【摘要】前文对网络驱动例子进行一个简单的梳理总结,本文贴出 net_device 的数据结构以及一些驱动中常用的数据结构。
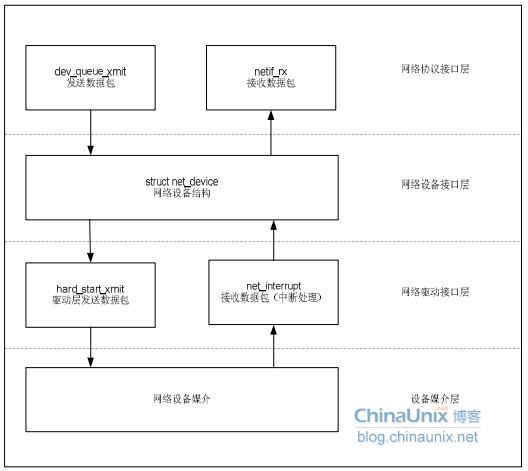
1、网络设备驱动结构
1)、网络协议接口层向网络层协议提供提供统一的数据包收发接口,不论上层协议为ARP还是IP,都通过dev_queue_xmit()函数发送数据,并通过netif_rx()函数接受数据。这一层的存在使得上层协议独立于具体的设备。
2)、网络设备接口层向协议接口层提供统一的用于描述具体网络设备属性和操作的结构体net_device,该结构体是设备驱动功能层中各函数的容器。实际上,网络设备接口层从宏观上规划了具体操作硬件的设备驱动功能层的结构。
3)、设备驱动功能层各函数是网络设备接口层net_device数据结构的具体成员,是驱使网络设备硬件完成相应动作的程序,他通过hard_start_xmit()函数启动发送操作,并通过网络设备上的中断触发接受操作。
4)、网络设备与媒介层是完成数据包发送和接受的物理实体,包括网络适配器和具体的传输媒介,网络适配器被驱动功能层中的函数物理上驱动。对于Linux系统而言,网络设备和媒介都可以是虚拟的。
2、网卡驱动中重要的数据结构
- struct softnet_data
- {
- int throttle;
- int cng_level;
- int avg_blog;
- struct sk_buff_head input_pkt_queue;
- struct list_head poll_list;
- struct net_device *output_queue;
- struct sk_buff *completion_queue;
- struct net_device backlog_dev; /* Sorry. 8) */
- };
- struct packet_type {
- unsigned short type; /* This is really htons(ether_type). */
- struct net_device *dev; /* NULL is wildcarded here */
- int (*func) (struct sk_buff *, struct net_device *,
- struct packet_type *);
- void *af_packet_priv;
- struct list_head list;
- };
- struct netif_rx_stats
- {
- unsigned total;
- unsigned dropped;
- unsigned time_squeeze;
- unsigned throttled;
- unsigned fastroute_hit;
- unsigned fastroute_success;
- unsigned fastroute_defer;
- unsigned fastroute_deferred_out;
- unsigned fastroute_latency_reduction;
- unsigned cpu_collision;
- };
- struct net_device_stats
- {
- unsigned long rx_packets; /* total packets received */
- unsigned long tx_packets; /* total packets transmitted */
- unsigned long rx_bytes; /* total bytes received */
- unsigned long tx_bytes; /* total bytes transmitted */
- unsigned long rx_errors; /* bad packets received */
- unsigned long tx_errors; /* packet transmit problems */
- unsigned long rx_dropped; /* no space in linux buffers */
- unsigned long tx_dropped; /* no space available in linux */
- unsigned long multicast; /* multicast packets received */
- unsigned long collisions;
- /* detailed rx_errors: */
- unsigned long rx_length_errors;
- unsigned long rx_over_errors; /* receiver ring buff overflow */
- unsigned long rx_crc_errors; /* recved pkt with crc error */
- unsigned long rx_frame_errors; /* recv'd frame alignment error */
- unsigned long rx_fifo_errors; /* recv'r fifo overrun */
- unsigned long rx_missed_errors; /* receiver missed packet */
- /* detailed tx_errors */
- unsigned long tx_aborted_errors;
- unsigned long tx_carrier_errors;
- unsigned long tx_fifo_errors;
- unsigned long tx_heartbeat_errors;
- unsigned long tx_window_errors;
- /* for cslip etc */
- unsigned long rx_compressed;
- unsigned long tx_compressed;
- };
- /* Media selection options. */
- enum {
- IF_PORT_UNKNOWN = 0,
- IF_PORT_10BASE2,
- IF_PORT_10BASET,
- IF_PORT_AUI,
- IF_PORT_100BASET,
- IF_PORT_100BASETX,
- IF_PORT_100BASEFX
- };
- struct net_device
- {
- /*
- * This is the first field of the "visible" part of this structure
- * (i.e. as seen by users in the "Space.c" file). It is the name
- * the interface.
