简述
几个重要的接口或类
AbstractBeanFactory类 :
getBean时
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类:
创建Bean的主要类
populateBean(自动注入属性)
initializeBean:
invokeAwareMethods(BeanNameAware BeanClassLoaderAware BeanFactoryAware )
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(@PostConstruct)
invokeInitMethods(afterPropertiesSet,init-method)
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()
InitializingBean接口 :
初始化时会回调afterPropertiesSet
InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 初始化和消亡
主要用于根据注解反射调用
如对bean中所有的@PreDestroy、@PostConstruct方法进行调用
DisposableBeanAdapter 消亡时会回调destroy()
@PreDestroy(最终通过InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 调用)
disposable.destroy();
destroy-method
产生到消亡的整体顺序:
(1)自动属性注入
(2)BeanNameAware:setBeanName(String)-》 BeanClassLoaderAware :setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader())-》BeanFactoryAware :setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this) 。按顺序依次回调实现的接口。
(3)applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization (@PostConstruct),遍历所有BeanPostProcessor的实现类的applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法。
(4)InitializingBean (afterPropertiesSet()) -》init-method
(5)applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization() :遍历所有BeanPostProcessor的实现类的applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法。
(6)@PreDestroy
(7)DisposableBean(实现接口):destroy()
(8)destroy-method现在开始初始化容器
这是BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类构造器!!
BeanFactoryPostProcessor调用postProcessBeanFactory方法
这是BeanPostProcessor实现类构造器!!
这是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter实现类构造器!!
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法
【构造器】调用Person的构造器实例化
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessPropertyValues方法
【注入属性】注入属性address
【注入属性】注入属性name
【注入属性】注入属性phone
【BeanNameAware接口】调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()
【BeanClassLoaderAware接口】调用setBeanClassLoader
