转载请注明出处:勿在浮沙筑高台http://blog.csdn.net/luoshixian099/article/details/51908175
关于图的几个概念定义:
- 连通图:在无向图中,若任意两个顶点vi” role=”presentation”>vivi都有路径相通,则称该无向图为连通图。
- 强连通图:在有向图中,若任意两个顶点vi” role=”presentation”>vivi都有路径相通,则称该有向图为强连通图。
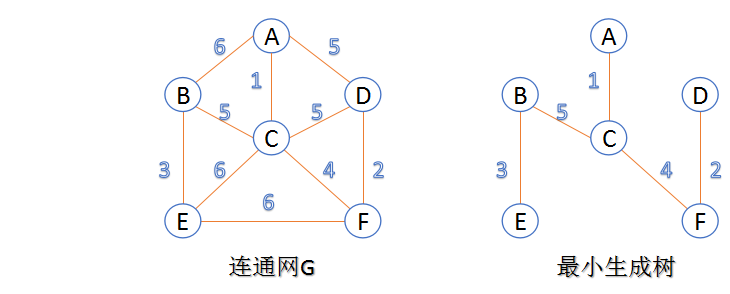
- 连通网:在连通图中,若图的边具有一定的意义,每一条边都对应着一个数,称为权;权代表着连接连个顶点的代价,称这种连通图叫做连通网。
- 生成树:一个连通图的生成树是指一个连通子图,它含有图中全部n个顶点,但只有足以构成一棵树的n-1条边。一颗有n个顶点的生成树有且仅有n-1条边,如果生成树中再添加一条边,则必定成环。
- 最小生成树:在连通网的所有生成树中,所有边的代价和最小的生成树,称为最小生成树。
下面介绍两种求最小生成树算法
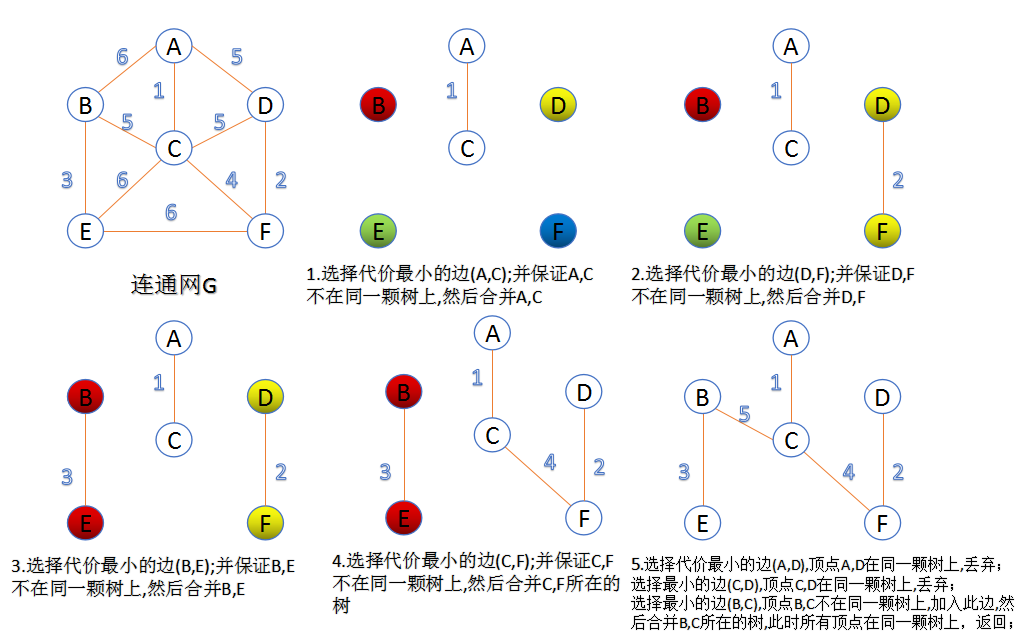
1.Kruskal算法
此算法可以称为“加边法”,初始最小生成树边数为0,每迭代一次就选择一条满足条件的最小代价边,加入到最小生成树的边集合里。
1. 把图中的所有边按代价从小到大排序;
2. 把图中的n个顶点看成独立的n棵树组成的森林;
3. 按权值从小到大选择边,所选的边连接的两个顶点ui,vi” role=”presentation”>ui,viui,vi,应属于两颗不同的树,则成为最小生成树的一条边,并将这两颗树合并作为一颗树。
4. 重复(3),直到所有顶点都在一颗树内或者有n-1条边为止。
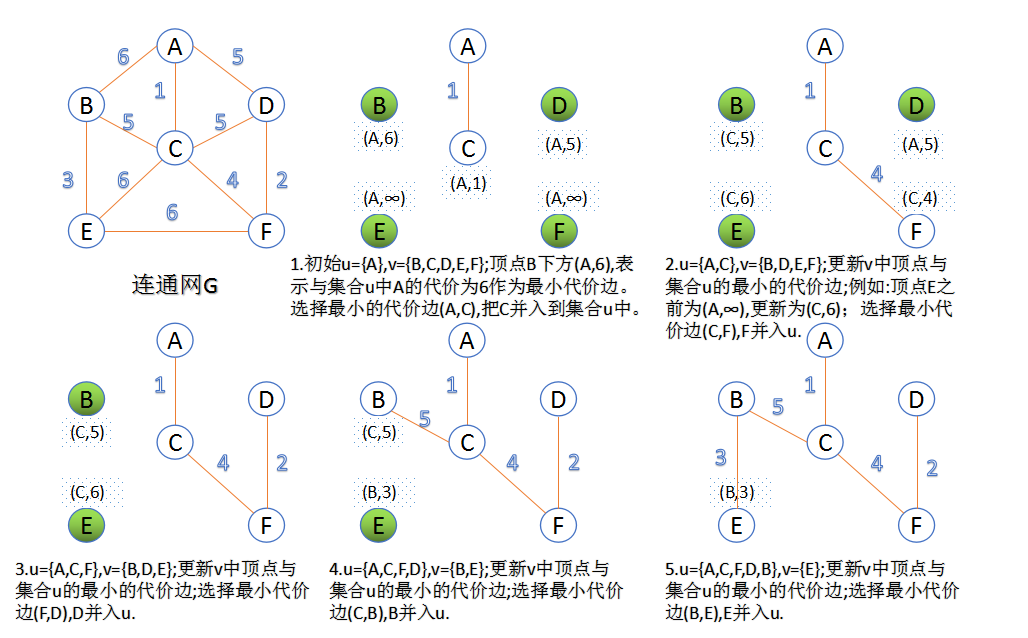
2.Prim算法
此算法可以称为“加点法”,每次迭代选择代价最小的边对应的点,加入到最小生成树中。算法从某一个顶点s开始,逐渐长大覆盖整个连通网的所有顶点。
- 图的所有顶点集合为V” role=”presentation”>VV;
- 在两个集合u,v” role=”presentation”>u,vu,v并入到集合u中。
- 重复上述步骤,直到最小生成树有n-1条边或者n个顶点为止。
由于不断向集合u中加点,所以最小代价边必须同步更新;需要建立一个辅助数组closedge,用来维护集合v中每个顶点与集合u中最小代价边信息,:
struct
{
char vertexData //表示u中顶点信息
UINT lowestcost //最小代价
}closedge[vexCounts]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
3.完整代码
/************************************************************************
CSDN 勿在浮沙筑高台 http://blog.csdn.net/luoshixian099算法导论--最小生成树(Prim、Kruskal)2016年7月14日
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define INFINITE 0xFFFFFFFF
#define VertexData unsigned int //顶点数据
#define UINT unsigned int
#define vexCounts 6 //顶点数量
char vextex[] = { 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F' };
struct node
{
VertexData data;
unsigned int lowestcost;
}closedge[vexCounts]; //Prim算法中的辅助信息
typedef struct
{
VertexData u;
VertexData v;
unsigned int cost; //边的代价
}Arc; //原始图的边信息
void AdjMatrix(unsigned int adjMat[][vexCounts]) //邻接矩阵表示法
{
