前言
本节将讨论Netty框架中的EventLoop接口与线程模型,Netty是如果处理I/O事件循环等问题;Netty如何对任务进行调度等问题。下面通过一张图来展示本文的内容:
EventLoop
在Netty的定义中EventLoop接口只有一个方法EventLoopGroup parent();方法用于返回当前EventLoop实现的实例所属的EventLoopGroup的引用。
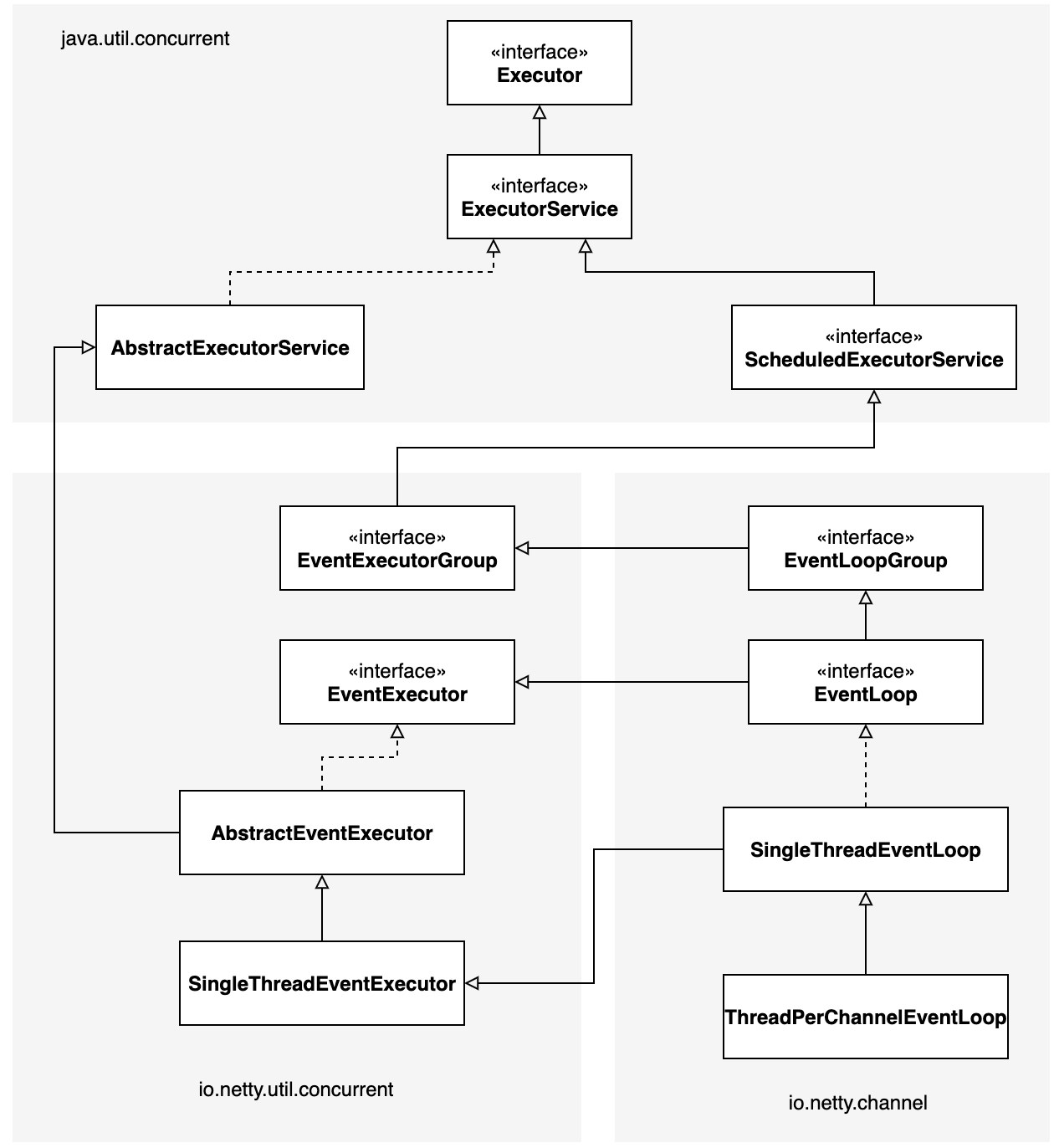
Netty的EventLoop是一个协同设计采用两个基本的API:并发和网络编程。首先io.netty.util.concurrent名构建在JDK的java.util.concurrent包的基本之上,用来提供线程执行器。其次io.netty.channel包中的类为了与Channel的事件进行交互,扩展了这些接口/类。下图展示了类的层次结构:
在使用EventLoop对任务作调度时能使用Java SDK提供的ScheduledExecutorService类型中的所有方法。例如服务间的心跳就可以直接使用EventLoop的任务调度实现:
//ctx为ChannelHandlerContext
Channel channel=ctx.channel();
ScheduledFuture<?> future = ctx.channel().eventLoop().scheduleAtFixedRate(()->{
//发送心跳与检查心跳
System.out.println("心跳");
},60,60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
如果需要检查或者取消调度任务则可以使用每个异步操作返回ScheduledFuture实例进行操作,ScheduledFuture是一个Future类型实例。
下面通过SingleThreadEventLoop抽象类来讲讲EventLoop的实现细节:
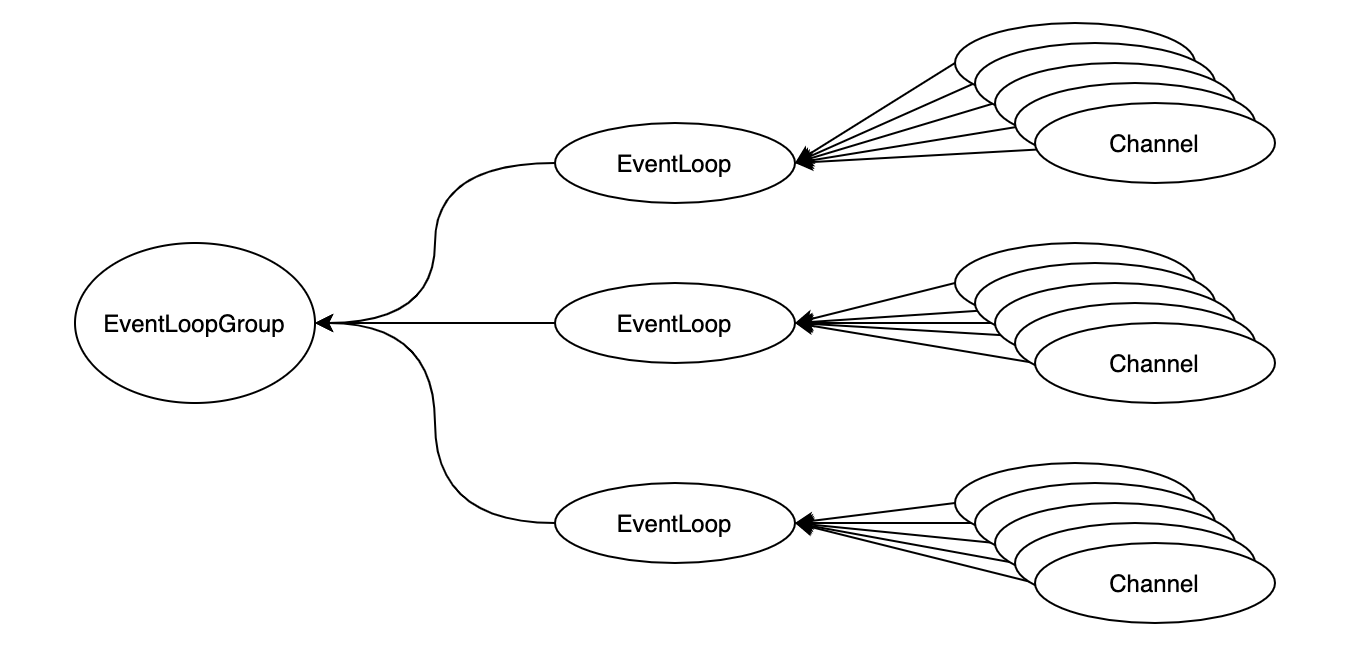
SingleThreadEventLoop继承于SingleThreadEventExecutor;SingleThreadEventExecutor相当于Java JDK中的线程池,作用是对事件进行异步调用,EventLoop的内部有一个单独的线程,负责处理所有分配给EventLoop的Channel的所有事件和任务,在EventLoop之上有EventLoopGroup;EventLoopGroup的责任是将新的连接(也就是新的Channel)分配给EventLoopGroup内关联的EventLoop。下面通过一张图来讲讲上面EventLoopGroup、EventLoop、Channel之前的关系:
关于SingleThreadEventExecutor暂时简单的理解一个任务池,负责异步任务的执行,任务队列的顺序使用FIFO的形式进行。
写到这我想你应该大概了解Netty的EventLoop了;而这样的事件驱动编程模型正式经典的Reactor网络模型;下面我们引入NioEventLoop来简单的讲下Netty是如果实现事件驱动的。看过我前面讲NIO编程的同学应该都清楚使用JAVA JDK提供的NIO写一个简单的网络程序时需要处理accept、connect、read、write事件,这些事件都需要注册到Selector当中,再通过Selector.selectedKeys()方法获取到所有事件并一一处理。