- */
- char name[IFNAMSIZ]; //eth0 eth1 ... ethn
- /*
- * I/O specific fields
- * FIXME: Merge these and struct ifmap into one
- */
- unsigned long mem_end; /* shared mem end */
- unsigned long mem_start; /* shared mem start */
- unsigned long base_addr; /* device I/O address */ //网络接口的I/O基地址,由驱动在设备探测时赋值 ifconfig可以显示或
- 修改当前值,该字段可以在系统启动时在内核命令行中显式赋值,或者
- 在模块加载时赋值。这个成员一般不被引用
- unsigned int irq; /* device IRQ number */ //网络设备使用的中断号。irq值常常在网络设备启动时加载设置,
- 并且在后来由ifconfig打印出来。
- /*
- * Some hardware also needs these fields, but they are not
- * part of the usual set specified in Space.c.
- */
- unsigned char if_port; /* Selectable AUI, TP,..*/ //多端口设备中使用的端口。该成员在同轴线(IF_PORT_10BASE2)和
- //双绞线(IF_PORT_100BASET)以太网连接时使用
- unsigned char dma; /* DMA channel */ //在某些外设总线时有意义,如ISA总线。它不在设备驱动自身以外使用
- unsigned long state; //网络设备和网络适配器的状态信息
- struct net_device *next; //下一个struct net_device Linux中所有网络设备都以dev_base指针开头的单线行链表管理
- /* The device initialization function. Called only once. */
- int (*init)(struct net_device *dev); 用来搜索并初始化网络设备。该方法负责寻找并初始化当前类型的网络适配器。首选必须创建net_device结构并将网络设备和网络驱动程序的数据(驱动相关的)填充进去。其次,register_netdevice()注册网络设备
- /* ------- Fields preinitialized in Space.c finish here ------- */
- struct net_device *next_sched;
- /* Interface index. Unique device identifier */
- int ifindex;
- int iflink;
- struct net_device_stats* (*get_stats)(struct net_device *dev); 应用程序需要获取网络接口的统计信息时会调用这个方法。例如,在运行ifconfig或netstat -i时,会调用该方法
- struct iw_statistics* (*get_wireless_stats)(struct net_device *dev);
- /* List of functions to handle Wireless Extensions (instead of ioctl).
- * See <net/iw_handler.h> for details. Jean II */
- const struct iw_handler_def * wireless_handlers;
- /* Instance data managed by the core of Wireless Extensions. */
- struct iw_public_data * wireless_data;
- struct ethtool_ops *ethtool_ops;
- /*
- * This marks the end of the "visible" part of the structure. All
- * fields hereafter are internal to the system, and may change at
- * will (read: may be cleaned up at will).
- */
- /* These may be needed for future network-power-down code. */
- unsigned long trans_start; /* Time (in jiffies) of last Tx */
- unsigned long last_rx; /* Time of last Rx */
- unsigned short flags; /* interface flags (a la BSD) */
- unsigned short gflags;
- unsigned short priv_flags; /* Like 'flags' but invisible to userspace. */
- unsigned short unused_alignment_fixer; /* Because we need priv_flags,
- * and we want to be 32-bit aligned.
