图的四种存储方式邻接矩阵,前向星,邻接表,链式前向星。
输入文件内容:
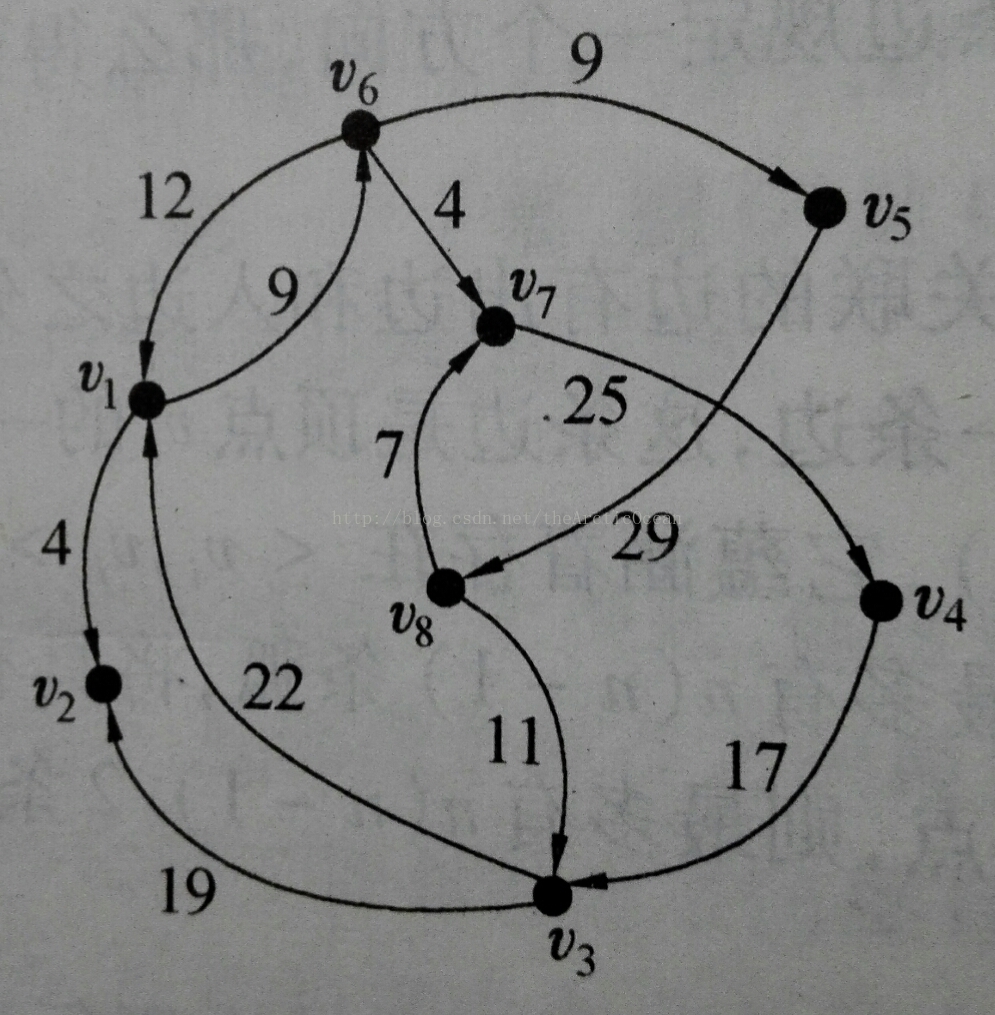
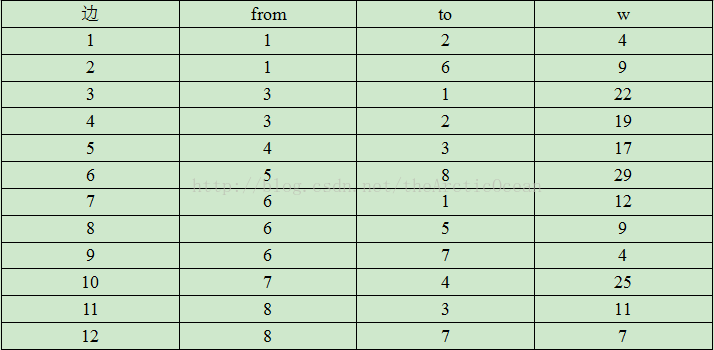
8 12
1 2 4
1 6 9
3 1 22
3 2 19
4 3 17
5 8 29
6 1 12
6 5 9
6 7 4
7 4 25
8 3 11
8 7 7
邻接矩阵:图的数据结构中最简单,最常用的一种。完成初始化后,对有向图,加边的操作就是graph[u][v]=c。对无向图,必须再加上graph[v][u]=c。它的缺点:遍历效率低,不能存储重边,大图的空间开销太大。//例如当n>10e7时建立一个int 一维数组 too large.
