property type="String" name="property1" value="Someone says"/>
<property type="String" name="property2" value="Hello World!"/>
<property type="lbwxxc.com.minis.test.BaseService" name="ref1" ref="baseservice"/>
</bean>
<bean id="baseservice" className="lbwxxc.com.minis.test.BaseService">
<property type="lbwxxc.com.minis.test.BaseBaseService" name="bbs" ref="basebaseservice" />
</bean>
将创建对象和设置属性相分离
创建对象
private Object doCreateBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Class<?> clz;
Object obj;
Constructor<?> con;
// 创建对象
try {
// 获取构造参数
ArgumentValues argumentValues = beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues();
Class<?>[] paraTypes = new Class[argumentValues.getArgumentCount()];
Object[] paraValues = new Object[argumentValues.getArgumentCount()];
if (argumentValues.getArgumentCount() != 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < argumentValues.getArgumentCount(); i++) {
ArgumentValue indexedArgumentValue = argumentValues.getIndexedArgumentValue(i);
if (indexedArgumentValue.getType().equals("String")) {
paraTypes[i] = String.class;
paraValues[i] = indexedArgumentValue.getValue();
} else if (indexedArgumentValue.getType().equals("int")) {
paraTypes[i] = int.class;
paraValues[i] = Integer.valueOf((String) indexedArgumentValue.getValue());
} else if (indexedArgumentValue.getType().equals("Integer")) {
paraTypes[i] = Integer.class;
paraValues[i] = Integer.valueOf((String) indexedArgumentValue.getValue());
} else {
paraTypes[i] = String.class;
paraValues[i] = indexedArgumentValue.getValue();
}
}
}
clz = Class.forName(beanDefinition.getClassName());
con = clz.getConstructor(paraTypes);
obj = con.newInstance(paraValues);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | NoSuchMethodException | InvocationTargetException | InstantiationException |
IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(beanDefinition.getId() + " bean created. " + beanDefinition.getClassName() + " : " + obj);
return obj;
}
通过反射获取构造方法,然后通过构造方法创建对象,然后放到 earlySingletonObjects 中
// 创建毛胚对象
Object obj = doCreateBean(beanDefinition);
earlySingletonObjects.put(beanDefinition.getId(), obj);
设置属性
//设置属性
handleProperties(beanDefinition, clz, obj);
// 设置属性
private void handleProperties(BeanDefinition bd, Class<?> clz, Object obj) {
// 设置属性
PropertyValues propertyValues = bd.getPropertyValues();
if (!propertyValues.isEmpty()) {
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : propertyValues.getPropertyValues()) {
String pType = propertyValue.getType();
String pName = propertyValue.getName();
Object pValue = propertyValue.getValue();
boolean ref = propertyValue.isRef();
Class<?>[] paraTypes = new Class[1];
Object[] paraValues = new Object[1];
if (!ref) {
if (pType.equals("String")) {
paraTypes[0] = String.class;
} else if (pType.equals("int")) {
paraTypes[0] = int.class;
} else if (pType.equals("Integer")) {
paraTypes[0] = Integer.class;
} else {
continue;
}
paraValues[0] = pValue;
} else {
try {
paraTypes[0] = Class.forName(pType);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
paraValues[0] = getBean((String) pValue);
}
String methodName = "set" + pName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + pName.substring(1);
try {
Method method = clz.getMethod(methodName, paraTypes);
method.invoke(obj, paraValues);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException | InvocationTargetException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
创建完对象后存放在 earlySingletonObjects 后,再设置属性,避免循环依赖
04 - 增强IoC容器:如何让我们的Spring支持注解?
