The optimizer can handle derived table references using two strategies (which also apply to view references):
优化器可以使用两种策略处理派生表引用(也适用于视图引用):
-
Merge the derived table into the outer query block
-
将派生表合并到外部查询块中
-
Materialize the derived table to an internal temporary table
-
将派生表具体化为内部临时表
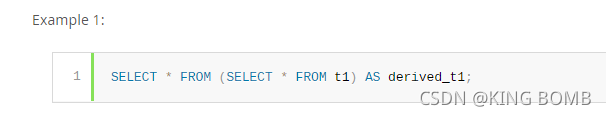
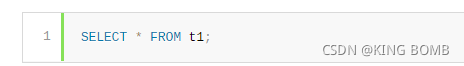
With merging of the derived table derived_t1, that query is executed similar to:
通过合并派生表derived_t1,该查询的执行方式类似于:
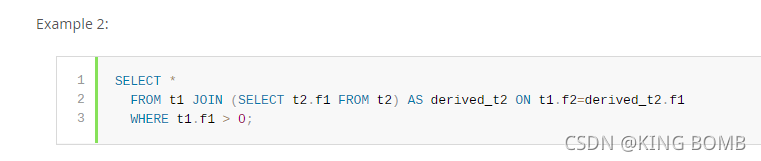
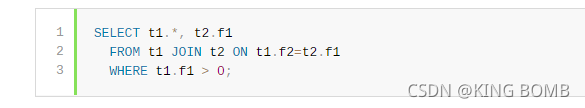
With merging of the derived table derived_t2, that query is executed similar to:
通过合并派生表derived_t2,该查询的执行方式类似于:
With materialization, derived_t1 and derived_t2 are each treated as a separate table within their respective queries.
使用物化,derived_t1和derived_t2在各自的查询中都被视为一个单独的表。
The optimizer handles derived tables and view references the same way: It avoids unnecessary materialization whenever possible, which enables pushing down conditions from the outer query to derived tables and produces more efficient execution plans.
优化器以同样的方式处理派生表和视图引用:它尽可能地避免不必要的物化,从而允许将条件从外部查询下推到派生表,并产生更有效的执行计划。
(For an example, see Section 8.2.2.2, “Optimizing Subqueries with Materialization”.)
If merging would result in an outer query block that references more than 61 base tables, the optimizer chooses materialization instead.
如果合并将导致引用超过61个基表的外部查询块,优化器将选择物化
The optimizer propagates an ORDER BY clause in a derived table or view reference to the outer query block if these conditions are all true:
如果这些条件都为真,优化器将派生表或视图引用中的ORDER BY子句传播到外部查询块:
-
The outer query is not grouped or aggregated.
- 外部查询没有分组或聚合。
-
The outer query does not specify
DISTINCT,HAVING, orORDER BY. -
外部查询没有指定DISTINCT、HAVING或ORDER BY
-
The outer query has this derived table or view reference as the only source in the
FROMclause. -
外部查询将这个派生表或视图引用作为FROM子句中的唯一来源
Otherwise, the optimizer ignores the ORDER BY clause.
否则,优化器将忽略ORDER BY子句。
The following means are available to influence whether the optimizer attempts to merge derived tables and view references into the outer query block:
以下方法可用于影响优化器是否试图将派生表和视图引用合并到外部查询块中:
The derived_merge flag of the optimizer_switch system variable can be used, assuming that no other rule prevents merging.
可以使用optimizer_switch系统变量的derived_merge标志,假设没有其他规则阻止合并。
See Section 8.9.2, “Switchable Optimizations”.
By default, the flag is enabled to permit merging. Disabling the flag prevents merging and avoids ER_UPDATE_TABLE_USED errors.
缺省情况下,允许归并。禁用该标志可以防止合并并避免ER_UPDATE_TABLE_USED错误。
The derived_merge flag also applies to views that contain no ALGORITHM clause.
derived_merge标志也适用于不包含ALGORITHM子句的视图。
Thus, if an ER_UPDATE_TABLE_USED error occurs for a view reference that uses an expression equivalent to the subquery, adding ALGORITHM=TEMPTABLE to the view definition prevents merging and takes precedence over the derived_merge value.
因此,如果使用与子查询等价的表达式的视图引用发生ER_UPDATE_TABLE_USED错误,则向视图定义添加ALGORITHM=TEMPTABLE可防止合并,并优先于derived_merge值。
It is possible to disable merging by using in the subquery any constructs that prevent merging, although these are not as explicit in their effect on materialization.
可以通过在子查询中使用任何防止合并的构造来禁用合并,尽管这些构造对物化的影响并不明显。
Constructs that prevent merging are the same for derived tables and view references:
对于派生表和视图引用,防止合并的构造是相同的:
-
Aggregate functions (SUM(), MIN(), MAX(), COUNT(), and so forth)
-
DISTINCT -
GROUP BY -
HAVING -
LIMIT -
Subqueries in the select list
-
Assignments to user variables 对用户变量的赋值
-
Refererences only to literal values (in this case, there is no underlying table)
-
仅引用文字值(在本例中,没有底层表)
The derived_merge flag also applies to views that contain no ALGORITHM clause.
derived_merge标志也适用于不包含ALGORITHM子句的视图。
Thus, if an ER_UPDATE_TABLE_USED error occurs for a view reference that uses an expression equivalent to the subquery, adding ALGORITHM=TEMPTABLE to the view definition prevents merging and takes precedence over the current derived_merge value.