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=101;
int graph[maxn][maxn];
int main()
{
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
int n,m,i,j,a,b,val;
cin>>n>>m; //规模以及实际的边数。例子中数据是8,12.
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&val);
graph[a][b]=val;
}
//遍历:
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=m;j++)
if(graph[i][j])printf("%d %d %d\n",i,j,graph[i][j]);
return 0;
}
前向星:将边存放在数组中,把数组中的边按照起点的顺序排序,为查询方便,经常有一个数组存储起点为Vi的第一条边的位置。
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); //全部成-1
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100,maxm=140;
int head[maxn]; //存储起点为Vi的第一条边的位置。
struct node{
int from,to,w;
}edge[maxm];
bool cmp(node a,node b){
if(a.from==b.from&&a.to==b.to)return a.w<b.w;
if(a.from==b.from)return a.to<b.to;
return a.from<b.from;
}
int main()
{
freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m; //规模以及实际的边数。例子中数据是8,12.
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)scanf("%d%d%d",&edge[i].from,&edge[i].to,&edge[i].w);
sort(edge+1,edge+m+1,cmp);
head[edge[1].from]=1; //head下标代表顶点的编号1--8。head本身代表边的序号0--11
for(i=2;i<=m;i++)if(edge[i].from!=edge[i-1].from)head[edge[i].from]=i; //起点为Vi的第一条边的位置
//遍历:
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=head[i];edge[j].from==i&&j<=m;j++)printf("%d %d %d\n",edge[j].from,edge[j].to,edge[j].w);
return 0;
}
邻接表的实现:动态建表,C++ STL vector模拟链表,链式前向星(静态建表)
动态建表的时间复杂度:O(m),空间复杂度:O(m),但是内存的释放和申请,判断任意两点的相连都是它的缺点。
vector模拟链表的方法和动态建表相比不用考虑内存申请释放问题,代码写的少且简单,但思想类似,所以注重研究这种方法:
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=101;