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Autowired {
}
public class AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Object result = bean;
Class<?> beanClass = result.getClass();
Field[] fields = beanClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
boolean isAutowired = field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class);
if (isAutowired) {
String fieldName = field.getName();
Object objAutowired = this.getBeanFactory().getBean(fieldName);
if (objAutowired != null) {
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(result, objAutowired);
System.out.println("autowire " + fieldName + " for bean " + beanName);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
public AutowireCapableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
return beanFactory;
}
public void setBeanFactory(AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
以处理器的方式处理注解
public class AutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory {
private final List<AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
public void addBeanPostProcessor(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) {
this.beanPostProcessors.remove(beanPostProcessor);
this.beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor);
}
public int getBeanPostProcessorCount() {
return this.beanPostProcessors.size();
}
public List<AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor> getBeanPostProcessors() {
return this.beanPostProcessors;
}
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
beanProcessor.setBeanFactory(this);
result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
}
Bean 工厂内部有 List<AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors
public Object getBean(String beanName) {
Object singleton = this.getSingleton(beanName);
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singleton == null) {
System.out.println("get bean null -------------- " + beanName);
BeanDefinition bd = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
singleton = createBean(bd);
this.registerBean(beanName, singleton);
//beanpostprocessor
//step 1 : postProcessBeforeInitialization
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(singleton, beanName);
//step 2 : init-method
if (bd.getInitMethodName() != null && !bd.getInitMethodName().equals("")) {
invokeInitMethod(bd, singleton);
}
//step 3 : postProcessAfterInitialization
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(singleton, beanName);
}
}
if (singleton == null) {
throw new BeansException("bean is null.");
}
return singleton;
}
在创建 Bean 时,会执行处理器
05 实现完整的IoC容器: 构建工厂体系并添加容器事件
- ListableBeanFactory : 将Factory内部管理的Bean作为一个集合来对待,获取Bean的数量, 得到所有Bean的名字,按照某个类型获取Bean列表等等。
- ConfigurableBeanFactory : 将维护Bean之间的依赖关系以及支持Bean处理器也看作一个独立的特性
- ConfigurableListableBeanFactory : 把 AutowireCapableBeanFactory、ListableBeanFactory和ConfigurableBeanFactory合并在一起