- */
- unsigned mtu; /* interface MTU value */ //最大传输单元。它指定链路层每帧有效载荷最大长度。网络层各协议必须
- 考虑该值,以确保不会向网络适配器发送多余的字节,以太网1500,通
- 过ifconfig命令可改变
- unsigned short type; /* interface hardware type */ //指定了网络适配器的硬件类型。这个成员由ARP用来决定网络适配器
- 支持的硬件地址。对以太网接口一般由ether_setup()函数设置其值为
- ARPHRD_ETHER
- unsigned short hard_header_len; /* hardware hdr length */ //指定链路层数据帧包头长度。对于以太网接口为14
- void *priv; /* pointer to private data */
- struct net_device *master; /* Pointer to master device of a group,
- * which this device is member of.
- */
- /* Interface address info. */
- unsigned char broadcast[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw bcast add */ //广播地址
- /*以太网地址长度是6个字节(我们指的是接口板的硬件ID),广播地址由6个0xff字节组成。这些字段一般由ether_setup()函数设置。驱动程序必须以特定于设备的方式从接口板读出,并复制到dev_addr结构。网络设备的硬件地址用来产生正确的以太网头*/
- unsigned char dev_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw address */ //存放设备硬件地址
- unsigned char addr_len; /* hardware address length */ //硬件(MAC)地址长度
- struct dev_mc_list *mc_list; /* Multicast mac addresses */ /*指向具有多播的第二层地址的线性表。当网络适配器收集到具有包含在dev_mc_list中目标地址后,网络适配器必须将包传递给更高层。驱动程序中方法set_multicast_list用来将该列表中的地址传递给网络适配器。该网络适配器的硬件过滤器(如果有)负责只将与该计算机有关的包传递给内核 */
- int mc_count; /* Number of installed mcasts */ //dev_mc_list包含的地址数量
- int promiscuity;
- int allmulti;
- /*下面两个变量用来发现适配器在发送包时遇到的问题。
- int watchdog_timeo;
- struct timer_list watchdog_timer; /*在网络设备启动时打开,每经过watch_timeo时间后立即被调用。处理程序dev_watchdog()检查从上一次(存储在stans_start中)包传输后是否经过watch_timeo单位长度的时间。如果是,那么上一个包的传输中出现问题,必须检查网络适配器。要检查网络适配器,需要调用驱动函数tx_timeout()。如果从上次传输开始还没有经过足够长的时间,那么除了watchdog计时器启动之外没有发生其他网络事件*/
- /* Protocol specific pointers */
- /*指向网络适配器的第三层协议的信息。如果网络设备被设置为Internet协议,那么ip_ptr指向in_device类型的结构,它管理有关的IP实例的信息和配置参数。例如in_device结构管理包含网络设备IP地址列表,包含多播组活动IP列表和ARP协议参数等*/
- void *atalk_ptr; /* AppleTalk link */
- void *ip_ptr; /* IPv4 specific data */
- void *dn_ptr; /* DECnet specific data */
- void *ip6_ptr; /* IPv6 specific data */
- void *ec_ptr; /* Econet specific data */
- void *ax25_ptr; /* AX.25 specific data */
- struct list_head poll_list; /* Link to poll list */
- int quota;
- int weight;
- struct Qdisc *qdisc;
- struct Qdisc *qdisc_sleeping;
- struct Qdisc *qdisc_ingress;
- struct list_head qdisc_list;
- unsigned long tx_queue_len; /* Max frames per queue allowed */ //该字段表示指定了网络设备发送队列中可以排列的最大帧数
- 这个值有ether_setup()设置为100.不要将tx_queue_len
- 与网络适配器的缓冲区想混淆。通常网络适配器有额外的环形
- 缓冲区,大小为16或32个包大小
- /* ingress path synchronizer */
- spinlock_t ingress_lock;
- /* hard_start_xmit synchronizer */
- spinlock_t xmit_lock;
- /* cpu id of processor entered to hard_start_xmit or -1,
- if nobody entered there.
