java集合框架之Collection
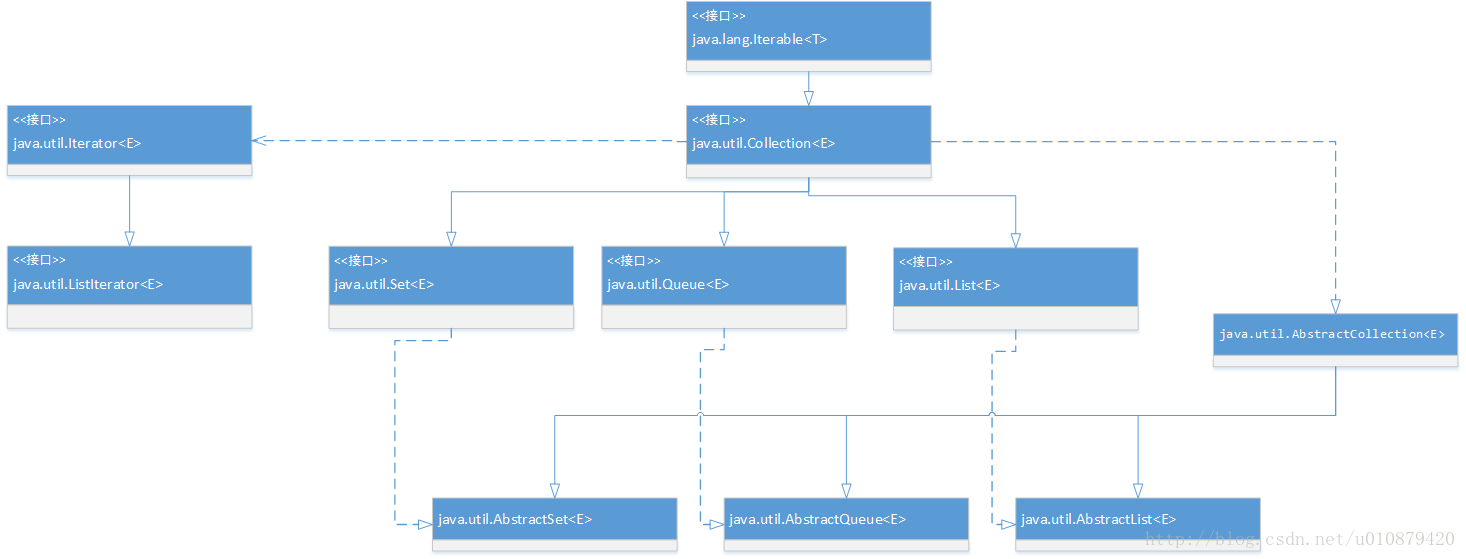
1.类图
List和Set都是接口,它们都继承自Collection。List是有序的队列,可以有重复的元素;set不能有重复的元素。
为了方便,抽象出了AbstractCollection类,让其他类继承,该类实现了Collection中的绝大部分方法。AbstractList、AbstractSet、AbstractQueue都继承自AbstractCollection。
Collection中有iterator()方法,作用是返回一个iterator接口,通过iterator迭代器遍历集合。ListIterator是List接口所特有的。
2.Collection
collection定义如下:
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>Collection接口的所有子类都必须实现两种构造函数:不带参数的和参数为Collection的构造函数。带参数的构造函数可以用来转换Collection类型。
//Collection的Api
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
Iterator<E> iterator();
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
boolean add(E e);
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
void clear();
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
/**
下面的函数从jdk1.8开始支持
@since 1.8
**/
default boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
boolean removed = false;
final Iterator<E> each = iterator();
while (each.hasNext()) {
if (filter.test(each.next())) {
each.remove();
removed = true;
}
}
return removed;
}
@Override
default Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, 0);
}
default Stream<E> stream() {
return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);
}
default Stream<E> parallelStream() {
return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), true);
}3.List
list代码实现
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {}//Collection集合API
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
Iterator<E> iterator();
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
boolean add(E e);
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
void clear();
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
//相比Collection,list新增的API
E get(int index); //获取指定位置的元素
E set(int index, E element); //修改指定位置的元素
void add(int index, E element); //添加元素到指定位置
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c);//在指定位置添加其他集合中的元素
E remove(int index);//删除指定位置的元素
int indexOf(Object o); //获取指定元素的索引
int lastIndexOf(Object o); //获取指定元素从右边的索引
ListIterator<E> listIterator(); //获得Iterator
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index);
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex);//获取子List
/**
下面的函数从jdk1.8开始支持
@since 1.8
**/
default void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final ListIterator<E> li = this.listIterator();
while (li.hasNext()) {
li.set(operator.apply(li.next()));
}
}
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
default void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
Object[] a = this.toArray();
Arrays.sort(a, (Comparator) c);
ListIterator<E> i = this.listIterator();
for (Object e : a) {
i.next();
i.set((E) e);
}
}
@Override
default Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}4.set
set实现代码
public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E>{}set也继承自Collection接口,且里面不能有重复元素。关于API,set与Collection的API完全一样。。。
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
Iterator<E> iterator();
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
boolean add(E e);
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
void clear();
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
@Override
default Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.DISTINCT);
}5.AbstractCollection
AbstracCollection实现代码
public abstract class AbstractCollection<E> implements Collection<E> {}AbstractCollection是一个抽象类,实现了collection中除了iterator()和size()之外的所有方法。
public abstract class AbstractCollection<E> implements Collection<E> {
protected AbstractCollection() {
}
//******Query Operations ********************//
//iterator()和size()方法未实现
public abstract Iterator<E> iterator();
public abstract int size();
//判断集合是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0; //判断集合大小是否为0
}
//检查集合中是否包含指定元素
public boolean contains(Object o) {
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
if (o==null) {//可以看出,任何非空集合都包含null
while (it.hasNext())
if (it.next()==null)
return true;
} else {
while (it.hasNext())
if (o.equals(it.next()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
//将集合转变为数组
public Object[] toArray() {
// Estimate size of array; be prepared to see more or fewer elements
Object[] r = new Object[size()]; //定义一个数组,大小为集合的大小
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {
if (! it.hasNext()) // fewer elements than expected
return Arrays.copyOf(r, i);
r[i] = it.next();
}
return it.hasNext() ? finishToArray(r, it) : r;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
// Estimate size of array; be prepared to see more or fewer elements
int size = size();
T[] r = a.length >= size ? a :
(T[])java.lang.reflect.Array
.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {
if (! it.hasNext()) { // fewer elements than expected
if (a == r) {
r[i] = null; // null-terminate
} else if (a.length < i) {
return Arrays.copyOf(r, i);
} else {
System.arraycopy(r, 0, a, 0, i);
if (a.length > i) {
a[i] = null;
}
}
return a;
}
r[i] = (T)it.next();
}
// more elements than expected
return it.hasNext() ? finishToArray(r, it) : r;
}
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static <T> T[] finishToArray(T[] r, Iterator<?> it) {
int i = r.length;