【BeanFactoryAware接口】调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()
BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessBeforeInitialization对属性进行更改!
【@PostConstruct注解】
【InitializingBean接口】调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()
【init-method】调用<bean>的init-method属性指定的初始化方法
BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessAfterInitialization对属性进行更改!
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法
容器初始化成功
Person [address=广州, name=张三, phone=110]
现在开始关闭容器!
【@PreDestroy注解】
【DiposibleBean接口】调用DiposibleBean.destory()
【destroy-method】调用<bean>的destroy-method属性指定的初始化方法
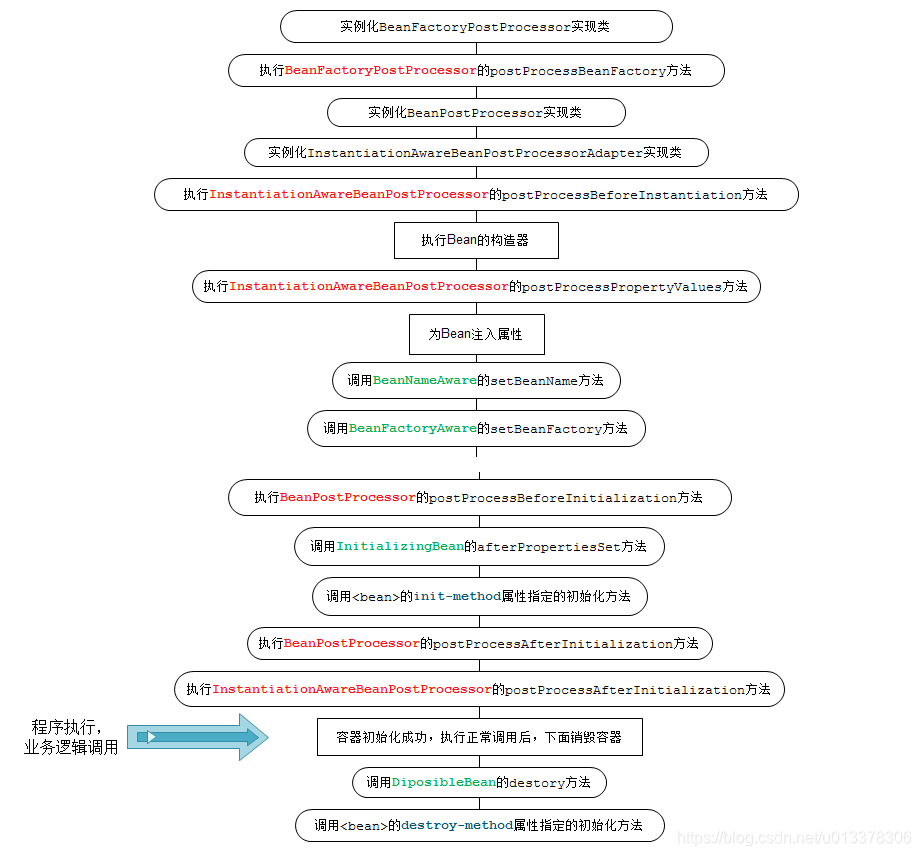
bean的产生和消亡可以回调的方法
关于在spring 容器初始化 bean 和销毁前所做的操作定义方式有三种:
第一种:通过@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 方法 实现初始化和销毁bean之前进行的操作
第二种是:通过 在xml中定义init-method 和 destory-method方法
第三种是: 通过bean实现InitializingBean和 DisposableBean接口
关于bean产生简述
所有的初始化方法在bean生成时只调用一次,在BeanPostProcessor的前置后置处理方法中可以 对原实例对象 做增强代理并作为新的bean返回。
(1)bean产生的重要入口类可见AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类的doCreateBean方法
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);//自动注入相关属性
if (exposedObject != null) {
//initializeBean 初始化时一些操作,
(1)回调所有实现了BeanNameAware BeanFactoryAware BeanClassLoaderAware 接口的类的相关方法
(2)回调所有实现了initializingBean接口的类 的afterPropertiesSet()方法。
(3)对所有实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的类进行方法回调,其中InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,在此类中会反射调用@PostConstruct注解的方法。
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
/注册一个bean消亡时的处理的DisposableBean,其实都是DisposableBeanAdapter的实例bean,
// 会存储在DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry类中的属性disposableBeans(Map)中,key为此bean的名字,value为DisposableBeanAdapter实例例对象
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); /
}
}(2)所有的bean在生成时都会注册一个消亡时的处理的bean,而且都是DisposableBeanAdapter实例,具体可见AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类的doCreateBean方法中调用的registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary方法。
