给一些电路上的两个点和这两个点之间最少要通过的电流,要求正极到负极间的流量再满足条件的情况下最少
有源汇点上下界最小流:
建图:
设原源汇点 s,t 建立超级源汇点S,T先不连接 t-->s 像无源汇点可行流判断一样的建图,对S,T跑一遍最大流,记录流量f1。。。 连接源汇点 t--->s 无下界,上界INF ....再对S,T跑一遍最大流,得到流量f2。。。
如果 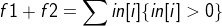
否则无解
Crazy Circuits
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 520 Accepted Submission(s): 262
Problem Description
You’ve just built a circuit board for your new robot, and now you need to power it. Your robot circuit consists of a number of electrical components that each require a certain amount of current to operate. Every component has a + and a - lead, which are connected on the circuit board at junctions. Current flows through the component from + to - (but note that a component does not "use up" the current: everything that comes in through the + end goes out the - end).
The junctions on the board are labeled 1, ..., N, except for two special junctions labeled + and - where the power supply terminals are connected. The + terminal only connects + leads, and the - terminal only connects - leads. All current that enters a junction from the - leads of connected components exits through connected + leads, but you are able to control how much current flows to each connected + lead at every junction (though methods for doing so are beyond the scope of this problem 1). Moreover, you know you have assembled the circuit in such a way that there are no feedback loops (components chained in a manner that allows current to flow in a loop).

Figure 1: Examples of two valid circuit diagrams.
In (a), all components can be powered along directed paths from the positive terminal to the negative terminal.
In (b), components 4 and 6 cannot be powered, since there is no directed path from junction 4 to the negative terminal.
In the interest of saving power, and also to ensure that your circuit does not overheat, you would like to use as little current as possible to get your robot to work. What is the smallest amount of current that you need to put through the + terminal (which you can imagine all necessarily leaving through the - terminal) so that every component on your robot receives its required supply of current to function?
The junctions on the board are labeled 1, ..., N, except for two special junctions labeled + and - where the power supply terminals are connected. The + terminal only connects + leads, and the - terminal only connects - leads. All current that enters a junction from the - leads of connected components exits through connected + leads, but you are able to control how much current flows to each connected + lead at every junction (though methods for doing so are beyond the scope of this problem 1). Moreover, you know you have assembled the circuit in such a way that there are no feedback loops (components chained in a manner that allows current to flow in a loop).