- */
- int xmit_lock_owner;
- /* device queue lock */
- spinlock_t queue_lock;
- /* Number of references to this device */
- atomic_t refcnt;
- /* delayed register/unregister */
- struct list_head todo_list;
- /* device name hash chain */
- struct hlist_node name_hlist;
- /* device index hash chain */
- struct hlist_node index_hlist;
- /* register/unregister state machine */
- enum { NETREG_UNINITIALIZED=0,
- NETREG_REGISTERING, /* called register_netdevice */
- NETREG_REGISTERED, /* completed register todo */
- NETREG_UNREGISTERING, /* called unregister_netdevice */
- NETREG_UNREGISTERED, /* completed unregister todo */
- NETREG_RELEASED, /* called free_netdev */
- } reg_state;
- /* Net device features */
- int features;
- #define NETIF_F_SG 1 /* Scatter/gather IO. */
- #define NETIF_F_IP_CSUM 2 /* Can checksum only TCP/UDP over IPv4. */
- #define NETIF_F_NO_CSUM 4 /* Does not require checksum. F.e. loopack. */
- #define NETIF_F_HW_CSUM 8 /* Can checksum all the packets. */
- #define NETIF_F_HIGHDMA 32 /* Can DMA to high memory. */
- #define NETIF_F_FRAGLIST 64 /* Scatter/gather IO. */
- #define NETIF_F_HW_VLAN_TX 128 /* Transmit VLAN hw acceleration */
- #define NETIF_F_HW_VLAN_RX 256 /* Receive VLAN hw acceleration */
- #define NETIF_F_HW_VLAN_FILTER 512 /* Receive filtering on VLAN */
- #define NETIF_F_VLAN_CHALLENGED 1024 /* Device cannot handle VLAN packets */
- #define NETIF_F_TSO 2048 /* Can offload TCP/IP segmentation */
- #define NETIF_F_LLTX 4096 /* LockLess TX */
- /* Called after device is detached from network. */
- void (*uninit)(struct net_device *dev); 用来注销网络设备,该方法用来执行驱动程序相关的函数,这些函数在删除网络设备时也是必须的。目前没有驱动程序使用该方法
- /* Called after last user reference disappears. */
- void (*destructor)(struct net_device *dev);
- /* Pointers to interface service routines. */
- int (*open)(struct net_device *dev); 打开一个已经命名的网络设备。可以使用ifconfig命令激活网络设备,在激活过程中,open方法应当注册它需要的系统资源(I/O口,IRQ,DMA,等等),以及进行其他的网络设备要求
- int (*stop)(struct net_device *dev); 停止网络适配器的活动并释放相关资源,此后网络设备不能活动
- int (*hard_start_xmit) (struct sk_buff *skb,
- struct net_device *dev); 在网络设备上发送数据包的方法。完整的报文(协议头和所有其他数据)包含在一个socket缓冲区(sk_buff)结构中。数据包如果成功发送到网络适配器该函数返回0,否则返回1
- #define HAVE_NETDEV_POLL
- int (*poll) (struct net_device *dev, int *quota);
- int (*hard_header) (struct sk_buff *skb,
- struct net_device *dev,
- unsigned short type,
- void *daddr,
- void *saddr,
- unsigned len); 用先前提取到的源和目的硬件地址来建立硬件头的函数(在hard_start_xmit 前调用)。它的工作是将传给它的参数信息组织成一个合适的特定于设备的硬件头
- int (*rebuild_header)(struct sk_buff *skb); 用来在ARP解析完成后、报文发送前,重建硬件头的函数
- #define HAVE_MULTICAST
- void (*set_multicast_list)(struct net_device *dev); 将多播MAC地址列表传递给网络适配器,适配器就可以根据这些地址接收包
- #define HAVE_SET_MAC_ADDR
- int (*set_mac_address)(struct net_device *dev,
- void *addr); 改变网络设备的硬件地址(MAC地址)
- #define HAVE_PRIVATE_IOCTL
- int (*do_ioctl)(struct net_device *dev,
- struct ifreq *ifr, int cmd);
- #define HAVE_SET_CONFIG
- int (*set_config)(struct net_device *dev,
- struct ifmap *map);
- #define HAVE_HEADER_CACHE
- int (*hard_header_cache)(struct neighbour *neigh,
- struct hh_cache *hh);