for (int i = 0; i < vexCounts; i++) //初始化邻接矩阵
for (int j = 0; j < vexCounts; j++)
{
adjMat[i][j] = INFINITE;
}
adjMat[0][1] = 6; adjMat[0][2] = 1; adjMat[0][3] = 5;
adjMat[1][0] = 6; adjMat[1][2] = 5; adjMat[1][4] = 3;
adjMat[2][0] = 1; adjMat[2][1] = 5; adjMat[2][3] = 5; adjMat[2][4] = 6; adjMat[2][5] = 4;
adjMat[3][0] = 5; adjMat[3][2] = 5; adjMat[3][5] = 2;
adjMat[4][1] = 3; adjMat[4][2] = 6; adjMat[4][5] = 6;
adjMat[5][2] = 4; adjMat[5][3] = 2; adjMat[5][4] = 6;
}
int Minmum(struct node * closedge) //返回最小代价边
{
unsigned int min = INFINITE;
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < vexCounts;i++)
{
if (closedge[i].lowestcost < min && closedge[i].lowestcost !=0)
{
min = closedge[i].lowestcost;
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
void MiniSpanTree_Prim(unsigned int adjMat[][vexCounts], VertexData s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < vexCounts;i++)
{
closedge[i].lowestcost = INFINITE;
}
closedge[s].data = s; //从顶点s开始
closedge[s].lowestcost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vexCounts;i++) //初始化辅助数组
{
if (i != s)
{
closedge[i].data = s;
closedge[i].lowestcost = adjMat[s][i];
}
}
for (int e = 1; e <= vexCounts -1; e++) //n-1条边时退出
{
int k = Minmum(closedge); //选择最小代价边
cout << vextex[closedge[k].data] << "--" << vextex[k] << endl;//加入到最小生成树
closedge[k].lowestcost = 0; //代价置为0
for (int i = 0; i < vexCounts;i++) //更新v中顶点最小代价边信息
{
if ( adjMat[k][i] < closedge[i].lowestcost)
{
closedge[i].data = k;
closedge[i].lowestcost = adjMat[k][i];
}
}
}
}
void ReadArc(unsigned int adjMat[][vexCounts],vector<Arc> &vertexArc) //保存图的边代价信息
{
Arc * temp = NULL;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < vexCounts;i++)
{
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if (adjMat[i][j]!=INFINITE)
{
temp = new Arc;
temp->u = i;
temp->v = j;
temp->cost = adjMat[i][j];
vertexArc.push_back(*temp);
}