while (it.hasNext()) {
int cap = r.length;
if (i == cap) {
int newCap = cap + (cap >> 1) + 1;
// overflow-conscious code
if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCap = hugeCapacity(cap + 1);
r = Arrays.copyOf(r, newCap);
}
r[i++] = (T)it.next();
}
// trim if overallocated
return (i == r.length) ? r : Arrays.copyOf(r, i);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError
("Required array size too large");
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
//******Modification Operations ********************//
public boolean add(E e) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//删除对象o
public boolean remove(Object o) {
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
if (o==null) {
while (it.hasNext()) {
if (it.next()==null) {
it.remove();
return true;
}
}
} else {
while (it.hasNext()) {
if (o.equals(it.next())) {
it.remove();
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//******Bulk Operations ********************//
//判断是否包含集合C中的所有元素
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
for (Object e : c)
if (!contains(e))
return false;
return true;
}
//添加集合C中所有元素
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
boolean modified = false;
for (E e : c)
if (add(e))
modified = true;
return modified;
}
//删除集合c中所有元素
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
boolean modified = false;
Iterator<?> it = iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
if (c.contains(it.next())) {
it.remove();
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* <p>This implementation iterates over this collection, checking each
* element returned by the iterator in turn to see if it's contained
* in the specified collection. If it's not so contained, it's removed
* from this collection with the iterator's <tt>remove</tt> method.
*/
//当前集合 指定集合C
//这个接口遍历整个集合,检测每个元素是否在指定集合C中,如果不存在就调用remove方法删除
//提示:两个集合的交集
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
boolean modified = false;
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
if (!c.contains(it.next())) {
it.remove();
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
}
//清空集合
public void clear() {
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
it.next();
it.remove();
}
}
//将集合元素显示为[String]
// String conversion
public String toString() {
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
if (! it.hasNext())
return "[]";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
for (;;) {
E e = it.next();
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
if (! it.hasNext())
return sb.append(']').toString();
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
}
}6.AbstractList
AbstractList代码实现
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {}package java.util;
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {
protected AbstractList() {
}
//**************下面几个方法会在子类中进行实现**********************************//
public boolean add(E e) {
add(size(), e);
return true;
}
abstract public E get(int index);
public E set(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public E remove(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//***************Search Operations**************************************//
//搜索对象O的索引
public int indexOf(Object o) {
ListIterator<E> it = listIterator();
if (o==null) {
while (it.hasNext())
if (it.next()==null)//执行it.next(),会先返回it指向位置的值,然后it会移到下一个位置
return it.previousIndex();//所以要返回it.previousIndex()
} else {
while (it.hasNext())
if (o.equals(it.next()))
return it.previousIndex();
}
return -1;
}
//反向索引
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
ListIterator<E> it = listIterator(size());
if (o==null) {
while (it.hasPrevious())
if (it.previous()==null)
return it.nextIndex();
} else {
while (it.hasPrevious())
if (o.equals(it.previous()))
return it.nextIndex();
}
return -1;
}
// Bulk Operations
//清除集合 调用removeRange()函数移除指定位置的元素
public void clear() {
removeRange(0, size());
}
//给指定位置添加集合
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
boolean modified = false;
for (E e : c) {
add(index++, e); //add()方法会在子类中实现
modified = true;
}
return modified;
}
// Comparison and hashing
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (!(o instanceof List))
return false;
ListIterator<E> e1 = listIterator();
ListIterator<?> e2 = ((List<?>) o).listIterator();
while (e1.hasNext() && e2.hasNext()) {
E o1 = e1.next();
Object o2 = e2.next();
if (!(o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2)))
return false;
}
return !(e1.hasNext() || e2.hasNext());
}
public int hashCode() {
int hashCode = 1;
for (E e : this)
hashCode = 31*hashCode + (e==null ? 0 : e.hashCode());
return hashCode;
}
//删除指定集合范围内的元素
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
ListIterator<E> it = listIterator(fromIndex);
for (int i=0, n=toIndex-fromIndex; i<n; i++) {
it.next();
it.remove();
}
}
//********************************迭代器*************************//
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr(); //内部类
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return listIterator(0);
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
/**
* Index of element to be returned by subsequent call to next.
