项目原因先用蹩脚英文写的,过些天我会用中文描述一下。查看不方便可以用浏览器的翻译菜单翻译一下。

summary
Android bootstap involves three stages.
1, Linux kernel bootstrap: The Linux kernel bootstrap from physical device is comprised of CPU boot rom, SBL, and bootloader. All these are based on CPU manufacturer’s design and particular LINUX kernel implementation on specific CPU architecture. These are not components of AOSP. Linux kernel can boot from a virtual machine as well. For example, QVM from QNX.
2, init process & native bootstrap: This step is AOSP open source. Including: loading system/vendor image, applying SElinux rules, loading android native process, encrypting data partition, etc
init - OpenGrok cross reference for /system/core/init/ (aospxref.com)
3, Android framework bootstrap: This is phase from starting process zygote to enabling screen. There is considerable number of mechanisms like: zygote & JVM, system services, boot progress.

Boot Rom & Boot Loader

1, PBL(Processor Boot Loader or Primary Boot Loader): Arm CPU will execute the first instruction from 0x0000000 (or 0xBFC00000 if MIPS). This instructions are PBL which record in Boot ROM. QC’s PBL also providers Emergency Download mode.
2,3 SBL(Secondary or Slave Boot Loader): PBL load SBL from EMMC/UFS/NAND/PCIe, etc.) to SRAM, then execute the SBL. SBL do something like initializing memory subsystem(buses, DDR, clocks), load Trust Environment, and then load LK.
4,5 LK(Little Kernel): LK is used to load Linux kernel, to enter recovery mode, to enter charge mode, to enable fastboot, etc. LK is open source. Different vendor may have different name for it. For example, fastboot.
DDR is one kind of Dynamic RAM, it is essential to initialize the Driver before CPU uses it due to different kind of DDR has difference attributes (for e.g. voltage, tCK, data rate, refresh rate). The configurations are customized in SBL. Hisilicon’s solution is as below: SBL set the voltage of different PINs for different kind of DDR. CPU loads the combination to map to driver & configurations then.
QNX GVM
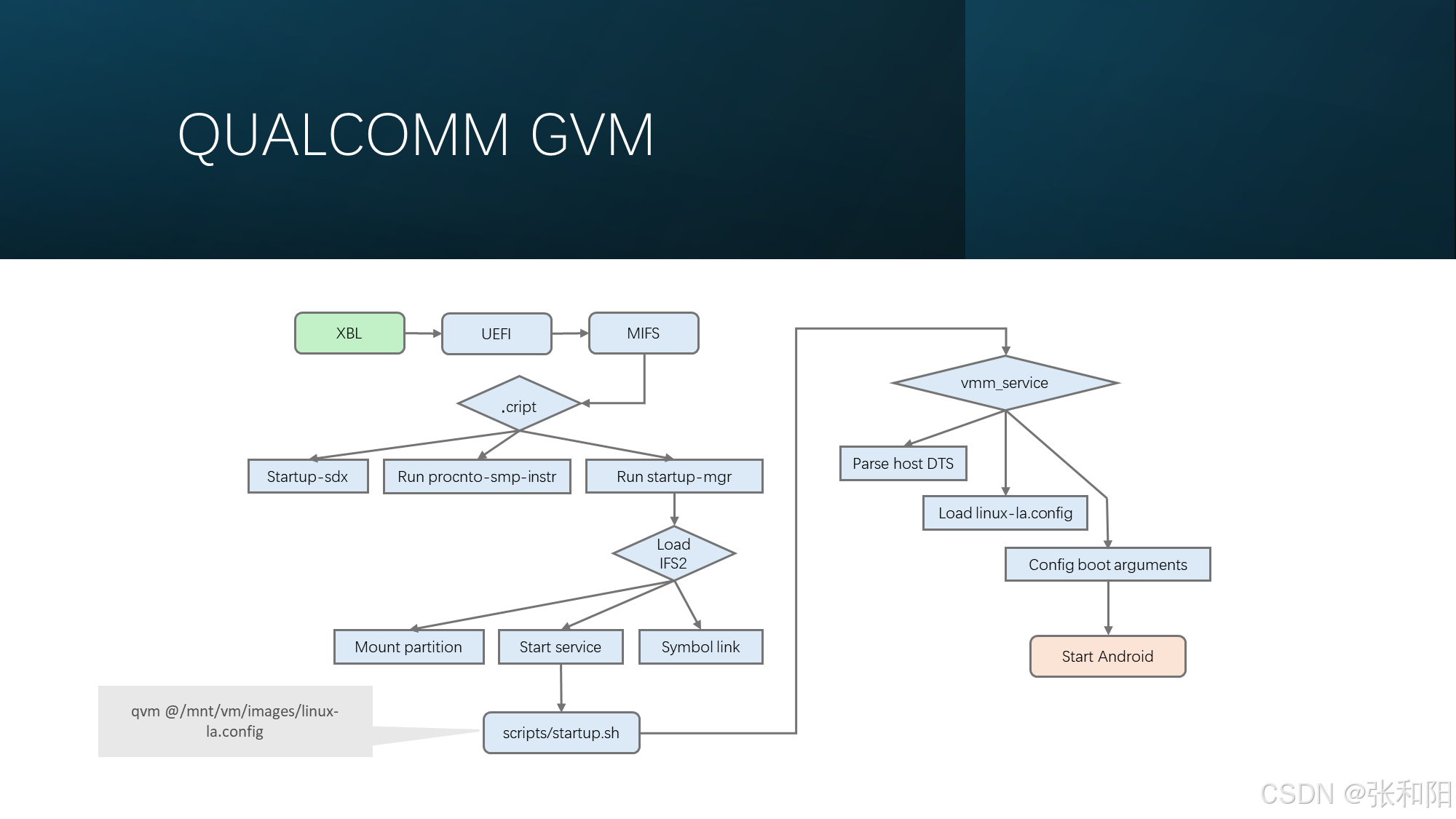
GVM(Gust Virtual machine): is used to provider a hypervisor VM to run gust OS like Android.
QVM: Qualcomm GVM. QNX is as host OS.
Start QVM reference command: qvm @/vm/images/linux-la.config
linux-la.config: has the boot arguments of QVM & Android. If you want to disable selinux, to modify “androidboot.selinux=enforce” as “androidboot.selinux=permissive” in file:
/usr/nfs_share/common/linux-la.config or
/mnt/vm/images/linux-la.configAndroid boot.img
Android boot Image

Boot image is comprised of kernel, rootfs, dtb(Device Rree Blob). Recovery image is similar to boot image. It has a extra partition recovery_dtbo. Dtbo (DTB Overlays) begins from Android 9. It is loaded from dtbo.img . It is convenient for vendor to upgrade without upgrade system.img since boot.img & system.img can not be flashed respectively now for security.





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 994
994

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