在 Java 语言的设计中, 一个 Interface 代表的是一种特性或者能力,我们把这些特性或能力一个个抽取出来, 各自独立互不干扰。如果一个具体的类,想具备某些特性或者能力,就去实现这些 interface, 随意组合。这是一种良好的设计原则,叫 interface segregation (接口隔离原则)。这 条原则在 Spring 框架中用得很多,你可以注意一下。
Spring的这个 interface-abstract-class 模式是值得我们学习的,它极大地增强了框架的扩 展性。
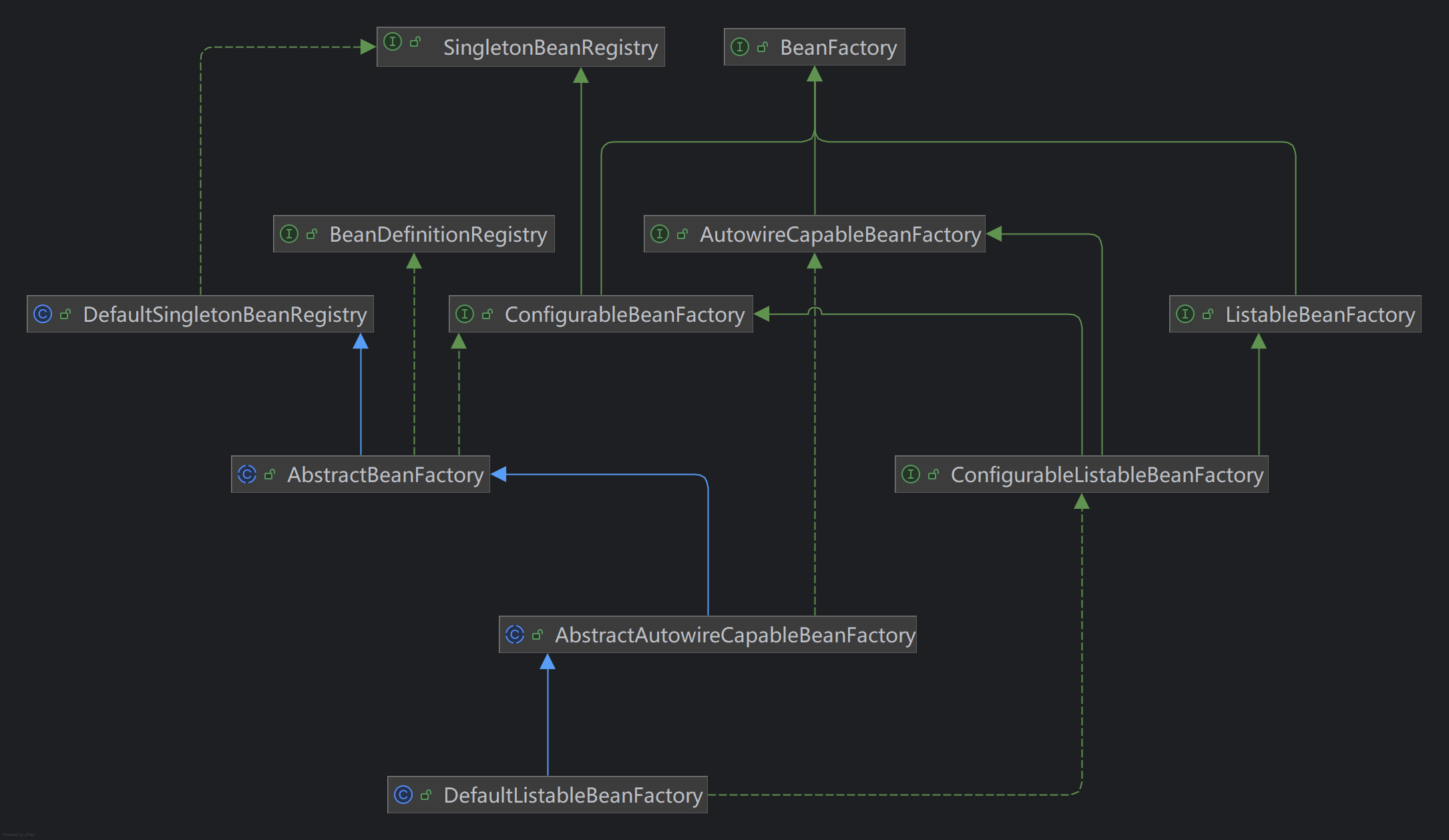
07 原始 MVC: 如何通过单一的 Servlet 拦截请求分派任务?
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
private Map<String, MappingValue> mappingValues;
private Map<String, Class<?>> mappingClz = new HashMap<>();
private String sContextConfigLocation;
private final List<String> packageNames = new ArrayList<>();
private final Map<String,Object> controllerObjs = new HashMap<>();
private final List<String> controllerNames = new ArrayList<>();
private final Map<String,Class<?>> controllerClasses = new HashMap<>();
private final List<String> urlMappingNames = new ArrayList<>();
private final Map<String,Object> mappingObjs = new HashMap<>();
private final Map<String,Method> mappingMethods = new HashMap<>();
public DispatcherServlet() {
super();
}
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
super.init(config);
System.out.println("初始化");
String path = "D:\\project\\MiniSpring\\src\\main\\resources\\web\\WEB-INF\\minisMVC-servlet.xml";
this.packageNames.addAll(XmlScanComponentHelper.getNodeValue(path));
refresh();
}
private void refresh() {
initController();
initMapping();
}
protected void initController() {
this.controllerNames.addAll(scanPackages(packageNames));
for (String controllerName : this.controllerNames) {
Object obj = null;
Class<?> clz = null;
try {
clz = Class.forName(controllerName);
this.controllerClasses.put(controllerName,clz);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (clz != null) {
obj = clz.newInstance();
}
this.controllerObjs.put(controllerName, obj);
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private List<String> scanPackages (List<String> packageNames) {
List<String> tempControllerNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String packageName : packageNames) {
tempControllerNames.addAll(scanPackage(packageName));
}
return tempControllerNames;
}
private List<String> scanPackage(String packageName) {
List<String> tempControllerNames = new ArrayList<>();
String packageNameAfter = packageName.replaceAll("\\.", "/");
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/" + packageNameAfter);
File dir = new File(url.getFile());
for (File file : dir.listFiles()) {
if(file.isDirectory()){
scanPackage(packageName+"."+file.getName());
}else{
String controllerName = packageName +"." +file.getName().replace(".class", "");
tempControllerNames.add(controllerName);
}
}
return tempControllerNames;
}
protected void initMapping() {
for (String controllerName : this.controllerNames) {
Class<?> clazz = this.controllerClasses.get(controllerName);
Object obj = this.controllerObjs.get(controllerName);
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
boolean isRequestMapping = method.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class);
