今天研读Java并发容器和框架时,看到为什么要使用ConcurrentHashMap时,其中有一个原因是:线程不安全的HashMap, HashMap在并发执行put操作时会引起死循环,是因为多线程会导致HashMap的Entry链表形成环形数据结构,查找时会陷入死循环。纠起原因看了其他的博客,都比较抽象,所以这里以图形的方式展示一下,希望支持!
(1)当往HashMap中添加元素时,会引起HashMap容器的扩容,原理不再解释,直接附源代码,如下:
- /**
- *
- * 往表中添加元素,如果插入元素之后,表长度不够,便会调用resize方法扩容
- */
- void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
- Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
- table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
- if (size++ >= threshold)
- resize(2 * table.length);
- }
- /**
- * resize()方法如下,重要的是transfer方法,把旧表中的元素添加到新表中
- */
- void resize(int newCapacity) {
- Entry[] oldTable = table;
- int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
- if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
- threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- return;
- }
- Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
- transfer(newTable);
- table = newTable;
- threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
- }
/**
*
* 往表中添加元素,如果插入元素之后,表长度不够,便会调用resize方法扩容
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
/**
* resize()方法如下,重要的是transfer方法,把旧表中的元素添加到新表中
*/
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
} - /**
- * Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
- */
- void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
- int newCapacity = newTable.length;
- for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
- while(null != e) {
- Entry<K,V> next = e.next; ---------------------(1)
- if (rehash) {
- e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