In (a), all components can be powered along directed paths from the positive terminal to the negative terminal.
In (b), components 4 and 6 cannot be powered, since there is no directed path from junction 4 to the negative terminal.
In the interest of saving power, and also to ensure that your circuit does not overheat, you would like to use as little current as possible to get your robot to work. What is the smallest amount of current that you need to put through the + terminal (which you can imagine all necessarily leaving through the - terminal) so that every component on your robot receives its required supply of current to function?
Hint
1 For those who are electronics-inclined, imagine that you have the ability to adjust the potential on any componentwithout altering its current requirement, or equivalently that there is an accurate variable potentiometer connected in series with each component that you can adjust. Your power supply will have ample potential for the circuit.
Input
The input file will contain multiple test cases. Each test case begins with a single line containing two integers:
N (0 <=
N <= 50), the number of junctions not including the positive and negative terminals, and
M (1 <=
M <= 200), the number of components in the circuit diagram. The next
M lines each contain a description of some component in the diagram. The
i
th component description contains three fields:
pi, the positive junction to which the component is connected,
ni, the negative junction to which the component is connected, and an integer
Ii (1 <=
Ii <= 100), the minimum amount of current required for component
i to function. The junctions
pi and
niare specified as either the character '+' indicating the positive terminal, the character '-' indicating the negative terminal, or an integer (between 1 and
N) indicating one of the numbered junctions. No two components have the same positive junction and the same negative junction. The end-of-file is denoted by an invalid test case with
N =
M = 0 and should not be processed.
Output
For each input test case, your program should print out either a single integer indicating the minimum amount of current that must be supplied at the positive terminal in order to ensure that every component is powered, or the message "
impossible" if there is no way to direct a sufficient amount of current to each component simultaneously.
Sample Input
6 10 + 1 1 1 2 1 1 3 2 2 4 5 + - 1 4 3 2 3 5 5 4 6 2 5 - 1 6 5 3 4 6 + 1 8 1 2 4 1 3 5 2 4 6 3 - 1 3 4 3 0 0
Sample Output
9 impossible
Source
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=50500;
const int maxm=1010000;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
struct Edge
{
int to,next,cap,flow;
}edge[maxm];
int Size,Adj[maxn];
int gap[maxn],dep[maxn],pre[maxn],cur[maxn];
void init()
{
Size=0; memset(Adj,-1,sizeof(Adj));
}
void addedge(int u,int v,int w,int rw=0)
{
edge[Size].to=v; edge[Size].cap=w; edge[Size].next=Adj[u];
edge[Size].flow=0; Adj[u]=Size++;
edge[Size].to=u; edge[Size].cap=rw; edge[Size].next=Adj[v];
edge[Size].flow=0; Adj[v]=Size++;
}
int sap(int start,int end,int N)
{
memset(gap,0,sizeof(gap));
memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep));
memcpy(cur,Adj,sizeof(Adj));
int u=start;
pre[u]=-1; gap[0]=N;
int ans=0;
while(dep[start]<N)
{
if(u==end)
{
int Min=INF;
for(int i=pre[u];~i;i=pre[edge[i^1].to])
if(Min>edge[i].cap-edge[i].flow)
Min=edge[i].cap-edge[i].flow;
for(int i=pre[u];~i;i=pre[edge[i^1].to])
{
edge[i].flow+=Min;
edge[i^1].flow-=Min;
}
u=start;
ans+=Min;
continue;
}
bool flag=false;
int v;
for(int i=cur[u];~i;i=edge[i].next)
{
v=edge[i].to;
if(edge[i].cap-edge[i].flow&&dep[v]+1==dep[u])
{
flag=true;
cur[u]=pre[v]=i;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
{
u=v;
continue;
}
int Min=N;
for(int i=Adj[u];~i;i=edge[i].next)
{
if(edge[i].cap-edge[i].flow&&dep[edge[i].to]<Min)
{
Min=dep[edge[i].to];
cur[u]=i;
}
}
gap[dep[u]]--;
if(!gap[dep[u]]) return ans;
dep[u]=Min+1;
gap[dep[u]]++;
if(u!=start) u=edge[pre[u]^1].to;
}
return ans;
}
int n,m;
int getInt()
{
int ret=0;
char ch;
bool ok=false;
while(ch=getchar())
{
if(ch=='-'||ch=='+'||(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'))
{
if(ch=='+') return 0;
else if(ch=='-') return n+1;
else
{
ok=true;
ret=ret*10+(ch-'0');
}
}
else if(ok==true)
{
break;
}
}
return ret;
}
int in[maxn];
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
if(n==0&&m==0) break;
init(); memset(in,0,sizeof(in));
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int u=getInt();
int v=getInt();
int w=getInt();
addedge(u,v,INF);
in[u]-=w;in[v]+=w;
}
int sum=0;
// Super S n+2 Super T n+3
for(int i=0;i<n+2;i++)
{
if(in[i]>0)
{
sum+=in[i];
addedge(n+2,i,in[i]);
}
if(in[i]<0) addedge(i,n+3,-in[i]);
}
int MaxFlow1=sap(n+2,n+3,n+4);
addedge(n+1,0,INF);
int MaxFlow2=sap(n+2,n+3,n+4);
if(MaxFlow1+MaxFlow2==sum)
{
printf("%d\n",edge[Size-2].flow);
}
else puts("impossible");
}
return 0;
}
























 506
506

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








