题目的描述比较长,总的意思就是给出两棵有根树,判断它们是不是同构树。
所谓的同构树,定义我也不太知道 。按字面上的意思就是两棵结构相同的树。
。按字面上的意思就是两棵结构相同的树。
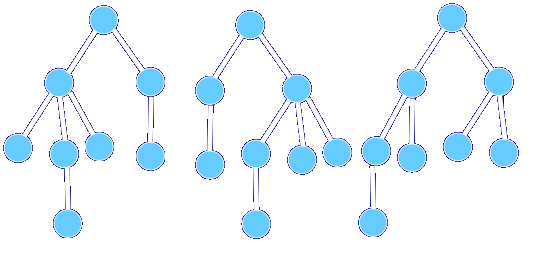
如第一棵树和第二棵树就是同构树,它们和第三棵树不是同构树:
并且,同构树它们有一一对应的点。
对于任意一棵有根树,都可以用括号表示法来表示,可以去http://www.byvoid.com/blog/directed-tree-bracket-sequence/看看。
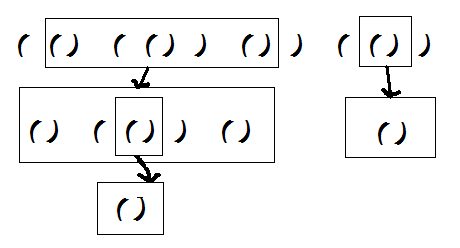
如上面的第一棵树,既可以表示成(()(())())(()),也可以表示成(())((())()()),有很多的表示方法,为了判断,我们要用最小表示法,就是字典序最小的一个。第一种括号可以分解成:
每一层都排一下序就可以找到字典树最小的一个啦 。
。
其实原题就是这样的一个括号序列,0代表左括号,1代表右括号。这样问题就很简单了,把这读入的两个字符串当做括号处理,如果它们的最小表示法是一样的,那么就是同构树啦。
但是,我们要对字符串进行分解,分解完了还要排序,不仅时间复杂度不乐观,空间处理也比较麻烦。所以,我们可以用哈希,把一个括号序列哈希掉。合并的时候将哈希值从小到大排序,再合成当前的哈希值。可以去看看《杨弋<Hash在信息学竞赛中的一类应用>》这篇文章。
我看到网上有一种方法,判断每一层的节点数是否相等,且相同层数子树大小经过排序后对应相等,那么就是同构。我不知道这种方法对不对,网上有的说这是错的。我写了一下,还真的过了,求证明。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <time.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n, P[3007];
bool d[6007];
// 这样读入会快些??
int read(int i) {
char ch = '*';
do ch = getchar(); while (ch < '0' || ch > '1');
for (; ch == '0' || ch == '1'; ch = getchar()) d[i ++] = ch == '1';
return i;
}
// 字符串的[L, R)的哈希值
int GetHash(int L, int R) {
if (L >= R) return 1;
// 只能用vector??我想不到更好的办法
vector<int> t;
t.clear();
int f = 0, cnt = 0;
for (int i = L; i < R; i ++) {
if (d[i]) f --; else f ++;
// 当括号匹配时就可以分解了
if (f == 0) {
t.push_back(GetHash(L + 1, i)), cnt ++;
L = i + 1;
}
}
// 排序
sort(t.begin(), t.end());
// 求出当前哈希值
int res = 1;
// 这要找个好的哈希函数,
// 一开始我写得不好,有很多重复
// 后来在网上看到如下的方法
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i ++)
res = (res ^ t[i]) * P[i] % 15237;
return res;
}
int main() {
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
srand((int)time(0));
for (int i = 0; i < 3000; i ++) P[i] = rand() % 15237;
int T;
scanf("%d\n", &T);
while (T --) {
int n = read(0);
int m = read(n);
if (GetHash(0, n) == GetHash(n, m)) printf("same\n");
else printf("different\n");
}
return 0;
}
奇怪的方法(代码有点烂, 其实不用构图的):
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3007;
struct Tree {
int n;
int father[N], head[N], to[N], next[N], cnt;
struct data {
int depth, size;
bool operator < (data const &o) const {
if (depth != o.depth) return depth < o.depth;
return size < o.size;
}
bool operator == (data const &o) const {
return depth == o.depth && size == o.size;
}
}d[N];
void Insert(int u, int v) {
to[++ cnt] = v;
next[cnt] = head[u];
head[u] = cnt;
}
int Q[N];
void Build(char *s) {
cnt = 0;
memset(head, 0, sizeof(head));
int len = strlen(s);
n = 1;
int cur = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i ++)
if (s[i] == '0') {
Insert(cur, ++ n);
father[n]= cur;
cur = n;
}
else cur = father[cur];
d[1].depth = 1;
int lo = 0, hi = 0;
Q[0] = 1;
for (; lo <= hi; lo ++) {
int u = Q[lo];
for (int e = head[u]; e; e = next[e]) {
int v = to[e];
d[v].depth = d[u].depth + 1;
Q[++ hi] = v;
}
}
for (; hi >= 0; hi --) {
int u = Q[hi];
d[u].size = 1;
for (int e = head[u]; e; e = next[e])
d[u].size += d[to[e]].size;
}
sort(d + 1, d + 1 + n);
}
bool operator == (Tree const &o) const {
if (n != o.n) return false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
if (!(d[i] == o.d[i])) return false;
return true;
}
}a, b;
char dat[N];
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d\n", &T);
while (T --) {
scanf("%s\n", dat);
a.Build(dat);
scanf("%s\n", dat);
b.Build(dat);
if (a == b) printf("same\n");
else printf("different\n");
}
return 0;
}






 本文介绍了一种通过括号表示法和哈希技术判断两棵有根树是否为同构树的方法,并提供两种不同的实现思路。
本文介绍了一种通过括号表示法和哈希技术判断两棵有根树是否为同构树的方法,并提供两种不同的实现思路。
















 40
40

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








