转自:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming/article/details/16871117
转帖请注明本文出自xiaanming的博客(http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming/article/details/17483273),请尊重他人的辛勤劳动成果,谢谢!
相信大家在平常的开发中,对网络的操作用到HTTP协议比较多,通过我们使用Get或者Post的方法调用一个数据接口,然后服务器给我们返回JSON格式的数据,我们解析JSON数据然后展现给用户,相信很多人很喜欢服务器给我们返回JSON数据格式,因为他解析方便,也有一些JSON的解析库,例如Google提供的GSON,阿里巴巴的FastJson,不过还是推荐大家使用FastJson来解析,我自己开发中也是用FastJson来解析,FastJson的介绍http://code.alibabatech.com/wiki/display/FastJSON/Home,不过有时候我们用到WebService接口来获取数据, WebService是一种基于SOAP协议的远程调用标准,通过webservice可以将不同操作系统平台、不同语言、不同技术整合到一块。在Android SDK中并没有提供调用WebService的库,因此,需要使用第三方的SDK来调用WebService。PC版本的WEbservice客户端库非常丰富,例如Axis2,CXF等,但这些开发包对于Android系统过于庞大,也未必很容易移植到Android系统中。因此,这些开发包并不是在我们的考虑范围内。适合手机的WebService客户端的SDK有一些,比较常用的有Ksoap2,可以从http://code.google.com/p/ksoap2-android/wiki/HowToUse?tm=2进行下载,将jar包加入到libs目录下就行了,接下来带大家来调用WebService接口
首先我们新建一个工程,取名WebServiceDemo,我们从http://www.webxml.com.cn/zh_cn/web_services.aspx来获取WebService接口,这里面有一些免费的WebService接口,我们就用里面的天气接口吧http://www.webxml.com.cn/WebServices/WeatherWebService.asmx
我们新建一个WebService的工具类,用于对WebService接口的调用,以后遇到调用WebService直接拷贝来用就行了
- package com.example.webservicedemo;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- import java.util.Map;
- import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
- import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
- import org.ksoap2.SoapEnvelope;
- import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapObject;
- import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapSerializationEnvelope;
- import org.ksoap2.transport.HttpResponseException;
- import org.ksoap2.transport.HttpTransportSE;
- import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParserException;
- import android.os.Handler;
- import android.os.Message;
- /**
- * 访问WebService的工具类,
- *
- * @see http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming
- *
- * @author xiaanming
- *
- */
- public class WebServiceUtils {
- public static final String WEB_SERVER_URL = "http://www.webxml.com.cn/WebServices/WeatherWebService.asmx";
- // 含有3个线程的线程池
- private static final ExecutorService executorService = Executors
- .newFixedThreadPool(3);
- // 命名空间
- private static final String NAMESPACE = "http://WebXml.com.cn/";
- /**
- *
- * @param url
- * WebService服务器地址
- * @param methodName
- * WebService的调用方法名
- * @param properties
- * WebService的参数
- * @param webServiceCallBack
- * 回调接口
- */
- public static void callWebService(String url, final String methodName,
- HashMap<String, String> properties,
- final WebServiceCallBack webServiceCallBack) {
- // 创建HttpTransportSE对象,传递WebService服务器地址
- final HttpTransportSE httpTransportSE = new HttpTransportSE(url);
- // 创建SoapObject对象
- SoapObject soapObject = new SoapObject(NAMESPACE, methodName);
- // SoapObject添加参数
- if (properties != null) {
- for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = properties.entrySet()
- .iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
- Map.Entry<String, String> entry = it.next();
- soapObject.addProperty(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
- }
- }
- // 实例化SoapSerializationEnvelope,传入WebService的SOAP协议的版本号
- final SoapSerializationEnvelope soapEnvelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(
- SoapEnvelope.VER11);
- // 设置是否调用的是.Net开发的WebService
- soapEnvelope.setOutputSoapObject(soapObject);
- soapEnvelope.dotNet = true;
- httpTransportSE.debug = true;
- // 用于子线程与主线程通信的Handler
- final Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
- @Override
- public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
- super.handleMessage(msg);
- // 将返回值回调到callBack的参数中
- webServiceCallBack.callBack((SoapObject) msg.obj);
- }
- };
- // 开启线程去访问WebService
- executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- SoapObject resultSoapObject = null;
- try {
- httpTransportSE.call(NAMESPACE + methodName, soapEnvelope);
- if (soapEnvelope.getResponse() != null) {
- // 获取服务器响应返回的SoapObject
- resultSoapObject = (SoapObject) soapEnvelope.bodyIn;
- }
- } catch (HttpResponseException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- } catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- } finally {
- // 将获取的消息利用Handler发送到主线程
- mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(0,
- resultSoapObject));
- }
- }
- });
- }
- /**
- *
- *
- * @author xiaanming
- *
- */
- public interface WebServiceCallBack {
- public void callBack(SoapObject result);