*/
int cursor = 0;
/**
* Index of element returned by most recent call to next or
* previous. Reset to -1 if this element is deleted by a call
* to remove.
*/
int lastRet = -1;
/**
* The modCount value that the iterator believes that the backing
* List should have. If this expectation is violated, the iterator
* has detected concurrent modification.
*/
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size();
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
E next = get(i);
lastRet = i;
cursor = i + 1;
return next;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
checkForComodification();
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet);
if (lastRet < cursor)
cursor--;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor - 1;
E previous = get(i);
lastRet = cursor = i;
return previous;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
checkForComodification();
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor-1;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
AbstractList.this.set(lastRet, e);
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
AbstractList.this.add(i, e);
lastRet = -1;
cursor = i + 1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return (this instanceof RandomAccess ?
new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex) :
new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex));
}
/**
* The number of times this list has been <i>structurally modified</i>.
记录集合被修改次数
*/
protected transient int modCount = 0;
//添加元素之前,检测添加的索引是否合法
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
//拼接索引越界消息
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size();
}
}
//**************************子列表SubList***********************************//
class SubList<E> extends AbstractList<E> {
private final AbstractList<E> l;
private final int offset;
private int size;
//当需要获取一个List时,底层并不是真正的返回一个子list 还是原来的list,
//只不过在操作时,索引全部限定在用户所需的子List部分而已
SubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);
if (toIndex > list.size())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);
if (fromIndex > toIndex)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
l = list; //原封不动的将原来的list赋值给l
offset = fromIndex; //偏移量
size = toIndex - fromIndex; //子LIST的大小
this.modCount = l.modCount;
}
//注:下面所有的操作都在索引上加偏移量offset,相当于在原来的list的副本上操作子List
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
return l.set(index+offset, element);
}
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
return l.get(index+offset);
}
public int size() {
checkForComodification();
return size;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
checkForComodification();
l.add(index+offset, element);
this.modCount = l.modCount;
size++;
}
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E result = l.remove(index+offset);
this.modCount = l.modCount;
size--;
return result;
}
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
checkForComodification();
l.removeRange(fromIndex+offset, toIndex+offset);
this.modCount = l.modCount;
size -= (toIndex-fromIndex);
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
int cSize = c.size();
if (cSize==0)
return false;
checkForComodification();
l.addAll(offset+index, c);
this.modCount = l.modCount;
size += cSize;
return true;
}
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return listIterator();
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {
checkForComodification();
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListIterator<E>() {
private final ListIterator<E> i = l.listIterator(index+offset);
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex() < size;
}
public E next() {
if (hasNext())
return i.next();
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return previousIndex() >= 0;
}
public E previous() {
if (hasPrevious())
return i.previous();
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
public int nextIndex() {
return i.nextIndex() - offset;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return i.previousIndex() - offset;
}
public void remove() {
i.remove();
SubList.this.modCount = l.modCount;
size--;
}
public void set(E e) {
i.set(e);
}
public void add(E e) {
i.add(e);
SubList.this.modCount = l.modCount;
size++;
}
};
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
private void checkForComodification() {
if (this.modCount != l.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
class RandomAccessSubList<E> extends SubList<E> implements RandomAccess {
RandomAccessSubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
super(list, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
}
7.AbstractSet
AbstractSet的定义如下:
public abstract class AbstractSet<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Set<E> {}和AbstractCollection一样
8.Iterator
public interface Iterator<E> {}集合的迭代器,
API有:是否存在下一个元素、获取下一个元素、删除当前元素
注意:fail-fast机制
当某个线程A通过iterator去遍历某集合的过程中,若该集合的内容被其他线程改变了,那么线程A访问集合时,就会抛出CurrentModificationException异常,产生fail-fast事件
9.ListIterator
专门遍历list,提供前遍历和后遍历
注意
迭代器执行it.next(),会先返回it指向位置的值,然后it会移到下一个位置





















 804
804











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