在Netty中EventLoop不光要处理I/O事件,还需要处理上面我们提到的任务;下面我们通过一段NIOEventLoop类中的源码来看看EventLoop是如何处理I/O事件和任务的:
@Override
protected void run() {
int selectCnt = 0;
//使用死循环进行轮询
for (;;) {
try {
int strategy;
try {
//hasTasks为ture执行selectNow(),否则返回SelectStrategy.SELECT,会优先处理I/O事件
strategy = selectStrategy.calculatStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks());
switch (strategy) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:
// fall-through to SELECT since the busy-wait is not supported with NIO
//返回SELECT表示当前没有任务
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
long curDeadlineNanos = nextScheduledTaskDeadlineNanos();
if (curDeadlineNanos == -1L) {
curDeadlineNanos = NONE; // nothing on the calendar
}
nextWakeupNanos.set(curDeadlineNanos);
try {
//再次判断是否有任务,没有时执行Selector.selectNow()方法获取I/O事件,
//没有时selectNow会阻塞线程,阻塞时间通过curDeadlineNanos控制
if (!hasTasks()) {
//没有任务时执行Selector.selectNow()查询当前的I/O事件
strategy = select(curDeadlineNanos);
}
} finally {
// This update is just to help block unnecessary selector wakeups
// so use of lazySet is ok (no race condition)
nextWakeupNanos.lazySet(AWAKE);
}
// fall through
default:
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// If we receive an IOException here its because the Selector is messed up. Let's rebuild
// the selector and retry. https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/8566
rebuildSelector0();
selectCnt = 0;