- }
- }
我们通过调用里面的callWebService(String url, final String methodName,HashMap<String, String> properties,final WebServiceCallBack webServiceCallBack)就可以来获取我们想要的数据,现在讲解下里面的实现思路
- 创建HttpTransportsSE对象。通过HttpTransportsSE类的构造方法可以指定WebService的WSDL文档的URL
- 创建SoapObject对象,里面的参数分别是WebService的命名空间和调用方法名
- 设置调用方法的参数值,如果没有参数,就不设置,有参数的话调用SoapObject对象的addProperty(String name, Object value)方法将参数加入到SoapObject对象中
- 实例化SoapSerializationEnvelope,传入WebService的SOAP协议的版本号,将上面的SoapObject对象通过setOutputSoapObject(Object soapObject)设置到里面,并设置是否调用的是.Net开发的WebService和是否debug等信息
- 因为涉及到网络操作,所以我们使用了线程池来异步操作调用WebService接口,我们在线程中调用HttpTransportsSE对象的call(String soapAction, SoapEnvelope envelope)方法就能实现对WebService的调用,并且通过soapEnvelope.bodyIn获取WebService返回的信息,但是返回的信息是在子线程中,我们需要利用Handler来实现子线程与主线程进行转换,然后在Handler的handleMessage(Message msg)中将结果回调到callBack的参数中,总体思路就是这个样子,接下来我们来使用这个工具类吧
我们先用一个ListView来显示所有的省份,然后点击每个省进去到市。市也用一个ListView来显示,最后点击市用TextView来显示获取的WebService天气情况,思路很简单
用来显示省份的布局,里面只有一个ListView
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent" >
- <ListView
- android:id="@+id/province_list"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:cacheColorHint="@android:color/transparent"
- android:fadingEdge="none" >
- </ListView>
- </RelativeLayout>
- package com.example.webservicedemo;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.List;
- import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapObject;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.widget.AdapterView;
- import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
- import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
- import android.widget.ListView;
- import android.widget.Toast;
- import com.example.webservicedemo.WebServiceUtils.WebServiceCallBack;
- /**
- * 显示天气省份的Activity
- *
- * @see http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming
- *
- * @author xiaanming
- *
- */
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
- private List<String> provinceList = new ArrayList<String>();
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- init();
- }
- private void init() {
- final ListView mProvinceList = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.province_list);
- //显示进度条
- ProgressDialogUtils.showProgressDialog(this, "数据加载中...");
- //通过工具类调用WebService接口
- WebServiceUtils.callWebService(WebServiceUtils.WEB_SERVER_URL, "getSupportProvince", null, new WebServiceCallBack() {
- //WebService接口返回的数据回调到这个方法中
- @Override
- public void callBack(SoapObject result) {
- //关闭进度条
- ProgressDialogUtils.dismissProgressDialog();
- if(result != null){
- provinceList = parseSoapObject(result);
- mProvinceList.setAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(MainActivity.this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, provinceList));
- }else{
- Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "获取WebService数据错误", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
- }
- }
- });
- mProvinceList.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view,
- int position, long id) {
- Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, CityActivity.class);
- intent.putExtra("province", provinceList.get(position));
- startActivity(intent);
- }
- });
- }
- /**
- * 解析SoapObject对象
- * @param result
- * @return
- */
- private List<String> parseSoapObject(SoapObject result){
- List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
- SoapObject provinceSoapObject = (SoapObject) result.getProperty("getSupportProvinceResult");
- if(provinceSoapObject == null) {
- return null;
- }
- for(int i=0; i<provinceSoapObject.getPropertyCount(); i++){
- list.add(provinceSoapObject.getProperty(i).toString());
- }
- return list;
- }
- }
- package com.example.webservicedemo;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.List;
- import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapObject;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.widget.AdapterView;
- import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
- import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
- import android.widget.ListView;
- import android.widget.Toast;
- import com.example.webservicedemo.WebServiceUtils.WebServiceCallBack;
- /**
- * 显示城市的Activity
- *
- * @see http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming
- *
- * @author xiaanming
- *
- */
- public class CityActivity extends Activity {
- private List<String> cityStringList;
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- init();