- void (*header_cache_update)(struct hh_cache *hh,
- struct net_device *dev,
- unsigned char * haddr); 在响应一个变化中,更新hh_cache结构中的目的地址方法
- #define HAVE_CHANGE_MTU
- int (*change_mtu)(struct net_device *dev, int new_mtu); 改变网络设备最大传输单元(MTU)函数
- #define HAVE_TX_TIMEOUT
- void (*tx_timeout) (struct net_device *dev); 网络驱动程序代码没有在一个合理的时间内将一个报文发送完成时会调用该方法,报文没有被及时发送的原因可能是丢失一个中断或某个接口被锁。此时该函数处理这个问题并恢复报文发送
- void (*vlan_rx_register)(struct net_device *dev,
- struct vlan_group *grp);
- void (*vlan_rx_add_vid)(struct net_device *dev,
- unsigned short vid);
- void (*vlan_rx_kill_vid)(struct net_device *dev,
- unsigned short vid);
- int (*hard_header_parse)(struct sk_buff *skb,
- unsigned char *haddr); 该方法完成的工作包括从skb中的报文中抽取源地址,复制到haddr的缓冲区中。函数的返回值是地址的长度信息
- int (*neigh_setup)(struct net_device *dev, struct neigh_parms *);
- int (*accept_fastpath)(struct net_device *, struct dst_entry*);
- #ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL
- int netpoll_rx;
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_NET_POLL_CONTROLLER
- void (*poll_controller)(struct net_device *dev);
- #endif
- /* bridge stuff */
- struct net_bridge_port *br_port;
- #ifdef CONFIG_NET_DIVERT
- /* this will get initialized at each interface type init routine */
- struct divert_blk *divert;
- #endif /* CONFIG_NET_DIVERT */
- /* class/net/name entry */
- struct class_device class_dev;
- /* how much padding had been added by alloc_netdev() */
- int padded;
- };
- struct netdev_boot_setup {
- char name[IFNAMSIZ];
- struct ifmap map;
- };
- struct hh_cache
- {
- struct hh_cache *hh_next; /* Next entry */
- atomic_t hh_refcnt; /* number of users */
- unsigned short hh_type; /* protocol identifier, f.e ETH_P_IP
- * NOTE: For VLANs, this will be the
- * encapuslated type. --BLG
- */
- int hh_len; /* length of header */
- int (*hh_output)(struct sk_buff *skb);
- rwlock_t hh_lock;
- /* cached hardware header; allow for machine alignment needs. */
- #define HH_DATA_MOD 16
- #define HH_DATA_OFF(__len) \
- (HH_DATA_MOD - ((__len) & (HH_DATA_MOD - 1)))
- #define HH_DATA_ALIGN(__len) \
- (((__len)+(HH_DATA_MOD-1))&~(HH_DATA_MOD - 1))
- unsigned long hh_data[HH_DATA_ALIGN(LL_MAX_HEADER) / sizeof(long)];
- };
- struct dev_mc_list
- {
- struct dev_mc_list *next;
- __u8 dmi_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN];
- unsigned char dmi_addrlen;
- int dmi_users;
- int dmi_gusers;
- };
- struct sk_buff_head {
- /* These two members must be first. */
- struct sk_buff *next;
- struct sk_buff *prev;
- __u32 qlen;
- spinlock_t lock;
- };
- struct sk_buff;
- /* To allow 64K frame to be packed as single skb without frag_list */
- #define MAX_SKB_FRAGS (65536/PAGE_SIZE + 2)
- typedef struct skb_frag_struct skb_frag_t;
- struct skb_frag_struct {
- struct page *page;
- __u16 page_offset;
- __u16 size;
- };
- struct sk_buff {
- /* These two members must be first. */
- struct sk_buff *next;
- struct sk_buff *prev; //双向链表指针
- struct sk_buff_head *list; 指向套接字缓存在队列中的当前位置
- struct sock *sk; 指向创建报文的socket
- struct timeval stamp; 报文到达Linux系统的时间
