排序是计算机算法中非常重要的一项,而排序算法又有不少实现方法,那么哪些排序算法比较有效率,哪些算法在特定场合比较有效,下面将用C++实现各种算法,并且比较他们的效率,让我们对各种排序有个更深入的了解。
1、冒泡排序
//n^2 冒泡排序V[n]不参与排序
void BubbleSort (int V[], int n )
{
bool exchange; //设置交换标志置
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ){
exchange=false;
for (int j=n-1; j>i; j--) { //反向检测,检查是否逆序
if (V[j-1] > V[j]) //发生逆序,交换相邻元素
{
int temp=V[j-1];
V[j-1]=V[j];
V[j]=temp;
exchange=true;//交换标志置位
}
}
if (exchange == false)
return; //本趟无逆序,停止处理
}
}2、插入排序
//插入排序,L[begin],L[end]都参与排序
void InsertionSort ( int L[], const int begin, const int end)
{
//按关键码 Key 非递减顺序对表进行排序
int temp;
int i, j;
for ( i = begin; i < end; i++ )
{
if (L[i]>L[i+1])
{
temp = L[i+1];
j=i;
do
{
L[j+1]=L[j];
if(j == 0)
{
j--;
break;
}
j--;
} while(temp<L[j]);
L[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}3、快速排序
//n*logn
//快速排序A[startingsub],A[endingsub]都参与排序
void QuickSort( int A[], int startingsub, int endingsub)
{
if ( startingsub >= endingsub )
;
else{
int partition;
int q = startingsub;
int p = endingsub;
int hold;
do{
for(partition = q ; p > q ; p--){
if( A[q] > A[p]){
hold = A[q];
A[q] = A[p];
A[p] = hold;
break;
}
}
for(partition = p; p > q; q++){
if(A[p] < A[q]){
hold = A[q];
A[q] = A[p];
A[p] = hold;
break;
}
}
}while( q < p );
QuickSort( A, startingsub, partition - 1 );
QuickSort( A, partition + 1, endingsub );
}
}4、希尔排序
//希尔排序,L[left],L[right]都参与排序
void Shellsort( int L[], const int left, const int right)
{
int i, j, gap=right-left+1; //增量的初始值
int temp;
do{
gap=gap/3+1; //求下一增量值
for(i=left+gap; i<=right; i++)
//各子序列交替处理
if( L[i]<L[i-gap]){ //逆序
temp=L[i]; j=i-gap;
do{
L[j+gap]=L[j]; //后移元素
j=j-gap; //再比较前一元素
}while(j>left&&temp<L[j]);
L[j+gap]=temp; //将vector[i]回送
}
}while(gap>1);
}5、计数排序
//n
//计数排序,L[n]不参与排序
void CountingSort( int L[], const int n )
{
int i,j;
const int k =1001;
int tmp[k];
int *R;
R = new int[n];
for(i=0;i<k;i++) tmp[i]= 0;
for(j=0;j<n;j++) tmp[L[j]]++;
//执行完上面的循环后,tmp[i]的值是L中等于i的元素的个数
for(i=1;i<k;i++)
tmp[i]=tmp[i]+tmp[i-1]; //执行完上面的循环后,
//tmp[i]的值是L中小于等于i的元素的个数
for(j=n-1;j>=0;j--) //这里是逆向遍历,保证了排序的稳定性
{
R[tmp[L[j]]-1] = L[j];
//L[j]存放在输出数组R的第tmp[L[j]]个位置上
tmp[L[j]]--;
//tmp[L[j]]表示L中剩余的元素中小于等于L[j]的元素的个数
}
for(j=0;j<n;j++) L[j] = R[j];
}6、基数排序
//基数排序
void printArray( const int Array[], const int arraySize );
int getDigit(int num, int dig);
const int radix=10; //基数
void RadixSort(int L[], int left, int right, int d){
//MSD排序算法的实现。从高位到低位对序列划分,实现排序。d是第几位数,d=1是最低位。left和right是待排序元素子序列的始端与尾端。
int i, j, count[radix], p1, p2;
int *auxArray;
int M = 5;
auxArray = new int[right-left+1];
if (d<=0) return; //位数处理完递归结束
if (right-left+1<M){//对于小序列可调用直接插入排序
InsertionSort(L,left,right); return;
