对于图来说,邻接矩阵是不错的一种图存储结构,但是我们也发现,对于边数相对顶点较少的图,这种结构是存在对存储空间的极大浪费的。因此我们考虑另外一种存储结构方式:邻接表(Adjacency List),即数组与链表相结合的存储方法。
邻接表的处理方法是这样的。
1、图中顶点用一个一维数组存储,另外,对于顶点数组中,每个数据元素还需要存储指向第一个邻接点的指针,以便于查找该顶点的边信息。
2、图中每个顶点vi的所有邻接点构成一个线性表,由于邻接点的个数不定,所以用单链表存储,无向图称为顶点vi的边表,有向图称为顶点vi作为弧尾的出边表。
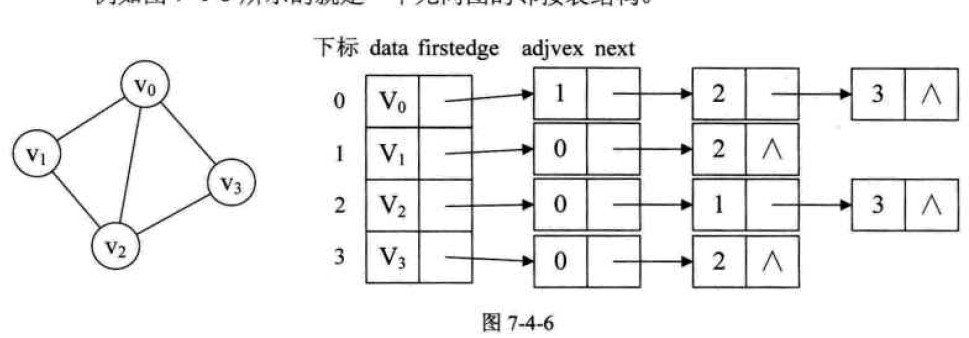
例如图7-4-6就是一个无向图的邻接表结构。
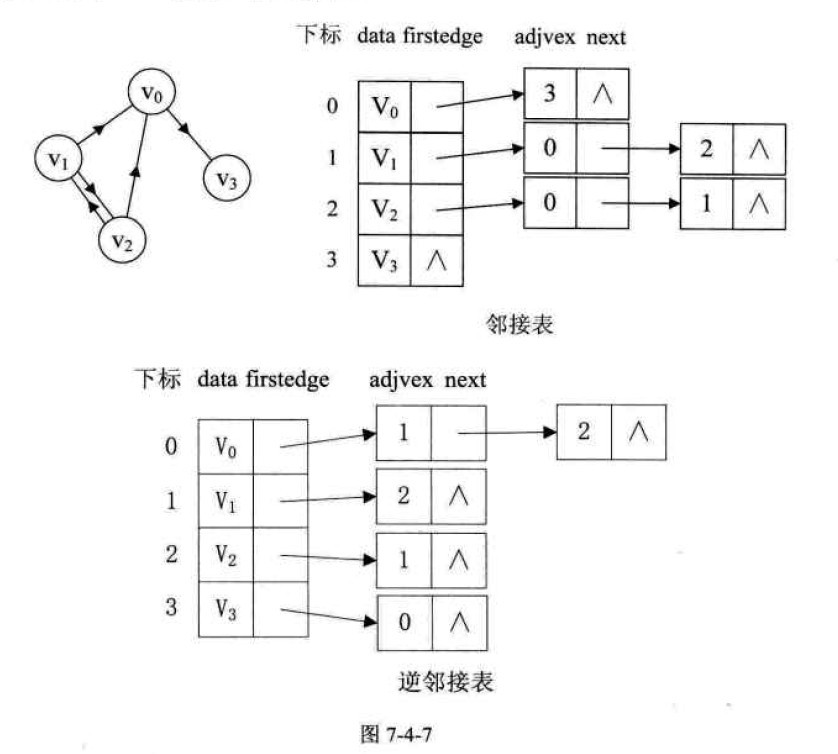
若是有向图,邻接表的结构是类似的,如图7-4-7,以顶点作为弧尾来存储边表容易得到每个顶点的出度,而以顶点为弧头的表容易得到顶点的入度,即逆邻接表。
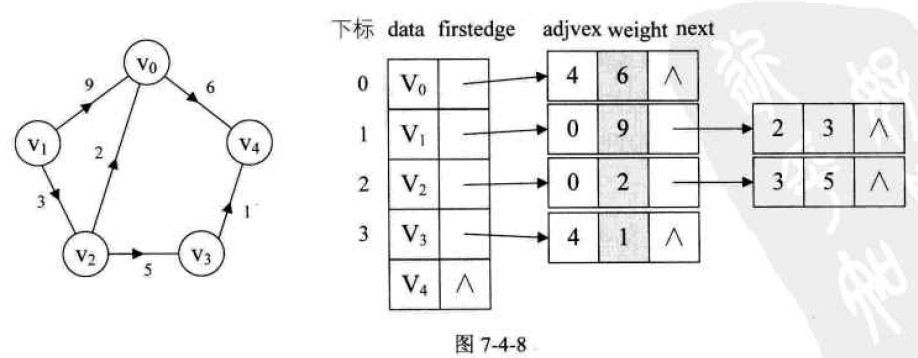
对于带权值的网图,可以在边表结点定义中再增加一个weight的数据域,存储权值信息即可,如图7-4-8所示。
下面示例无向图的邻接表创建:(改编自《大话数据结构》)
C++ Code
|
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 |
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #define MAXVEX 100 /* 最大顶点数,应由用户定义 */ typedef char VertexType; /* 顶点类型应由用户定义 */ typedef int EdgeType; /* 边上的权值类型应由用户定义 */ typedef struct EdgeNode /* 边表结点 */ { int adjvex; /* 邻接点域,存储该顶点对应的下标 */ EdgeType weight; /* 用于存储权值,对于非网图可以不需要 */ struct EdgeNode *next; /* 链域,指向下一个邻接点 */ } EdgeNode; typedef struct VextexNode /* 顶点表结点 */ { VertexType data; /* 顶点域,存储顶点信息 */ EdgeNode *firstedge; /* 边表头指针 */ } VextexNode, AdjList[MAXVEX]; typedef struct { AdjList adjList; int numNodes, numEdges; /* 图中当前顶点数和边数 */ } GraphAdjList; void CreateALGraph(GraphAdjList *Gp) { int i, j, k; EdgeNode *pe; cout << "输入顶点数和边数(空格分隔):" << endl; cin >> Gp->numNodes >> Gp->numEdges; for (i = 0 ; i < Gp->numNodes; i++) { cout << "输入顶点信息:" << endl; cin >> Gp->adjList[i].data; Gp->adjList[i].firstedge = NULL; /* 将边表置为空表 */ } for (k = 0; k < Gp->numEdges; k++) /* 建立边表 */ { cout << "输入边(vi,vj)的顶点序号i,j(空格分隔):" << endl; cin >> i >> j; pe = (EdgeNode *)malloc( sizeof(EdgeNode)); pe->adjvex = j; /* 邻接序号为j */ /* 将pe的指针指向当前顶点上指向的结点 */ pe->next = Gp->adjList[i].firstedge; Gp->adjList[i].firstedge = pe; /* 将当前顶点的指针指向pe */ pe = (EdgeNode *)malloc( sizeof(EdgeNode)); pe->adjvex = i; pe->next = Gp->adjList[j].firstedge; Gp->adjList[j].firstedge = pe; } } int main( void) { GraphAdjList GL; CreateALGraph(&GL); return 0; } |
这里的邻接点插入使用了单链表创建中的头插法,对于无向图来说,一条边对应都是两个顶点,所以在循环中,一次就针对i和j分别进行了插入。
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