- }
- private void init() {
- final ListView mCityList = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.province_list);
- //显示进度条
- ProgressDialogUtils.showProgressDialog(this, "数据加载中...");
- //添加参数
- HashMap<String, String> properties = new HashMap<String, String>();
- properties.put("byProvinceName", getIntent().getStringExtra("province"));
- WebServiceUtils.callWebService(WebServiceUtils.WEB_SERVER_URL, "getSupportCity", properties, new WebServiceCallBack() {
- @Override
- public void callBack(SoapObject result) {
- ProgressDialogUtils.dismissProgressDialog();
- if(result != null){
- cityStringList = parseSoapObject(result);
- mCityList.setAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(CityActivity.this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, cityStringList));
- }else{
- Toast.makeText(CityActivity.this, "获取WebService数据错误", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
- }
- }
- });
- mCityList.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view,
- int position, long id) {
- Intent intent = new Intent(CityActivity.this, WeatherActivity.class);
- intent.putExtra("city", cityStringList.get(position));
- startActivity(intent);
- }
- });
- }
- /**
- * 解析SoapObject对象
- * @param result
- * @return
- */
- private List<String> parseSoapObject(SoapObject result){
- List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
- SoapObject provinceSoapObject = (SoapObject) result.getProperty("getSupportCityResult");
- for(int i=0; i<provinceSoapObject.getPropertyCount(); i++){
- String cityString = provinceSoapObject.getProperty(i).toString();
- list.add(cityString.substring(0, cityString.indexOf("(")).trim());
- }
- return list;
- }
- }
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
- <ScrollView
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
- <LinearLayout
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent" >
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/weather"
- android:textColor="#336598"
- android:textSize="16sp"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent" />
- </LinearLayout>
- </ScrollView>
- </RelativeLayout>
- package com.example.webservicedemo;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapObject;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- import android.widget.Toast;
- import com.example.webservicedemo.WebServiceUtils.WebServiceCallBack;
- /**
- * 显示天气的Activity
- *
- * @see http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming
- *
- * @author xiaanming
- *
- */
- public class WeatherActivity extends Activity{
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.weather_layout);
- init();
- }
- private void init() {
- final TextView mTextWeather = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.weather);
- ProgressDialogUtils.showProgressDialog(this, "数据加载中...");
- HashMap<String, String> properties = new HashMap<String, String>();
- properties.put("theCityName", getIntent().getStringExtra("city"));
- WebServiceUtils.callWebService(WebServiceUtils.WEB_SERVER_URL, "getWeatherbyCityName", properties, new WebServiceCallBack() {
- @Override
- public void callBack(SoapObject result) {
- ProgressDialogUtils.dismissProgressDialog();
- if(result != null){
- SoapObject detail = (SoapObject) result.getProperty("getWeatherbyCityNameResult");
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- for(int i=0; i<detail.getPropertyCount(); i++){
- sb.append(detail.getProperty(i)).append("\r\n");
- }
- mTextWeather.setText(sb.toString());
- }else{
- Toast.makeText(WeatherActivity.this, "获取WebService数据错误", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
- }
- }
- });
- }
- }
- <application
- android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
- android:label="@string/app_name"
- android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
- <activity
- android:name="com.example.webservicedemo.MainActivity"
- android:label="@string/title_activity_main" >
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
- </intent-filter>
- </activity>
- <activity android:name=".CityActivity"/>
- <activity android:name=".WeatherActivity"></activity>
- </application>
- <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>

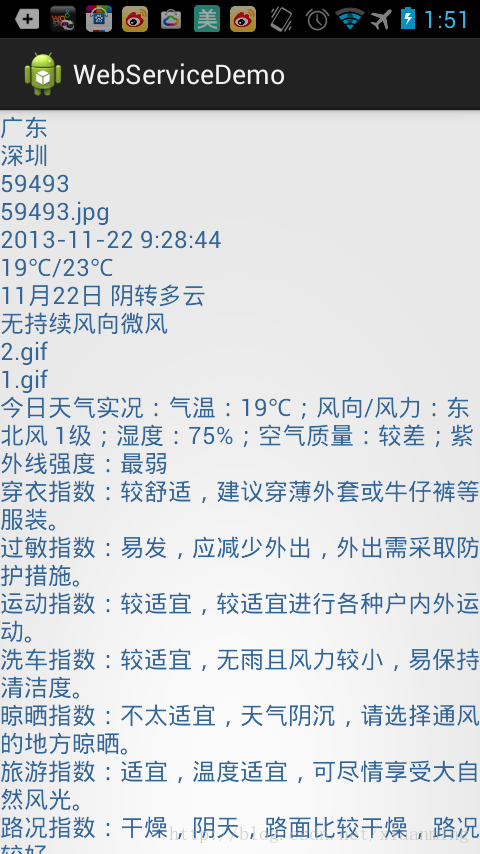
省份,城市列表可以加上A-Z的排序功能,可以参考下Android实现ListView的A-Z字母排序和过滤搜索功能,实现汉字转成拼音,我这里就不添加了,需要添加的朋友自行实现,好了,今天的讲解到此结束,有疑问的朋友请在下面留言。






















 158
158

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








