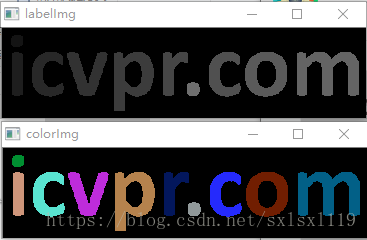
一,原图和效果图
二,代码
//#########################产生随机颜色#########################
cv::Scalar icvprGetRandomColor()
{
uchar r = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
uchar g = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
uchar b = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
return cv::Scalar(b, g, r);
}
//#########################产生随机颜色#########################
//########################种子填充法)#########################
void ConnectedCountBySeedFill(const cv::Mat& _binImg, cv::Mat& _lableImg, int &iConnectedAreaCount)
{
//拓宽1个像素的原因是:如果连通域在边缘,运行此函数会异常崩溃,所以需要在周围加一圈0值,确保连通域不在边上
//==========图像周围拓宽1个像素============================================
int top, bottom; //【添加边界后的图像尺寸】
int leftImage, rightImage;
int borderType = BORDER_CONSTANT; //BORDER_REPLICATE
//【初始化参数】
top = (int)(1); bottom = (int)(1);
leftImage = (int)(1); rightImage = (int)(1);
Mat _binImg2, _binImg3;
_binImg.copyTo(_binImg2);
//初始化参数value
Scalar value(0); //填充值
//创建图像边界
copyMakeBorder(_binImg2, _binImg3, top, bottom, leftImage, rightImage, borderType, value);
//==========图像周围拓宽1个像素============================================
// connected component analysis (4-component)
// use seed filling algorithm
// 1. begin with a foreground pixel and push its foreground neighbors into a stack;
// 2. pop the top pixel on the stack and label it with the same label until the stack is empty
//
// foreground pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 1
// background pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 0
if (_binImg3.empty() ||
_binImg3.type() != CV_8UC1)
{
return;
}
_lableImg.release();
_binImg3.convertTo(_lableImg, CV_32SC1);
int icount = 0;
int label = 1; // start by 2
int rows = _binImg3.rows - 1;
int cols = _binImg3.cols - 1;
for (int i = 1; i < rows - 1; i++)
{
int* data = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i); //取一行数据
for (int j = 1; j < cols - 1; j++)
{
if (data[j] == 1) //像素不为0
{
std::stack<std::pair<int, int>> neighborPixels; //新建一个栈
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(i, j)); // 像素坐标: <i,j> ,以该像素为起点,寻找连通域
++label; // 开始一个新标签,各连通域区别的标志
while (!neighborPixels.empty())
{
// 获取堆栈中的顶部像素并使用相同的标签对其进行标记
std::pair<int, int> curPixel = neighborPixels.top();
int curX = curPixel.first;
int curY = curPixel.second;
_lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY) = label; //对图像对应位置的点进行标记
// 弹出顶部像素 (顶部像素出栈)
neighborPixels.pop();
// 加入8邻域点
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY - 1) == 1)
{// 左点
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX, curY - 1)); //左边点入栈
}
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY + 1) == 1)
{// 右点
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX, curY + 1)); //右边点入栈
}
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX - 1, curY) == 1)
{// 上点
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX - 1, curY)); //上边点入栈
}
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX + 1, curY) == 1)
{// 下点
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX + 1, curY)); //下边点入栈
}
//===============补充到8连通域======================================================
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX - 1, curY - 1) == 1)
{// 左上点
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX - 1, curY - 1)); //左上点入栈
}
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX - 1, curY + 1) == 1)
{// 右上点
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX - 1, curY + 1)); //右上点入栈
}
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX + 1, curY - 1) == 1)
{// 左下点
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX + 1, curY - 1)); //左下点入栈
}
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX + 1, curY + 1) == 1)
{// 右下点
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX + 1, curY + 1)); //右下点入栈
}
//===============补充到8连通域======================================================
}
}
}
}
iConnectedAreaCount = label - 1; //因为label从2开始计数的
int a = 0;
}
###########################################################
//#############添加颜色#####################################
Mat PaintColor(Mat src, int iConnectedAreaCount)
{
int rows = src.rows;
int cols = src.cols;
//cv::Scalar(b, g, r);
std::map<int, cv::Scalar> colors;
for (int n = 1; n <= iConnectedAreaCount + 1; n++)
{
colors[n] = icvprGetRandomColor(); //根据不同标志位产生随机颜色
cv::Scalar color = colors[n];
int a = color[0];
int b = color[1];
int c = color[2];
int d = 0;
}
Mat dst2(rows, cols, CV_8UC3);
dst2 = cv::Scalar::all(0);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
int value = src.at<int>(i, j);
if (value>1)
{
cv::Scalar color = colors[value];
int a = color[0];
int b = color[1];
int c = color[2];
dst2.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[0] = color[0];
dst2.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[1] = color[1];
dst2.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[2] = color[2];
}
}
}
return dst2;
}
//#############添加颜色##################################
//########调用##########################################
Mat binImage = cv::imread("D:\\sxl\\处理图片\\testImages\\22.jpg", 0);
threshold(binImage, binImage, 50, 1, CV_THRESH_BINARY_INV);
// 连通域标记
Mat labelImg;
int iConnectedAreaCount = 0; //连通域个数
ConnectedCountBySeedFill(binImage, labelImg, iConnectedAreaCount);//针对黑底白字
int a=iConnectedAreaCount;
// 显示结果
Mat dstColor2=PaintColor(labelImg,iConnectedAreaCount);
imshow("colorImg", dstColor2);
Mat grayImg;
labelImg *= 10;
labelImg.convertTo(grayImg, CV_8UC1);
imshow("labelImg", grayImg);
waitKey(0);
//########调用##########################################
欢迎扫码关注我的微信公众号























 6525
6525











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