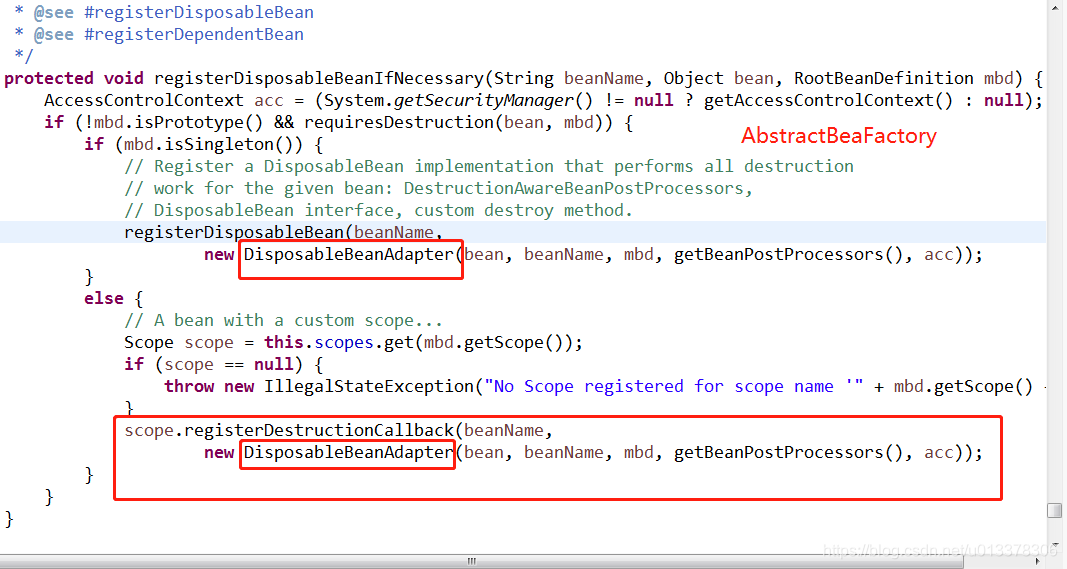
DisposableBeanAdapter类构造方法

关于bean消亡简述
由于创建bean的时候都会注册一个 DisposableBean实例,并且都是DisposableBeanAdapter的实例bean,
此映射关系会存储在DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry类中的属性disposableBeans(Map类型)中,key为此bean的名字,value为DisposableBeanAdapter实例例对象,例如:{“UserService类的beanname”:DisposableBeanAdapter实例对象};
所以在bean消亡时,最终会调用DisposableBeanAdapter的destroy()方法(不管bean有没有实现DisposableBean接口都会调用)。
bean的产生
一、从AbstractBeanFactory.class的getBean开始追踪
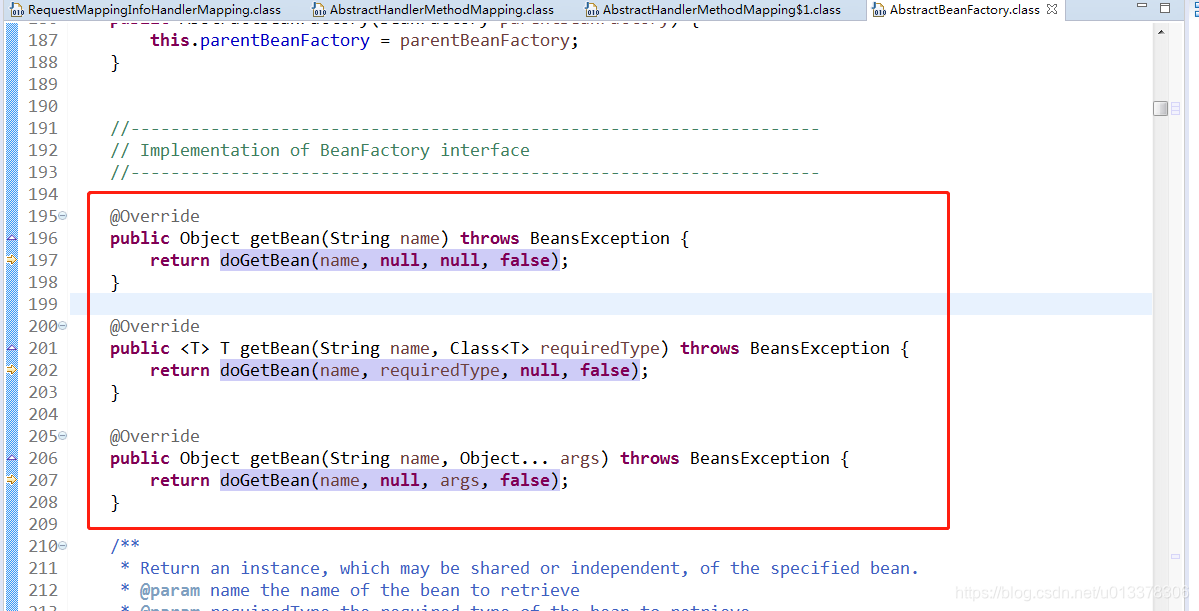
二、 继续追踪,如果单例缓存中存在bean,则直接返回bean。否则判断是单例还是多例,并进行相关操作,如果是单例,则生成bean后要存储到内存,以便下次调用。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> T doGetBean(
final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { //如果在单例缓存中存在直接使用
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dependsOnBean : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dependsOnBean)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dependsOnBean + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dependsOnBean, beanName);
getBean(dependsOnBean);
}
}
// Create bean instance. 是单例
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); //创建bean
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {//不是单例
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); //创建bean
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isAssignableFrom(bean.getClass())) {
try {
return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type [" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "]", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}三、继续追踪到AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.class
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args); //创建bean
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}四、调用populate方法对原实例对象属性自动注入,并调用initializeBean对原实例对象的相关处理(重要)
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);//创建原对象的实例包装
}
//bean=原实例对象,此时是已经实例化过的对象。
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ?
instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null);
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
}
});
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;//此时的bean已经是原始的实例对象
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);//根据注解自动注入属性到原实例
if (exposedObject != null) {
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);//对原实例进行处理,如果需要增强就封装成新的代理对象(就是真正的IOC容器中的Bean)。
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
//注册一个实现Disposable接口的类,当bean destory的时候调用,最终注册的的是DisposableBeanAdapter类
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}五、自动注入属性的方法 populateBean方法解析(重要)
/**
* Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values
* from the bean definition.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param bw BeanWrapper with bean instance
*/
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
if (bw == null) {
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);//注意这里
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}I实现nstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor这个接口的postProcessPropertyValues方法的类,可以获得带有带有注解的字段和方法,并注入到Bean中。
六、调用initializeBean方法对原实例对象做其他初始化操作(三个bena初始化回调顺序)
具体包括:
(1)实现了BeanNameAware 回调setBeanName(beanName)、BeanFactoryAware 回调setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this)、BeanClassLoaderAware 回调setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader())。作用是,可以在bean类中获得这些回调的参数。
(2)实现了initializingBean接口 ,回调afterPropertiesSet()。
(3)实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的类在bean初始化中 ,可以回调,此接口具体有如下两个方法
1)wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean原bean实例对象, beanName);
其中InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,并且InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor中的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法实现了:对@PostConstruct注解表示的方法进行反射调用。
2)wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean原bean实例对象, beanName);。
BeanPostProcessor接口重要作用:实现BeanPostProcessor接口,可以postProcessBeforeInitialization或者 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization中做代理,并返回代理后的bean实例。
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);//(第一个)
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//这里会反射调用Bean中所有被@PostConstruct注解的方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);//(第二个)
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);//(第三个)
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);//第四个
}
return wrappedBean;
} private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader());
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
} protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() throws Exception {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
if (mbd != null) {
//获取bean的初始化方法,也就init-method指定的方法
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}追踪开始applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization,看看如何进行 被@PostConstruct注解的方法回调的
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}继续追踪,发现有个InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,进入查看
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//这里获得所有的PreDestory和PostConstruct注解的方法,如何获得本文最后统一讲
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass());
try {
metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName);//进行反射调用
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex.getTargetException());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Failed to invoke init method", ex);
}
return bean;
}继续追踪
public void invokeInitMethods(Object target, String beanName) throws Throwable {
Collection<LifecycleElement> initMethodsToIterate =
(this.checkedInitMethods != null ? this.checkedInitMethods : this.initMethods);
if (!initMethodsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
//遍历所有的被PostConstruct注解的方法
for (LifecycleElement element : initMethodsToIterate) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Invoking init method on bean '" + beanName + "': " + element.getMethod());
}
element.invoke(target);//反射调用
}
}
}七、回到 第四步 的registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary方法,讨论实现了DisposableBean接口的bean的后续问题
protected void registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
AccessControlContext acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null ? getAccessControlContext() : null);
if (!mbd.isPrototype() && requiresDestruction(bean, mbd)) {
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// Register a DisposableBean implementation that performs all destruction
// work for the given bean: DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors,
// DisposableBean interface, custom destroy method.
//注册的key=beanName,value=DisposableBeanAdapter 对象.
//所以当bean销毁时,经过DisposableBeanAdapter的destroy方法处理
registerDisposableBean(beanName,
new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
}
else {
// A bean with a custom scope...