}
for (j=0; j<radix; j++) count[j]=0;
for (i=left; i<=right; i++) //统计各桶元素的存放位置
count[getDigit(L[i],d)]++;
for (j=1; j<radix; j++) //安排各桶元素的存放位置
count[j]=count[j]+count[j-1];
for (i=right; i>=left; i--){ //将待排序序列中的元素按位置分配到各个桶中,存于助数组auxArray中
j=getDigit(L[i],d); //取元素L[i]第d位的值
auxArray[count[j]-1]=L[i]; //按预先计算位置存放
count[j]--; //计数器减1
}
for (i=left, j=0; i<=right; i++, j++)
L[i]=auxArray[j]; //从辅助数组顺序写入原数组
delete []auxArray;
for (j=0; j<radix; j++){ //按桶递归对d-1位处理
p1=count[j]+left; //取桶始端,相对位置,需要加上初值$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$
(j+1 <radix )?(p2=count[j+1]-1+left):(p2=right) ; //取桶尾端
// delete []count;
if(p1<p2){
RadixSort(L, p1, p2, d-1); //对桶内元素进行基数排序
// printArray(L,10);
}
}
}
int getDigit(int num, int dig)
{
int myradix = 1;
/* for(int i = 1;i<dig;i++)
{
myradix *= radix;
}*/
switch(dig)
{
case 1:
myradix = 1;
break;
case 2:
myradix = 10;
break;
case 3:
myradix = 1000;
break;
case 4:
myradix = 10000;
break;
default:
myradix = 1;
break;
}
return (num/myradix)%radix;
}7、堆排序
//使用时注意将关键码加入
#ifndef MINHEAP_H
#define MINHEAP_H
#include <assert.h>
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::cerr;
#include <stdlib.h>
//const int maxPQSize = 50;
template <class Type> class MinHeap {
public:
MinHeap ( int maxSize );//根据最大长度建堆
MinHeap ( Type arr[], int n );//根据数组arr[]建堆
~MinHeap ( ) { delete [] heap; }
const MinHeap<Type> & operator = ( const MinHeap &R );//重载赋值运算符
int Insert ( const Type &x );//插入元素
int RemoveMin ( Type &x );//移除关键码最小的元素,并赋给x
int IsEmpty ( ) const { return CurrentSize == 0; }//检查堆是否为空
int IsFull ( ) const { return CurrentSize == MaxHeapSize; }//检查对是否满
void MakeEmpty ( ) { CurrentSize = 0; }//使堆空
private:
enum { DefaultSize = 50 };//默认堆的大小
Type *heap;
int CurrentSize;
int MaxHeapSize;
void FilterDown ( int i, int m );//自上向下调整堆
void FilterUp ( int i );//自下向上调整堆
};
template <class Type> MinHeap <Type>::MinHeap ( int maxSize )
{
//根据给定大小maxSize,建立堆对象
MaxHeapSize = (DefaultSize < maxSize ) ? maxSize : DefaultSize; //确定堆大小
heap = new Type [MaxHeapSize]; //创建堆空间
CurrentSize = 0; //初始化
}
template <class Type> MinHeap <Type>::MinHeap ( Type arr[], int n )
{
//根据给定数组中的数据和大小,建立堆对象
MaxHeapSize = DefaultSize < n ? n : DefaultSize;
heap = new Type [MaxHeapSize];
if(heap==NULL){cerr <<"fail" <<endl;exit(1);}
for(int i =0; i< n; i++)
heap[i] = arr[i]; //数组传送
CurrentSize = n; //当前堆大小
int currentPos = (CurrentSize-2)/2; //最后非叶
while ( currentPos >= 0 ) {
//从下到上逐步扩大,形成堆
FilterDown ( currentPos, CurrentSize-1 );
currentPos-- ;
//从currentPos开始,到0为止, 调整currentPos--; }
}
}
template <class Type> void MinHeap<Type>::FilterDown ( const int start, const int EndOfHeap )
