4,分发Event
4.1 System分发
流程长而杂,仅分析关键点,
dispatchOnceInnerLocked方法首先从mInboundQueue中取出KeyEntry,然后根据不同类型的KeyEntry分别进行处理。
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
•••
mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.dequeueAtHead();
•••
switch (mPendingEvent->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED: {
ConfigurationChangedEntry* typedEntry =
static_cast<ConfigurationChangedEntry*>(mPendingEvent);
done = dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked(currentTime, typedEntry);
dropReason = DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED; // configuration changes are never dropped
break;
}
case EventEntry::TYPE_DEVICE_RESET: {
DeviceResetEntry* typedEntry =
static_cast<DeviceResetEntry*>(mPendingEvent);
done = dispatchDeviceResetLocked(currentTime, typedEntry);
dropReason = DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED; // device resets are never dropped
break;
}
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
KeyEntry* typedEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(mPendingEvent);
if (isAppSwitchDue) {
if (isAppSwitchKeyEventLocked(typedEntry)) {
resetPendingAppSwitchLocked(true);
isAppSwitchDue = false;
} else if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_APP_SWITCH;
}
}
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED
&& isStaleEventLocked(currentTime, typedEntry)) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_STALE;
}
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED && mNextUnblockedEvent) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_BLOCKED;
}
done = dispatchKeyLocked(currentTime, typedEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
break;
}
case EventEntry::TYPE_MOTION: {
MotionEntry* typedEntry = static_cast<MotionEntry*>(mPendingEvent);
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED && isAppSwitchDue) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_APP_SWITCH;
}
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED
&& isStaleEventLocked(currentTime, typedEntry)) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_STALE;
}
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED && mNextUnblockedEvent) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_BLOCKED;
}
done = dispatchMotionLocked(currentTime, typedEntry,
&dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
break;
}
•••
}void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection) {
•••
switch (eventEntry->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
KeyEntry* keyEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(eventEntry);
// Publish the key event.
status = connection->inputPublisher.publishKeyEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,
keyEntry->deviceId, keyEntry->source,
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags,
keyEntry->keyCode, keyEntry->scanCode,
keyEntry->metaState, keyEntry->repeatCount, keyEntry->downTime,
keyEntry->eventTime);
break;
}
case EventEntry::TYPE_MOTION: {
•••
status = connection->inputPublisher.publishMotionEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,
motionEntry->deviceId, motionEntry->source,
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, motionEntry->actionButton,
dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags, motionEntry->edgeFlags,
motionEntry->metaState, motionEntry->buttonState,
xOffset, yOffset, motionEntry->xPrecision, motionEntry->yPrecision,
motionEntry->downTime, motionEntry->eventTime,
motionEntry->pointerCount, motionEntry->pointerProperties,
usingCoords);
break;
•••
}直接看最后的sendMessage方法,
status_t InputChannel::sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg) {
size_t msgLength = msg->size();
ssize_t nWrite;
do {
nWrite = ::send(mFd, msg, msgLength, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);
} while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
•••
}sendMessage方法调用系统的send()方法来发送输入消息,这样输入消息就通过socket从SystemServer进程传输到应用进程中了,那么应用进程在哪儿接收呢?
4.2 System分发原理
startDispatchCycleLocked根据方法的不同分别调用publishKeyEvent和publishMotionEvent方法,那么是谁的方法呢? 首先得弄清楚connection是什么对象,慢慢往回查看。
Connection 对象是dispatchEventLocked方法中获取的,
sp<Connection> connection = mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
prepareDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, &inputTarget);mConnectionsByFd只是一个Connection数组,什么时候添加Connection呢?
KeyedVector<int, sp<Connection> > mConnectionsByFd;sp<Connection> connection = new Connection(inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);
int fd = inputChannel->getFd();
mConnectionsByFd.add(fd, connection);现在确定了 connection 就是Connection对象。
InputPublisher inputPublisher;inputPublisher 只是Connection 类中的一个变量。
Connection 是 InputDispatcher.h 中的内部类,而InputPublisher 是InputTransport.h 中的内部类,这扯着有点远。
还是顺藤摸瓜, 首先看InputDispatcher.cpp 中Connection 的构造函数,
InputDispatcher::Connection::Connection(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, bool monitor) :
status(STATUS_NORMAL), inputChannel(inputChannel), inputWindowHandle(inputWindowHandle),
monitor(monitor),
inputPublisher(inputChannel), inputPublisherBlocked(false) {
}Connection 构造函数中又调用了inputPublisher的构造函数,
InputPublisher::InputPublisher(const sp<InputChannel>& channel) :
mChannel(channel) {
}sp<InputChannel> mChannel;mChannel只是InputPublisher的一个变量,至此,我们总算知道到底调用谁的publishKeyEvent和publishMotionEvent方法了, 非InputPublisher莫属。
先暂停一下,那么registerInputChannel是如何调用的呢?完整的流程图如下:
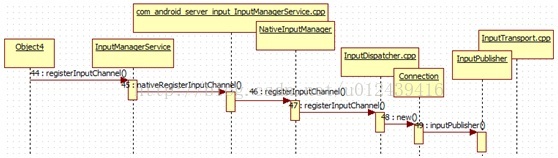
IMS中registerInputChannel方法如下,
public void registerInputChannel(InputChannel inputChannel,
InputWindowHandle inputWindowHandle) {
if (inputChannel == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("inputChannel must not be null.");
}
nativeRegisterInputChannel(mPtr, inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, false);
}还有monitorInput方法,
public InputChannel monitorInput(String inputChannelName) { // 显示器
if (inputChannelName == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("inputChannelName must not be null.");
}
InputChannel[] inputChannels = InputChannel.openInputChannelPair(inputChannelName);
nativeRegisterInputChannel(mPtr, inputChannels[0], null, true);
inputChannels[0].dispose(); // don't need to retain the Java object reference
return inputChannels[1];
}在nativeRegisterInputChannel方法中,
static void nativeRegisterInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,
jlong ptr, jobject inputChannelObj, jobject inputWindowHandleObj, jboolean monitor) {
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env,
inputChannelObj);
if (inputChannel == NULL) {
throwInputChannelNotInitialized(env);
return;
}
sp<InputWindowHandle> inputWindowHandle =
android_server_InputWindowHandle_getHandle(env, inputWindowHandleObj);
status_t status = im->registerInputChannel(
env, inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);
if (status) {
String8 message;
message.appendFormat("Failed to register input channel. status=%d", status);
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, message.string());
return;
}
if (! monitor) {
android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback(env, inputChannelObj,
handleInputChannelDisposed, im);
}
}看到了吧,将Java层的InputChannel, InputWindowHandle分别和C/C++层的NativeInputChannel等相对应。
sp<InputChannel> android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jobject inputChannelObj) {
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel =
android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, inputChannelObj);
return nativeInputChannel != NULL ? nativeInputChannel->getInputChannel() : NULL;
}static NativeInputChannel* android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(JNIEnv* env,
jobject inputChannelObj) {
jlong longPtr = env->GetLongField(inputChannelObj, gInputChannelClassInfo.mPtr);
return reinterpret_cast<NativeInputChannel*>(longPtr);
}首先利用本java层的InputChannel 创建NativeInputChannel,然后返回其内部变量InputChannel,这个有点绕。
C/C++层的 InputChannel类是InputTransport.cpp的一个内部类。
现在的问题有2个,
1, registerInputChannel/ monitorInput一般什么时候调用?
2, InputChannel 还未露出真身。






















 970
970

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