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(mbd.getScope());
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + mbd.getScope() + "'");
}
//注册的key=beanName,value=DisposableBeanAdapter 对象.
//所以当bean销毁时,经过DisposableBeanAdapter的destroy方法处理
scope.registerDestructionCallback(beanName,
new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
}
}
}public void registerDisposableBean(String beanName, DisposableBean bean) {
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
this.disposableBeans.put(beanName, bean);
}
}最终(只讨论单例模式下)会被注册到 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry类的disposableBeans属性中
/** Disposable bean instances: bean name --> disposable instance */
private final Map<String, Object> disposableBeans = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
什么时候被调用Disposable 中的 dispose?,在单例销毁或者容器关闭
容器关闭(bean消亡)
context.registerShutdownHook(); 是一个钩子方法,当jvm关闭退出的时候会调用这个钩子方法,在设计模式之 模板模式中 通过在抽象类中定义这样的钩子方法由实现类进行实现,这里的实现类是AbstractApplicationContext,这是spring 容器优雅关闭的方法。
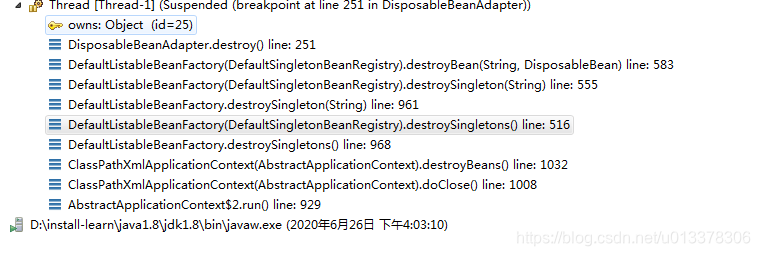
容器关闭入口 AbstractApplicationContext:(重要)
public void registerShutdownHook() {
if (this.shutdownHook == null) {
this.shutdownHook = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (startupShutdownMonitor) {
doClose(); /*关闭容器*/
}
}
};
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook);
}
}AbstractApplicationContext:
在容器注册的关闭钩子的关闭方法中都调用了doClose方法,我们来分析这个方法:
protected void doClose() {
//判断active激活标记(在初始化上下文时被设置为true用于标记激活状态)并且将closed标记设置为true
if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Closing " + this);
}
LiveBeansView.unregisterApplicationContext(this); //卸载注册的JMX的MBean
try {
publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this)); //发布容器关闭事件
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", ex);
}
try {
getLifecycleProcessor().onClose(); //调用实现了Lifecycle的bean的stop方法,关于Lifecycle,我们在标签解析的文章中分析过
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from LifecycleProcessor on context close", ex);
}
destroyBeans(); /*销毁bean*/
closeBeanFactory(); //关闭BeanFactory,将BeanFactory序列化id和本身置为null
onClose(); //子类扩展
this.active.set(false); //将激活标记置为false
}
}AbstractApplicationContext:
protected void destroyBeans() {
getBeanFactory().destroySingletons(); //销毁单例bean
}DefaultListableBeanFactory:
public void destroySingletons() {
super.destroySingletons(); /*调用父类的销毁方法销毁单例bean*/
this.manualSingletonNames.clear(); //清空手工注册的beanName的缓存
clearByTypeCache(); //清空类型-->beanName的映射缓存
}DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry:回调所有的实现DisposableBean 接口的类的destory方法
public void destroySingletons() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Destroying singletons in " + this);
}
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = true; //设置正在销毁的标记为true
}
String[] disposableBeanNames;
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
disposableBeanNames = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.disposableBeans.keySet());
}
