GCD Array
Time Limit: 11000/5500 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 856 Accepted Submission(s): 209
Maintain an array a with index from 1 to l. There are two kinds of operations:
1. Add v to a x for every x that gcd(x,n)=d.
2. Query
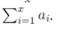
For each test case, the first line contains two integers l,Q(1<=l,Q<=5*10^4), indicating the length of the array and the number of the operations.
In following Q lines, each line indicates an operation, and the format is "1 n d v" or "2 x" (1<=n,d,v<=2*10^5,1<=x<=l).
Then output the answer to each query.
6 4 1 4 1 2 2 5 1 3 3 3 2 3 0 0
Case #1: 6 7
2014 Multi-University Training Contest 8
题意:首先给你n个数,这n个数刚开始都是0,然后你有两种操作:
1.告诉你y,d,v,然后你要让每个gcd(x,y)=d的ax加上v。
2.告诉你x,求a1+a2+..+ax的和。
首先根据莫比乌斯反演的两个公式。
以及另一种写法F(n)=E(n|d)f(d)
和f(n)=E(n|d)u(d/n)F(d)
这道题要让gcd(x,y)=d的ax加上v,那么如何运用莫比乌斯反演呢
首先设F(d)为d|gcd(x,y)的对数
f(d)为gcd(x,y)=d的对数
那么发现满足另一种写法的第一个式子
于是f(n)=E(n|d)u(d/n)F(d)
那么f(1)=E(d)u(d)F(d)
由于gcd(x,y)=d(1<=x<=n,y)
可以转化为gcd(x,y)=1(1<=x/d<=n,y/d)
这样f(n)=E(d)u(d)F(d),即改变函数的上下界
但这样求出的是x/d和y/d的gcd==1的x/d的位置,那么求出后x/d要乘以d才是x
然后发现每次将该位置的数字加上v,即x的倍数加上v,那么可以用树状数组来维护,更新时只让x加上v,x的倍数暂时不变化
对于1-d中多少个数是x的倍数,就是d/x。
那么只要判断查询内有多少个该数字的倍数,然后乘以v就是该数字的增长。
这里光这样还是不能解决这道题,要用到分块思想。考虑x处于[i,p/(p/i)]的范围时,该数字倍数的个数是相同的,那么可以合并同类项。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
#define CLR(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 200000+20;
bool check[N];
int mu[N],prime[N];
vector<int> fac[N];
LL f[N];
int l,q;
void Mobius()
{
CLR(check, 0);
mu[1] = 1;
int tot = 0;
for(int i = 2; i < N ; i++){
if(!check[i]){
prime[tot ++] = i;
mu[i] = -1;
}
for(int j = 0 ;j < tot; j ++){
if(i * prime[j] >= N)break;
check[i * prime[j]] = true;
if(i % prime[j] == 0){
mu[i * prime[j]] = 0;
break;
}else{
mu[i * prime[j]] = -mu[i];
}
}
}
for(int i = 1 ;i < N ; i++){
for(int j = i ; j < N ; j += i){
fac[j].push_back(i);
}
}
}
inline LL sum(int p){
LL s = 0;
while(p > 0){
s += f[p];
p -= p & (-p);
}
return s;
}
inline void add(int p,int v){
while(p <= l){
f[p] += v;
p += (p) & (-p);
}
}
void update(int n,int d,int v){
if(n % d != 0)return;
n = n/d;
for(int i = 0 ;i < fac[n].size() ; i++){
int q = fac[n][i];
add(q * d, v * mu[q]);
}
}
LL query(int p)
{
LL ans = 0;
for(int i = 1,last = i ; i <= p ; i = last + 1){
last = p/(p/i);
ans += (LL)(p/i) * (sum(last) - sum(i-1)) ;//分块
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
Mobius();
int cas = 0;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&l,&q)){
if(l == 0 && q == 0)break;
CLR(f, 0);
cas ++;
printf("Case #%d:\n",cas);
while(q--){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
if(t == 1){
int n,d,v;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&d,&v);
update(n, d, v);
}else{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
printf("%I64d\n",query(x));
}
}
}
return 0;
}






















 128
128

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