if (isRequestMapping) {
String urlmapping = method.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class).value();
this.urlMappingNames.add(urlmapping);
this.mappingObjs.put(urlmapping, obj);
this.mappingMethods.put(urlmapping, method);
}
}
}
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
String servletPath = req.getServletPath();
if (servletPath == null || servletPath.equals("/")) {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
System.out.println("servletPath: " + servletPath);
Object objectResult = null;
try {
Method method = mappingMethods.get(servletPath);
Object obj = mappingObjs.get(servletPath);
objectResult = method.invoke(obj);
} catch (InvocationTargetException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
resp.getWriter().append(objectResult.toString());
}
}
Servlet: 俗理解成运行在Web服务器上的程序
MVC的基本思路是屏蔽Servlet的概念,让程序员主要写业务逻辑代码。浏览器访问的URL通过映射 机制找到实际的业务逻辑方法。按照Servlet规范,可以通过 Filter 拦截,也可以通过Servlet 拦截。 MiniSpring 的实现过程中,我模仿 Spring MVC 通过 Servlet 拦截所有请求,处理映射关系,调用业务 逻辑代码,处理返回值回递给浏览器。程序员写的业务逻辑程序,也叫做Bean。
08 整合 IoC 和 MVC: 如何在Web环境中启动IoC容器?
public class AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext extends ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements WebApplicationContext {
private ServletContext servletContext;
public AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(String fileName) {
super(fileName);
}
@Override
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
return servletContext;
}
@Override
public void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
}
public class ContextLoaderListener implements ServletContextListener {
public static final String CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM = "contextConfigLocation";
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = null;
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("初始化上下文");
ServletContextListener.super.contextInitialized(sce);
initWebApplicationContext(sce.getServletContext());
}
private void initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
String sContextLocation = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
sContextLocation = "beans.xml";
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext awc = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(sContextLocation);
this.context = awc;
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, awc);
}
}
这节课,我们把MVC与IoC整合在了一起。具体过程是这样的:在T omcat启动的过程中先拿 context-param, 初始化Listener,在初始化过程中,创建IoC容器构建WAC (WebApplicationContext), 加载所管理的Bean对象,并把WAC关联到servlet context里。
然后在DispatcherServlet初始化的时候, 从sevletContext里获取属性拿到WAC,放到servlet的属 性中,然后拿到Servlet的配置路径参数, 之后再扫描路径下的包,调用refresh()方法加载Bean,最 后配置url mapping。
我们之所以有办法整合这二者, 核心的原因是Servlet规范中规定的时序,从listerner到filter再到 servlet, 每一个环节都预留了接口让我们有机会干预,写入我们需要的代码。我们在学习过程中, 更重要的是要学习如何构建可扩展体系的思路, 在我们自己的软件开发过程中, 记住不要将程序流程固定死, 那样没有任何扩展的余地, 而应该想着预留出一些接口理清时序, 让别人在关节处也可以插入自己的逻辑。
容器是一个框架,之所以叫做框架而不是应用程序,关键就在于这套可扩展的体系
09 分解Dispatcher:如何把专⻔的事情交给专门的部件去做?