for (int i = disposableBeanNames.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
/*遍历销毁之前注册的所有disposableBean,所有的类在注册为bean时都会注册一个对应的disposableBean,而且都是DisposableBeanAdapter*/
destroySingleton(disposableBeanNames[i]);
}
this.containedBeanMap.clear(); //清空beanName --> 它包含的所有内部beanName集合的映射缓存
this.dependentBeanMap.clear(); //清空beanName --> 它依赖的所有beanName集合的映射缓存
this.dependenciesForBeanMap.clear(); //清空beanName --> 依赖它的所有beanName集合的映射缓存
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.clear(); //清空单例bean缓存
this.singletonFactories.clear(); //清空单例工厂缓存
this.earlySingletonObjects.clear(); //清空提前暴露的beanName --> bean的映射缓存
this.registeredSingletons.clear(); //清空已经注册的单例bean缓存
this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false; //设置正在销毁的标记为false
}
}DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry:
public void destroySingleton(String beanName) {
removeSingleton(beanName); //清除bean的相应缓存
DisposableBean disposableBean;
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
//移除并获取disposableBean(DisposableBeanAdapter)
disposableBean = (DisposableBean) this.disposableBeans.remove(beanName);
}
destroyBean(beanName, disposableBean); /*销毁*/
}DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry:此处会调用DisposableBeanAdapter类的destory方法。
protected void destroyBean(String beanName, DisposableBean bean) {
Set<String> dependencies = this.dependentBeanMap.remove(beanName);
if (dependencies != null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Retrieved dependent beans for bean '" + beanName + "': " + dependencies);
}
for (String dependentBeanName : dependencies) {
destroySingleton(dependentBeanName); //首选递归销毁所有当前bean依赖的bean
}
}
if (bean != null) {
try {
//此bean为DisposableBeanAdapter实例
//调用bean生成时注册的Disposablebean,所有bean注册的时候都是DisposableBeanAdapter实例,
//所以都会调用DisposableBeanAdapter类的destory方法!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
bean.destroy();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.error("Destroy method on bean with name '" + beanName + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
Set<String> containedBeans = this.containedBeanMap.remove(beanName);
if (containedBeans != null) {
for (String containedBeanName : containedBeans) {
destroySingleton(containedBeanName); //递归销毁当前bean包含的所有内部bean
}
}
synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) {
//遍历找出所有依赖当前bean的列表,将当前bean从被依赖的列表中移除
for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Set<String>>> it = this.dependentBeanMap.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry<String, Set<String>> entry = it.next();
Set<String> dependenciesToClean = entry.getValue();
dependenciesToClean.remove(beanName);
if (dependenciesToClean.isEmpty()) {
it.remove();
}
}
}
this.dependenciesForBeanMap.remove(beanName); //从所有依赖当前bean的映射中移除依赖关系
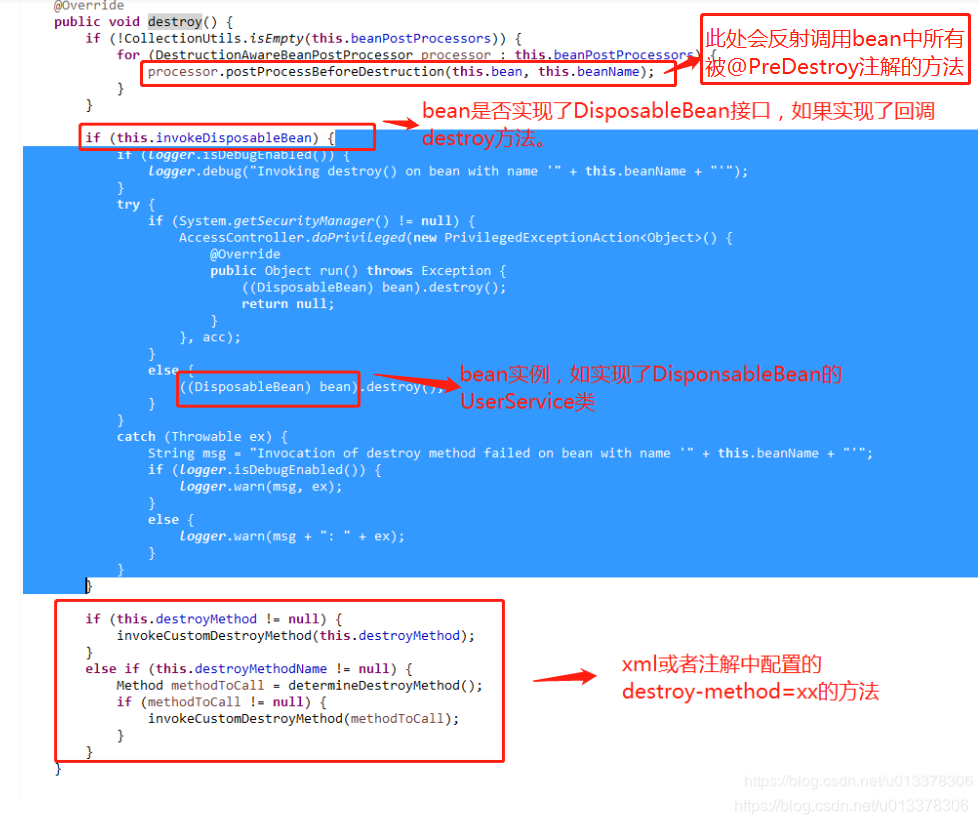
}关于DisposableBeanAdapter类三个bean销毁时自定义的回调方法的顺序(重要)
由于创建所有bean的时候注册消亡的disposablebean都是DisposableBeanAdapter(具体可看doCreateBean方法中调用的registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary方法),所以所有的bean的消亡都会经过DisposableBeanAdapter的destroy方法。
