下面程序创建了一个子进程,子进程使用exec族的函数来执行新的程序,以新的进程代替原有的进程。
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
if((pid = fork()) < 0)
{
printf("fork error\n");
exit(1);
}
else if(0 == pid)
{
printf("Child process PID: %d\n",getpid());
setenv("PS1","CHILD\\$",1);//设置环境变量
printf("Process%4d: calling exec.\n",getpid());
//if(execl("/bin/sh","/bin/sh","arg2",NULL) < 0)
if(execl("/bin/ls","/bin/ls",NULL) < 0)//调用/bin/ls程序来代替子进程
{
printf("Process%4d: execle error!\n",getpid());
exit(0);
}
printf("Process%4d: You should never see this because the chiled is already gone. \n",getpid());
printf("Precess%4d: The child process is exiting\n");
}
else
{
printf("Parent process PID:%4d.\n",getpid());
printf("Process%4d: The parent has fork process %d.\n",getpid(),pid);
printf("Process%4d: The child has called exec or has exited.\n",getpid());
}
return 0;
}
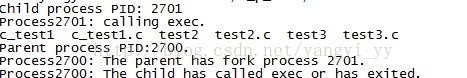
执行结果:
从结果可以看到,子进程执行了ls程序,并且没有打印
You should never see this because the chiled is already gone.Precess%4d: The child process is exiting
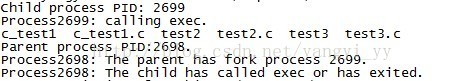
setenv函数的作用是什么?我们把这条语句注释掉后来看结果:
似乎结果并没有什么变化
那么setenv函数到底是干什么的?
函数原型:
int setenv(const char *name,const char * value,int overwrite);
第一个参数是环境变量名称,第二是参数是值,第三个为1则表示覆盖已有值,为0表示若有已有值则不覆盖。
那可不可以使用execl()函数来调用自己写的程序呢?
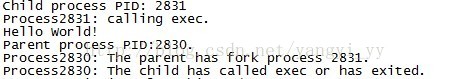
我们将程序中的execl语句换成
if(execl("/root/c_p_t/test1","test1:",NULL))
我们看结果:
结论是可以的。






















 1915
1915

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