- }
- int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
- e.next = newTable[i];
- newTable[i] = e;
- e = next;
- } // while
- }
- }
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next; ---------------------(1)
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} // while
}
}(3)假设:
- Map<Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer>(2); // 只能放置两个元素,其中的threshold为1(表中只填充一个元素时),即插入元素为1时就扩容(由addEntry方法中得知)
- //放置2个元素 3 和 7,若要再放置元素8(经hash映射后不等于1)时,会引起扩容
Map<Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer>(2); // 只能放置两个元素,其中的threshold为1(表中只填充一个元素时),即插入元素为1时就扩容(由addEntry方法中得知)
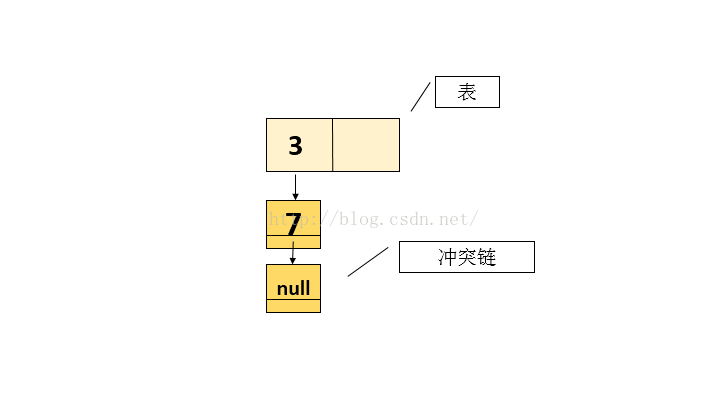
//放置2个元素 3 和 7,若要再放置元素8(经hash映射后不等于1)时,会引起扩容假设放置结果图如下:
现在有两个线程A和B,都要执行put操作,即向表中添加元素,即线程A和线程B都会看到上面图的状态快照
执行顺序如下:
执行一: 线程A执行到transfer函数中(1)处挂起(transfer函数代码中有标注)。此时在线程A的栈中
- e = 3
- next = 7
e = 3
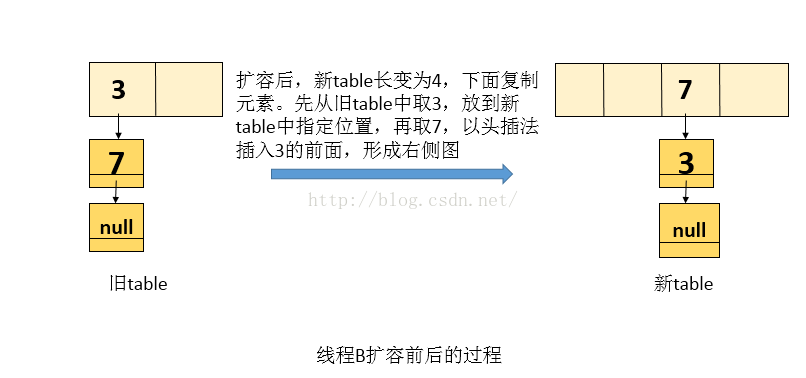
next = 7执行二:线程B执行 transfer函数中的while循环,即会把原来的table变成新一table(线程B自己的栈中),再写入到内存中。如下图(假设两个元素在新的hash函数下也会映射到同一个位置)
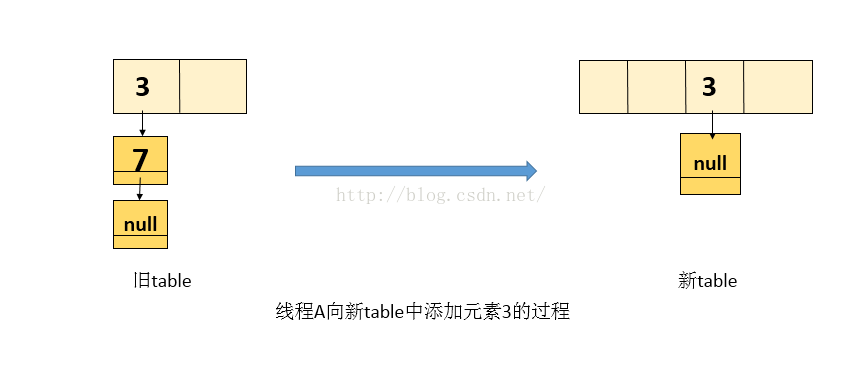
执行三: 线程A解挂,接着执行(看到的仍是旧表),即从transfer代码(1)处接着执行,当前的 e = 3, next = 7, 上面已经描述。
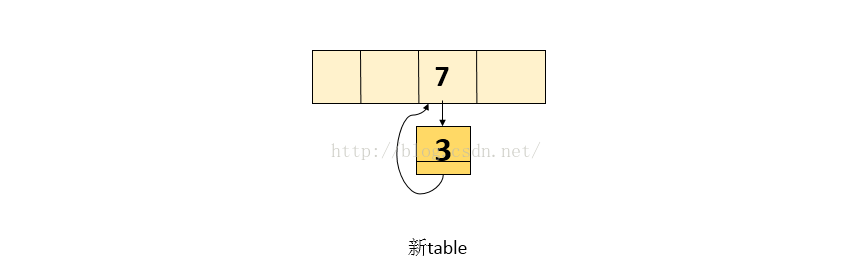
1. 处理元素 3 , 将 3 放入 线程A自己栈的新table中(新table是处于线程A自己栈中,是线程私有的,不肥线程2的影响),处理3后的图如下:
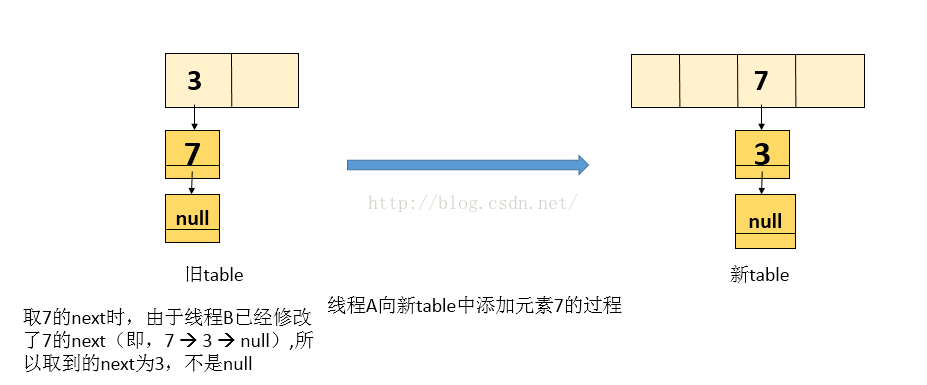
2. 线程A再复制元素 7 ,当前 e = 7 ,而next值由于线程 B 修改了它的引用,所以next 为 3 ,处理后的新表如下图
3. 由于上面取到的next = 3, 接着while循环,即当前处理的结点为3, next就为null ,退出while循环,执行完while循环后,新表中的内容如下图:
4. 当操作完成,执行查找时,会陷入死循环!
欢迎大家指正!





















 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