这节课我们的主要工作就是拆解Dispatcher。首先拆解的是ApplicationContext,现在我们有了两 级上下文,一级用于IoC容器,我们叫parent上下文,一级用于Web上下文,
WebApplicationContext持有对parent上下文的引用。方便起⻅,我们还增加了@RequestMapping 注解来声明URL映射,然后新增RequestMappingHandlerMapping 与 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,分别包装URL映射关系和映射后的处理过程
bug
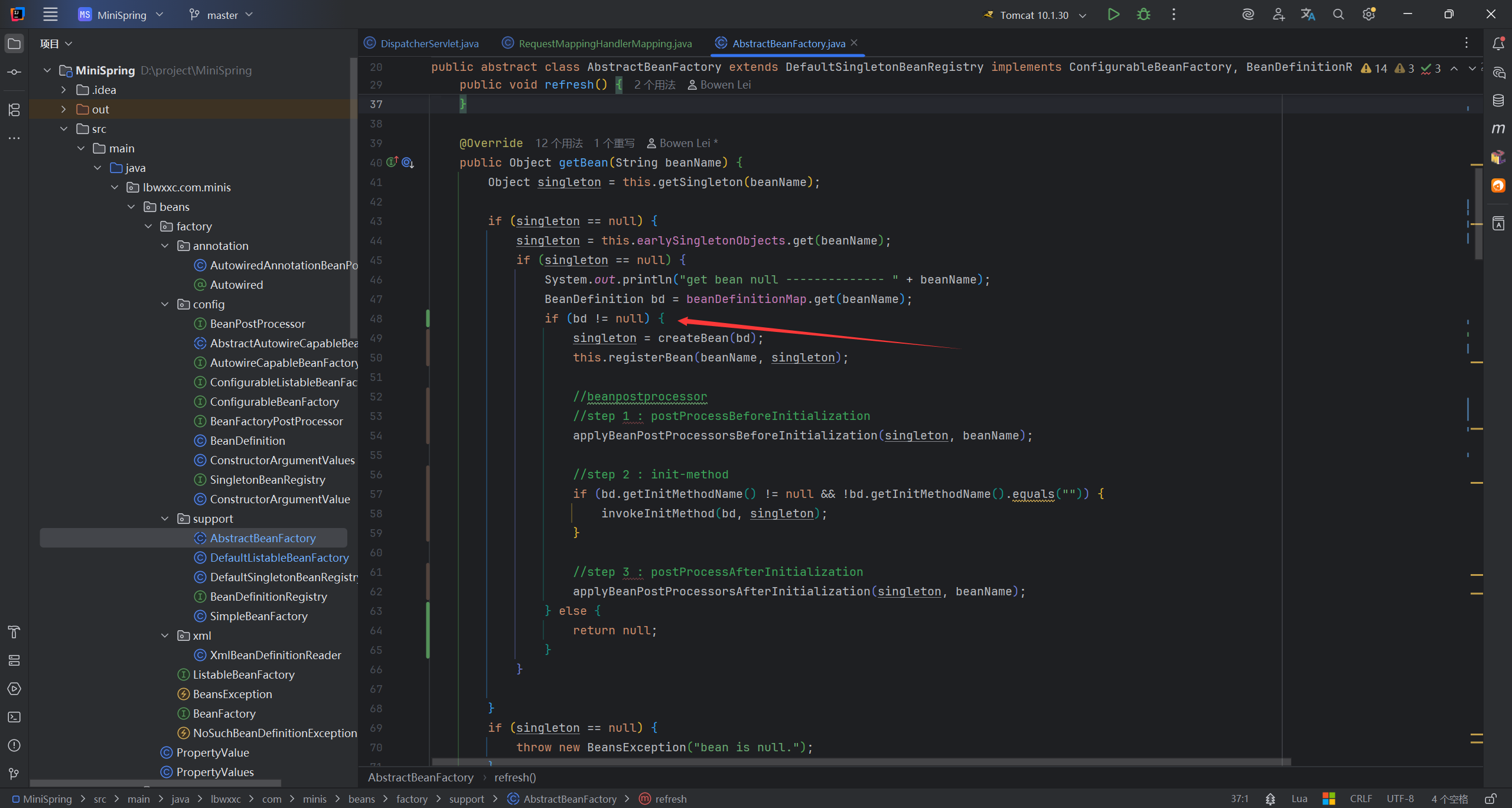
要进行判空处理
10 数据绑定: 如何自动转换传入的参数?