struct node{
int to,w;
};
int main()
{
freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
vector<node> qn[maxn]; //考虑重边,所以"[]"
int n,m,i,j,a,b,val;
cin>>n>>m; //规模以及实际的边数。例子中数据是8,12.
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&val);
node t;
t.to=b; t.w=val;
qn[a].push_back(t);
}
//遍历:
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(vector<node>::iterator k=qn[i].begin();k!=qn[i].end();k++){
node t1=*k; //一定要新建一个node变量才能顺利输出to,w,不能直接"*k.to,*k.w"
printf("%d %d %d\n",i,t1.to,t1.w);
}
//清除操作:
for(i=0;i<m;i++)qn[i].clear();//qn.erase(qn.begin(),b.end())
return 0;
}
输出结果:
1 2 4
1 6 9
3 1 22
3 2 19
4 3 17
5 8 29
6 1 12
6 5 9
6 7 4
7 4 25
8 3 11
8 7 7
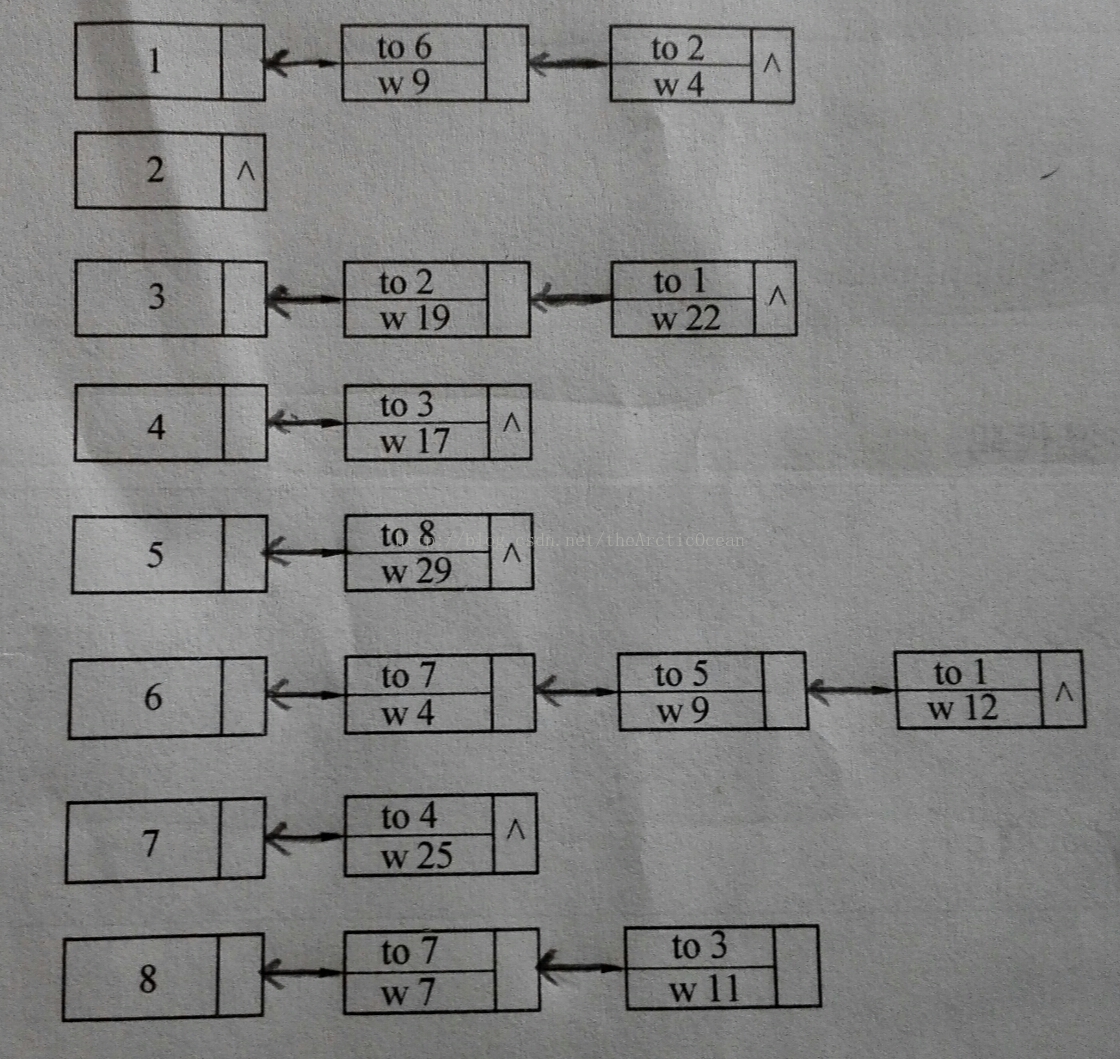
链式前向星,遍历效率高,额外空间少,时间复杂度O(m),这是一种很优秀的图的数据存储结构。
存储图:
输出结果:
1 6 9
1 2 4
3 2 19
3 1 22
4 3 17
5 8 29
6 7 4
6 5 9
6 1 12
7 4 25
8 7 7
8 3 11
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=101,maxm=141;
int head[maxn];
struct node{
int to,w,next;
}edge[maxm];
int main(){
freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
freopen("cout1.txt","w",stdout);
int n,m,k,i; cin>>n>>m; //规模以及实际的边数。例子中数据是8,12.
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
k=i+1;
int a,b,c;
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
edge[k].to=b;
edge[k].w=c;
edge[k].next=head[a];
head[a]=k;
}
//遍历:
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(k=head[i];k!=0;k=edge[k].next){ printf("%d %d %d\n",i,edge[k].to,edge[k].w); }
return 0;
}





















 100
100











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