{
// 结点i的左、右子树均为堆,调整结点i
int i = start, j = 2*i+1; // j 是 i 的左子女
Type temp = heap[i];
while ( j <= EndOfHeap ) {
if ( j < EndOfHeap && heap[j] > heap[j+1] )
j++;//两子女中选小者
if ( temp<= heap[j] ) break;
else { heap[i] = heap[j]; i = j; j = 2*j+1; }
}
heap[i] = temp;
}
template <class Type> int MinHeap<Type>::Insert ( const Type &x )
{
//在堆中插入新元素 x
if ( CurrentSize == MaxHeapSize ) //堆满
{
cout << "堆已满" << endl; return 0;
}
heap[CurrentSize] = x; //插在表尾
FilterUp (CurrentSize); //向上调整为堆
CurrentSize++; //堆元素增一
return 1;
}
template <class Type> void MinHeap<Type>::FilterUp ( int start )
{
//从 start 开始,向上直到0,调整堆
int j = start, i = (j-1)/2; // i 是 j 的双亲
Type temp = heap[j];
while ( j > 0 ) {
if ( (heap[i].root->data.key )<= (temp.root->data.key) ) break;
else { heap[j] = heap[i]; j = i; i = (i -1)/2; }
}
heap[j] = temp;
}
template <class Type> int MinHeap <Type>::RemoveMin ( Type &x )
{
if ( !CurrentSize )
{
cout << "堆已空 " << endl;
return 0;
}
x = heap[0]; //最小元素出队列
heap[0] = heap[CurrentSize-1];
CurrentSize--; //用最小元素填补
FilterDown ( 0, CurrentSize-1 );
//从0号位置开始自顶向下调整为堆
return 1;
}
#endif性能测试程序:
#include<iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include<iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::ios;
using std::cerr;
using std::endl;
#include<iomanip>
using std::setw;
using std::fixed;
#include<fstream>
using std::ifstream;
using std::ofstream;
using std::flush;
#include<string>
using std::string;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include"minheap.h"
void BubbleSort(int arr[], int size);//冒泡排序
void QuickSort( int A[], int startingsub, int endingsub);//快速排序
void InsertionSort ( int L[], const int begin,const int n);//插入排序
void Shellsort( int L[], const int left, const int right);//希尔排序
void CountingSort( int L[], const int n );//计数排序
int getDigit(int num, int dig);//基数排序中获取第dig位的数字
void RadixSort(int L[], int left, int right, int d);//基数排序
void printArray( const int Array[], const int arraySize );//输出数组
int main()
{
clock_t start, finish;
double duration;
/* 测量一个事件持续的时间*/
ofstream *ofs;
string fileName = "sortResult.txt";
ofs = new ofstream(fileName.c_str(),ios::out|ios::app);
const int size = 100000;
int a[size];
int b[size];
srand(time(0));
ofs->close();
for(int i = 0; i < 20;i++)
{
ofs->open(fileName.c_str(),ios::out|ios::app);
if( ofs->fail()){
cout<<"!!";
ofs->close();
}
for(int k =0; k <size;k++)
{
a[k] = rand()%1000;
b[k] = a[k];
}
/* for( k =0; k <size;k++)
{
a[k] = k;
b[k] = a[k];
} */
//printArray(a,size);
//计数排序
for( k =0; k <size;k++)
{
a[k] = b[k];
}
start = clock();
CountingSort(a,size);
finish = clock();
// printArray(a,size);