handleLoopException(e);
continue;
}
selectCnt++;
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
//IO事件的比率
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
boolean ranTasks;
//为100时立即处理I/O事件
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
//通过SelectNow获取的事件数量
if (strategy > 0) {
//执行I/O事件
processSelectedKeys();
}
} finally {
// 执行完I/O事件后执行一次任务
ranTasks = runAllTasks();
}
//ioRatio没有100时且当前有I/O事件时
} else if (strategy > 0) {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
//执行I/O事件
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// 通过ioRatio与I/O事件执行时间计算出任务执行超时时间
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
ranTasks = runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
//没有I/O事件时将时间全部分配给任务执行
} else {
ranTasks = runAllTasks(0); // This will run the minimum number of tasks
}
//通过selectCnt计数解决多次selectNow后没有I/O事件的问题
if (ranTasks || strategy > 0) {
//执行过任务或者I/O事件认为是有效的就重置selectCnt
if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",
selectCnt - 1, selector);
}
selectCnt = 0;
//无效时rebuild selector
} else if (unexpectedSelectorWakeup(selectCnt)) { // Unexpected wakeup (unusual case)
selectCnt = 0;
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
// Harmless exception - log anyway
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",
selector, e);
}
} catch (Error e) {
throw (Error) e;
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
} finally {
// Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception.