将 reuqest 携带的参数转换为 Java 实体类
public class CustomNumberEditor implements PropertyEditor {
private Class<? extends Number> numberClass;
private NumberFormat numberFormat;
private boolean allowEmpty;
private Object value;
public CustomNumberEditor(Class<? extends Number> numberClass, boolean allowEmpty) {
this(numberClass, null, allowEmpty);
}
public CustomNumberEditor(Class<? extends Number> numberClass, NumberFormat numberFormat, boolean allowEmpty) {
this.numberClass = numberClass;
this.numberFormat = numberFormat;
this.allowEmpty = allowEmpty;
}
@Override
public void setAsText(String text) {
if (this.allowEmpty && !StringUtils.hasText(text)) {
// Treat empty String as null value.
setValue(null);
}
else if (this.numberFormat != null) {
// Use given NumberFormat for parsing text.
setValue(NumberUtils.parseNumber(text, this.numberClass, this.numberFormat));
}
else {
// Use default valueOf methods for parsing text.
setValue(NumberUtils.parseNumber(text, this.numberClass));
}
}
@Override
public void setValue(Object value) {
if (value instanceof Number) {
this.value = NumberUtils.convertNumberToTargetClass((Number) value, this.numberClass);
} else {
this.value = value;
}
}
@Override
public String getAsText() {
Object value = this.value;
if (value == null) {
return "";
}
if (this.numberFormat != null) {
// Use NumberFormat for rendering value.
return this.numberFormat.format(value);
}
else {
// Use toString method for rendering value.
return value.toString();
}
}
@Override
public Object getValue() {
return this.value;
}
}
这个类是一个在文本 (String) 和不同类型的数字 (Number) 之间进行自定义转换 ↔️ 的“翻译器”。
public class PropertyEditorRegistrySupport {
private Map<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> defaultEditors;
private Map<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> customEditors;
public PropertyEditorRegistrySupport() {
registerDefaultEditors();
}
protected void registerDefaultEditors() {
createDefaultEditors();
}
public PropertyEditor getDefaultEditor(Class<?> requiredType) {
return this.defaultEditors.get(requiredType);
}
private void createDefaultEditors() {
this.defaultEditors = new HashMap<>(64);
// Default instances of collection editors.
this.defaultEditors.put(int.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Integer.class, false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Integer.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Integer.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(long.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Long.class, false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Long.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Long.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(float.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Float.class, false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Float.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Float.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(double.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Double.class, false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Double.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Double.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(BigDecimal.class, new CustomNumberEditor(BigDecimal.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(BigInteger.class, new CustomNumberEditor(BigInteger.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(String.class, new StringEditor(String.class, true));
}
public void registerCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType, PropertyEditor propertyEditor) {
if (this.customEditors == null) {
this.customEditors = new LinkedHashMap<>(16);
}
this.customEditors.put(requiredType, propertyEditor);
}
public PropertyEditor findCustomEditor( Class<?> requiredType) {
Class<?> requiredTypeToUse = requiredType;
return getCustomEditor(requiredTypeToUse);
}
public boolean hasCustomEditorForElement( Class<?> elementType) {
// No property-specific editor -> check type-specific editor.
return (elementType != null && this.customEditors != null && this.customEditors.containsKey(elementType));
}
public PropertyEditor getCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType) {
if (requiredType == null || this.customEditors == null) {
return null;
}
// Check directly registered editor for type.