因此,如果使用与子查询等价的表达式的视图引用发生ER_UPDATE_TABLE_USED错误,则向视图定义添加ALGORITHM=TEMPTABLE可防止合并,并优先于当前的derived_merge值。
If the optimizer chooses the materialization strategy rather than merging for a derived table, it handles the query as follows:
如果优化器为派生表选择了物化策略而不是合并策略,那么它将按如下方式处理查询:
-
The optimizer postpones derived table materialization until its contents are needed during query execution. This improves performance because delaying materialization may result in not having to do it at all. Consider a query that joins the result of a derived table to another table: If the optimizer processes that other table first and finds that it returns no rows, the join need not be carried out further and the optimizer can completely skip materializing the derived table.
-
优化器推迟派生表的物化,直到查询执行期间需要它的内容。这提高了性能,因为延迟物化可能导致根本不需要做它。考虑一个将派生表的结果连接到另一个表的查询:如果优化器首先处理另一个表并发现它不返回任何行,则不需要进一步执行连接,优化器可以完全跳过具体化派生表。
-
During query execution, the optimizer may add an index to a derived table to speed up row retrieval from it.
-
在执行查询期间,优化器可能会向派生表添加索引,以加速从它检索行。
Consider the following EXPLAIN statement, for a SELECT query that contains a derived table:
对于包含派生表的SELECT查询,考虑下面的EXPLAIN语句:
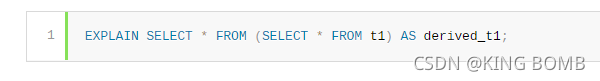
The optimizer avoids materializing the derived table by delaying it until the result is needed during SELECT execution. In this case, the query is not executed (because it occurs in an EXPLAIN statement), so the result is never needed.
优化器通过延迟派生表,直到SELECT执行期间需要结果,从而避免具体化派生表。在这种情况下,查询不会执行(因为它发生在EXPLAIN语句中),因此不需要结果。
Even for queries that are executed, delay of derived table materialization may enable the optimizer to avoid materialization entirely. When this happens, query execution is quicker by the time needed to perform materialization. Consider the following query, which joins the result of a derived table to another table:
即使对于正在执行的查询,派生表物化的延迟也可能使优化器完全避免物化。当发生这种情况时,查询执行的速度会比执行物化所需的时间更快。考虑以下查询,它将派生表的结果连接到另一个表:
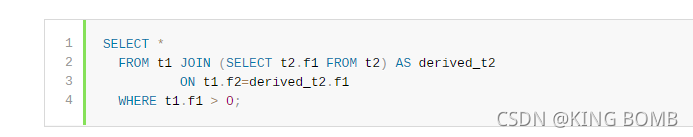
If the optimization processes t1 first and the WHERE clause produces an empty result, the join must necessarily be empty and the derived table need not be materialized.
如果优化首先处理t1, WHERE子句产生一个空结果,则连接必须为空,派生表不需要被物化。
For cases when a derived table requires materialization, the optimizer may add an index to the materialized table to speed up access to it. If such an index enables ref access to the table, it can greatly reduce amount of data read during query execution. Consider the following query:
对于派生表需要物化的情况,优化器可以向物化表添加索引,以加速对它的访问。如果这样的索引允许引用访问表,它可以大大减少查询执行期间的数据读取量。考虑以下查询:
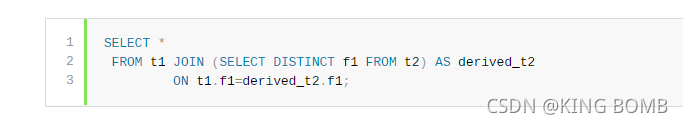
The optimizer constructs an index over column f1 from derived_t2 if doing so would enable use of ref access for the lowest cost execution plan.
优化器从derived_t2构造列f1上的索引,如果这样做可以使成本最低的执行计划使用ref访问。
After adding the index, the optimizer can treat the materialized derived table the same as a regular table with an index, and it benefits similarly from the generated index.
在添加索引之后,优化器可以将物化派生表与带有索引的普通表一样对待,它也可以从生成的索引中获得类似的好处。
The overhead of index creation is negligible compared to the cost of query execution without the index. If ref access would result in higher cost than some other access method, the optimizer creates no index and loses nothing.
与没有索引的查询执行成本相比,创建索引的开销可以忽略不计。如果ref访问的代价比其他访问方法高,优化器不会创建索引,也不会损失任何东西。
For optimizer trace output, a merged derived table or view reference is not shown as a node. Only its underlying tables appear in the top query's plan.
对于优化器跟踪输出,合并的派生表或视图引用不会显示为节点。只有它的底层表出现在顶部查询的计划中。








 这篇博客探讨了数据库优化器处理派生表和视图引用的两种策略:合并和物化。优化器尽可能避免不必要的物化,允许条件下推以提高执行效率。当合并可能导致查询块引用过多基表时,优化器会选择物化。物化策略下,优化器可能在执行时延迟派生表的物化或为其添加索引以加速访问。此外,博客还提到了如何通过optimizer_switch系统变量和ALGORITHM子句影响这种行为。
这篇博客探讨了数据库优化器处理派生表和视图引用的两种策略:合并和物化。优化器尽可能避免不必要的物化,允许条件下推以提高执行效率。当合并可能导致查询块引用过多基表时,优化器会选择物化。物化策略下,优化器可能在执行时延迟派生表的物化或为其添加索引以加速访问。此外,博客还提到了如何通过optimizer_switch系统变量和ALGORITHM子句影响这种行为。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