- struct net_device *dev; 表明套接字缓存当前操作所在的网络设备。网络路由器被确定下来后,dev就指向报文离开计算机时经过的网络适配器。知道报文的输出适配器已知之前,dev都指向输入适配器
- struct net_device *input_dev;
- struct net_device *real_dev;
- union {
- struct tcphdr *th;
- struct udphdr *uh;
- struct icmphdr *icmph;
- struct igmphdr *igmph;
- struct iphdr *ipiph;
- struct ipv6hdr *ipv6h;
- unsigned char *raw;
- } h; 传输层报文帧头的指针
- union {
- struct iphdr *iph;
- struct ipv6hdr *ipv6h;
- struct arphdr *arph;
- unsigned char *raw;
- } nh; 网络层报文帧头的指针
- union {
- unsigned char *raw;
- } mac; MAC层报文帧头的指针
- struct dst_entry *dst; 指向路由高速缓存中的一条记录,它包含着有关报文进一步前进的路由信息
- struct sec_path *sp;
- /*
- * This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every
- * layer. Please put your private variables there. If you
- * want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone()
- * first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM.
- */
- char cb[40];
- unsigned int len, 指明套接字缓存所代表的报文长度,这里只考虑内核可访问的数据。在以太网报文中两个MAC地址和类型/长度域被考虑其中。其他的域(报头、链接和检验)以后再在网络适配器中进行添加
- data_len,
- mac_len,
- csum;
- unsigned char local_df,
- cloned,
- pkt_type, 报文的类型
- ip_summed;
- __u32 priority;
- unsigned short protocol,
- security;
- void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb);
- #ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER
- unsigned long nfmark;
- __u32 nfcache;
- __u32 nfctinfo;
- struct nf_conntrack *nfct;
- #ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER_DEBUG
- unsigned int nf_debug;
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER
- struct nf_bridge_info *nf_bridge;
- #endif
- #endif /* CONFIG_NETFILTER */
- #if defined(CONFIG_HIPPI)
- union {
- __u32 ifield;
- } private;
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
- __u32 tc_index; /* traffic control index */
- #ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
- __u32 tc_verd; /* traffic control verdict */
- __u32 tc_classid; /* traffic control classid */
- #endif
- #endif
- /* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */
- unsigned int truesize;
- atomic_t users;
- unsigned char *head,
- *data,
- *tail,
- *end;
- };
- struct skb_shared_info {
- atomic_t dataref;
- unsigned int nr_frags;
- unsigned short tso_size;
- unsigned short tso_segs;
- struct sk_buff *frag_list;
- skb_frag_t frags[MAX_SKB_FRAGS];
- };
- struct skb_iter {
- /* Iteration functions set these */
- unsigned char *data;
- unsigned int len;
- /* Private to iteration */
- unsigned int nextfrag;
- struct sk_buff *fraglist;
- };
- #ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER
- struct nf_conntrack {
- atomic_t use;
- void (*destroy)(struct nf_conntrack *);
- };
- #ifdef CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER
- struct nf_bridge_info {
- atomic_t use;
- struct net_device *physindev;
- struct net_device *physoutdev;
- #if defined(CONFIG_VLAN_8021Q) || defined(CONFIG_VLAN_8021Q_MODULE)
- struct net_device *netoutdev;
- #endif
- unsigned int mask;
- unsigned long data[32 / sizeof(unsigned long)];
- };






















 9147
9147

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