PropertyEditor editor = this.customEditors.get(requiredType);
return editor;
}
}
注册一些默认的翻译器,也提供方法实习自定义注册器
public abstract class AbstractPropertyAccessor extends PropertyEditorRegistrySupport {
PropertyValues pvs;
public AbstractPropertyAccessor() {
super();
}
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs) {
this.pvs = pvs;
for (PropertyValue pv : this.pvs.getPropertyValues()) {
setPropertyValue(pv);
}
}
public abstract void setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) ;
}
抽象类,实现一些基本方法,实现代码复用
public class BeanWrapperImpl extends AbstractPropertyAccessor {
Object wrappedObject;
Class<?> clz;
public BeanWrapperImpl(Object object) {
super();
this.wrappedObject = object;
this.clz = object.getClass();
}
@Override
public void setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) {
BeanPropertyHandler propertyHandler = new BeanPropertyHandler(pv.getName());
PropertyEditor pe = this.getCustomEditor(propertyHandler.getPropertyClz());
if (pe == null) {
pe = this.getDefaultEditor(propertyHandler.getPropertyClz());
}
if (pe != null) {
pe.setAsText((String) pv.getValue());
propertyHandler.setValue(pe.getValue());
}
else {
propertyHandler.setValue(pv.getValue());
}
}
class BeanPropertyHandler {
Method writeMethod = null;
Method readMethod = null;
Class<?> propertyClz = null;
public Class<?> getPropertyClz() {
return propertyClz;
}
public BeanPropertyHandler(String propertyName) {
try {
Field field = clz.getDeclaredField(propertyName);
propertyClz = field.getType();
this.writeMethod = clz.getDeclaredMethod("set"
+ propertyName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()
+ propertyName.substring(1)
, propertyClz);
this.readMethod = clz.getDeclaredMethod("get"
+ propertyName.substring(0,1).toUpperCase()
+ propertyName.substring(1));
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Object getValue() {
Object result = null;
writeMethod.setAccessible(true);
try {
result = readMethod.invoke(wrappedObject);
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException | IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
public void setValue(Object value) {
writeMethod.setAccessible(true);
try {
writeMethod.invoke(wrappedObject, value);
} catch (IllegalAccessException | IllegalArgumentException | InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
这个类是一个JavaBean 的属性控制器。它的核心功能是让你能够通过属性名称(一个字符串)来动态地获取或设置一个 Java 对象的属性值
13 JDBC 访问框架:如何抽取JDBC模板并隔离数据库?
public Object query(String sql, Object[] args, PreparedStatementCallback callback) {
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Object result = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:3307;databasename=my_sql_study;user=root;password=123456;");
stmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
int len = args.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (args[i] instanceof Integer) {
stmt.setInt(i + 1, (Integer) args[i]);
} else if (args[i] instanceof String) {
stmt.setString(i + 1, (String) args[i]);
}
}
return callback.doInPreparedStatement(stmt);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if (con != null) {
con.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
} catch (SQLException ignored) {
}
}
}
public class UserService {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
public User getUser(int id) {
String sql = "select * from user where id = ?";
return (User) jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new Object[]{new Integer(id)}, (ptsmt) -> {
User user = new User();
try {
ResultSet resultSet = ptsmt.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
user.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
user.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return user;
});
}
}
函数回调
14 增强模板:如何抽取专⻔的部件完成专⻔的任务?