}
}
}
bool compare(Arc A, Arc B)
{
return A.cost < B.cost ? true : false;
}
bool FindTree(VertexData u, VertexData v,vector<vector<VertexData> > &Tree)
{
unsigned int index_u = INFINITE;
unsigned int index_v = INFINITE;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < Tree.size();i++) //检查u,v分别属于哪颗树
{
if (find(Tree[i].begin(), Tree[i].end(), u) != Tree[i].end())
index_u = i;
if (find(Tree[i].begin(), Tree[i].end(), v) != Tree[i].end())
index_v = i;
}
if (index_u != index_v) //u,v不在一颗树上,合并两颗树
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < Tree[index_v].size();i++)
{
Tree[index_u].push_back(Tree[index_v][i]);
}
Tree[index_v].clear();
return true;
}
return false;
}
void MiniSpanTree_Kruskal(unsigned int adjMat[][vexCounts])
{
vector<Arc> vertexArc;
ReadArc(adjMat, vertexArc);//读取边信息
sort(vertexArc.begin(), vertexArc.end(), compare);//边按从小到大排序
vector<vector<VertexData> > Tree(vexCounts); //6棵独立树
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < vexCounts; i++)
{
Tree[i].push_back(i); //初始化6棵独立树的信息
}
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < vertexArc.size(); i++)//依次从小到大取最小代价边
{
VertexData u = vertexArc[i].u;
VertexData v = vertexArc[i].v;
if (FindTree(u, v, Tree))//检查此边的两个顶点是否在一颗树内
{
cout << vextex[u] << "---" << vextex[v] << endl;//把此边加入到最小生成树中
}
}
}
int main()
{
unsigned int adjMat[vexCounts][vexCounts] = { 0 };
AdjMatrix(adjMat); //邻接矩阵
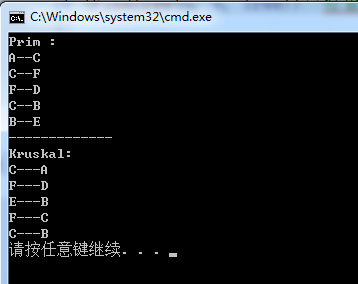
cout << "Prim :" << endl;
MiniSpanTree_Prim(adjMat,0); //Prim算法,从顶点0开始.
cout << "-------------" << endl << "Kruskal:" << endl;
MiniSpanTree_Kruskal(adjMat);//Kruskal算法
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
Reference:
数据结构–耿国华
算法导论–第三版
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/template/css/markdown_views-ea0013b516.css">
</div>





















 4万+
4万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