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Error e) {
throw (Error) e;
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
}
这段代码中的主要作用是分配I/O事件与任务之间的执行时间片,通过变量ioRatio进行比率的计算来分配执行时间。
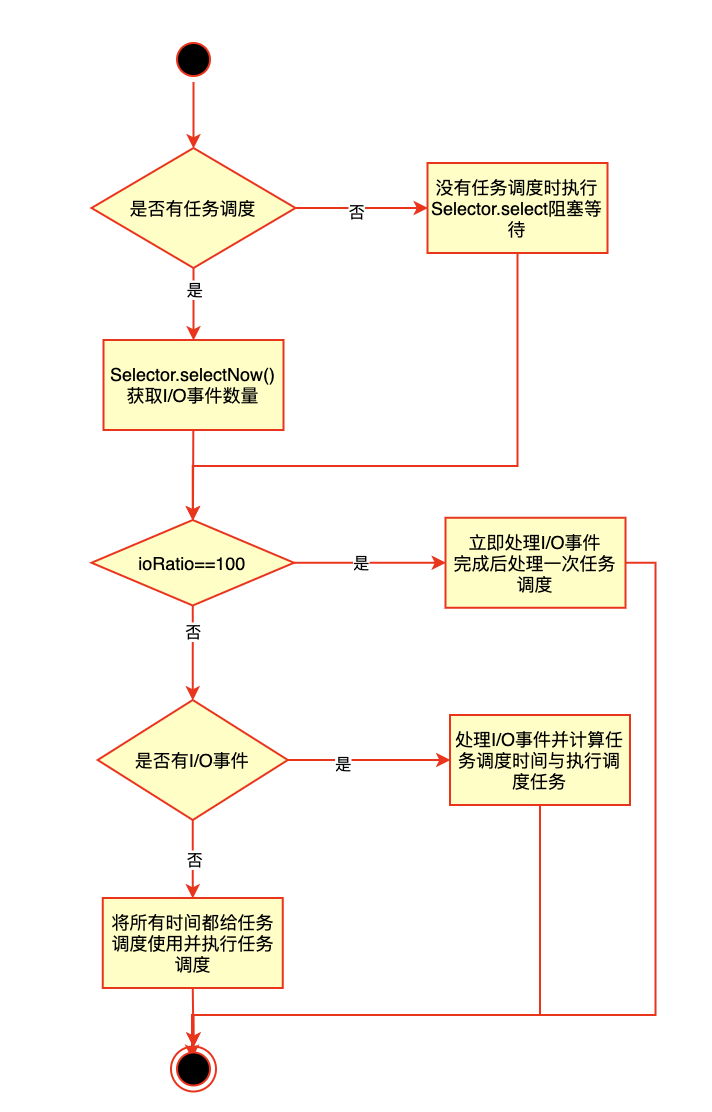
通过对上面代码的分析可以总结出如下三点:
- 每一个EventLoop中都由一个单独的线程处理并与EventLoop一一对应
- EventLoop将注册的Channel产生的I/O事件和通过EventLoop添加的任务调度都放在同一线程内处理,通过ioRatio分配执行时间
- EventLoop会优先处理I/O事件
- 处理I/O事件时如果出现阻塞会同时阻塞I/O事件和任务调度队列
- 任务调度队列中的任务阻塞调用时会同时阻塞I/O事件的处理
最后用一个简单的流程图贯穿下EventLoop的核心代码吧:
往期推荐:
Netty框架:ChannelInboundHandler与ChannelOutbountHandler使用讲解
Netty框架:ByteBuf 堆缓冲区与直接缓冲区使用讲解
网络I/O : Netty 体系结构概述
Netty源码解析系列(正在更新中)

新开的公众号,欢迎订阅。最新的文章都会在这里更新哦~~~






















 1914
1914











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