public class PooledDataSource implements DataSource {
private List<PooledConnection> connections = null;
private String driverClassName;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
private int initialSize = 2;
private Properties connectionProperties;
public PooledDataSource() {
}
private void initPool() {
this.connections = new ArrayList<>(initialSize);
try {
for(int i = 0; i < initialSize; i++){
Connection connect = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
PooledConnection pooledConnection = new PooledConnection(connect, false);
this.connections.add(pooledConnection);
System.out.println("********add connection pool*********");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() {
return getConnectionFromDriver(getUsername(), getPassword());
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) {
return getConnectionFromDriver(username, password);
}
protected Connection getConnectionFromDriver(String username, String password) {
Properties mergedProps = new Properties();
Properties connProps = getConnectionProperties();
if (connProps != null) {
mergedProps.putAll(connProps);
}
if (username != null) {
mergedProps.setProperty("user", username);
}
if (password != null) {
mergedProps.setProperty("password", password);
}
if (this.connections == null) {
initPool();
}
PooledConnection pooledConnection= getAvailableConnection();
while(pooledConnection == null){
pooledConnection = getAvailableConnection();
if(pooledConnection == null){
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(30);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return pooledConnection;
}
private PooledConnection getAvailableConnection() {
for(PooledConnection pooledConnection : this.connections){
if (!pooledConnection.isActive()){
pooledConnection.setActive(true);
return pooledConnection;
}
}
return null;
}
protected Connection getConnectionFromDriverManager(String url, Properties props) throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, props);
}
public String getDriverClassName() {
return driverClassName;
}
public void setDriverClassName(String driverClassName) {
this.driverClassName = driverClassName;
try {
Class.forName(this.driverClassName);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load JDBC driver class [" + driverClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public int getInitialSize() {
return initialSize;
}
public void setInitialSize(int initialSize) {
this.initialSize = initialSize;
}
public Properties getConnectionProperties() {
return connectionProperties;
}
public void setConnectionProperties(Properties connectionProperties) {
this.connectionProperties = connectionProperties;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter arg0) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int arg0) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> arg0) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> arg0) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
}
线程池
17 动态代理:如何在运行时插入逻辑?
仿照 Spring 创建一个工厂
public interface FactoryBean<T> {
T getObject();
Class<?> getObjectType();
default boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
一个用 JDK 实现的动态代理
public class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler {
Object object;
public JdkDynamicAopProxy(Object object) {
this.object = object;
}
@Override
public Object getProxy() {
//object.getClass().getInterfaces(): 这就是为什么标准的 JDK 动态代理只能为实现了至少一个接口的对象工作的根本原因。代理需要通过接口来了解它应该暴露哪些方法
ClassLoader classLoader = JdkDynamicAopProxy.class.getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = object.getClass().getInterfaces();
Object proxy = null;
try {
proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, this);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return proxy;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (method.getName().equals("doAction")) {
System.out.println("-----before call real object, dynamic proxy........");
return method.invoke(object, args);
}
return null;
}
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanName) {
Object singleton = this.getSingleton(beanName);
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singleton == null) {
System.out.println("get bean null -------------- " + beanName);
BeanDefinition bd = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (bd != null) {
singleton = createBean(bd);
this.registerBean(beanName, singleton);
//beanpostprocessor
//step 1 : postProcessBeforeInitialization
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(singleton, beanName);
//step 2 : init-method
if (bd.getInitMethodName() != null && !bd.getInitMethodName().equals("")) {
invokeInitMethod(bd, singleton);
}
//step 3 : postProcessAfterInitialization
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(singleton, beanName);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
if (singleton == null) {
throw new BeansException("bean is null.");
}
if (singleton instanceof FactoryBean) {
return getObjectForBeanInstance(singleton, beanName);
}
return singleton;
}
if (singleton instanceof FactoryBean) {
return getObjectForBeanInstance(singleton, beanName);
}
在获取 bean 的最后,会检测是否为 FactoryBean,如果是工厂会生成一个一个代理对象























 1027
1027

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