duration = (double)(finish - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf( "%s%f secondsn", "计数排序:",duration );
*ofs<<"第"<<i<<"次:n " <<"排序内容:0~999共" << size << " 个整数n" ;
*ofs<<"第"<<i<<"次计数排序:n " <<" Time: " <<fixed<< duration << " secondsn";
//基数排序
for( k =0; k <size;k++)
{
a[k] = b[k];
}
start = clock();
RadixSort(a, 0,size-1, 3);
finish = clock();
// printArray(a,size);
duration = (double)(finish - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf( "%s%f secondsn", "基数排序:",duration );
*ofs<<"第"<<i<<"次基数排序:n " <<" Time: " << duration << " secondsn";
//堆排序
MinHeap<int> mhp(a,size);
start = clock();
for( k =0; k <size;k++)
{
mhp.RemoveMin(a[k]);
}
finish = clock();
// printArray(a,size);
duration = (double)(finish - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf( "%s%f secondsn", "堆排序:",duration );
*ofs<<"第"<<i<<"次堆排序:n " <<" Time: " << duration << " secondsn";
//快速排序
for( k =0; k <size;k++)
{
a[k] = b[k];
}
//printArray(a,size);
start = clock();
QuickSort(a,0,size-1);
finish = clock();
// printArray(a,size);
duration = (double)(finish - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf( "%s%f secondsn", "快速排序:",duration );
*ofs<<"第"<<i<<"次快速排序:n " <<" Time: " << duration << " secondsn";
//希尔排序
for( k =0; k <size;k++)
{
a[k] = b[k];
}
start = clock();
Shellsort(a,0,size-1);
finish = clock();
// printArray(a,size);
duration = (double)(finish - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf( "%s%f secondsn", "希尔排序:",duration );
*ofs<<"第"<<i<<"次希尔排序:n " <<" Time: " << duration << " secondsn";
//插入排序
for( k =0; k <size;k++)
{
a[k] = b[k];
}
start = clock();
InsertionSort (a,0,size-1);
finish = clock();
// printArray(a,size);
duration = (double)(finish - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf( "%s%f secondsn", "插入排序:",duration );
*ofs<<"第"<<i<<"次插入排序:n " <<" Time: " << duration << " secondsn";
//冒泡排序
for( k =0; k <size;k++)
{
a[k] = b[k];
}
start = clock();
BubbleSort(a,size);
finish = clock();
// printArray(a,size);
duration = (double)(finish - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf( "%s%f secondsn", "冒泡排序:",duration );
*ofs<<"第"<<i<<"次冒泡排序:n " <<" Time: " << duration << " secondsn";
ofs->close();
}
return 0;
}
void printArray( const int Array[], const int arraySize )
{
for( int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++ ) {
cout << Array[ i ] << " ";
if ( i % 20 == 19 )
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}性能仿真:
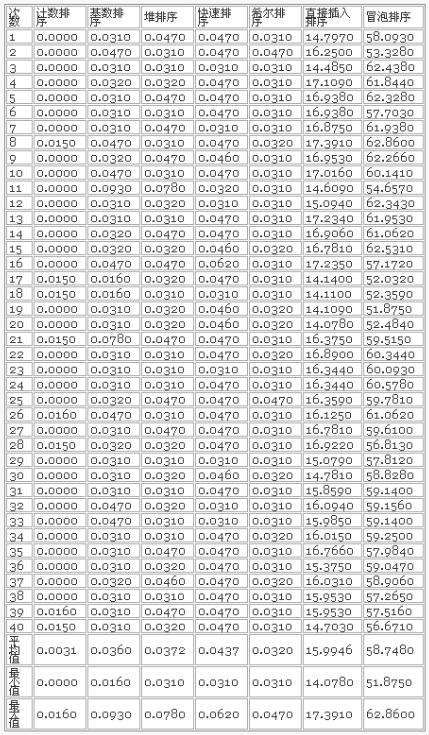
(排序内容:从0~999中随机产生,共100000 个整数,该表中单位为秒)






















 1247
1247











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