DisposableBeanAdapter实现了DisposableBean接口类,当bean销毁时也会调用此类的destory()方法,此类中有关于三个bean销毁时的回调方法。
@Override
public void destroy() {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.beanPostProcessors)) {
for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this.beanPostProcessors) {
//此处会反射调用 @PreDestory注解的方法
processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this.bean, this.beanName);
}
}
if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {//判断是否是实现DisposableBean接口的类
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking destroy() on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() throws Exception {
((DisposableBean) bean).destroy();
return null;
}
}, acc);
}
else {
((DisposableBean) bean).destroy();//实现DisposableBean接口的类的回调
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
String msg = "Invocation of destroy method failed on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'";
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.warn(msg, ex);
}
else {
logger.warn(msg + ": " + ex);
}
}
}
// xml自定义 destory-method 方法反射调用
if (this.destroyMethod != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod);
}
else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) {
Method methodToCall = determineDestroyMethod();
if (methodToCall != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(methodToCall);
}
}
}追踪DisposableBean的destory()方法。
进入到DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
public void destroySingleton(String beanName) {
// Remove a registered singleton of the given name, if any.
removeSingleton(beanName);
// Destroy the corresponding DisposableBean instance.
DisposableBean disposableBean;
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
disposableBean = (DisposableBean) this.disposableBeans.remove(beanName);
}
destroyBean(beanName, disposableBean);
}继续追踪postProcessBeforeDestruction方法。
发现有个InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类实现了DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
@Override
public void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass());//获得此bean中所有的PreDestory注解的方法 (1)
try {
metadata.invokeDestroyMethods(bean, beanName); //执行PreDestory (2)
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
String msg = "Invocation of destroy method failed on bean with name '" + beanName + "'";
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.warn(msg, ex.getTargetException());
}
else {
logger.warn(msg + ": " + ex.getTargetException());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.error("Failed to invoke destroy method on bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}上述代码(1)中findLifecycleMetadata方法是为了获当前Bean所有注解了PreDestory和PostConstruct的方法,最后我们会统一讲。
继续追踪上述代码(2)
public void invokeDestroyMethods(Object target, String beanName) throws Throwable {
Collection<LifecycleElement> destroyMethodsToUse =
(this.checkedDestroyMethods != null ? this.checkedDestroyMethods : this.destroyMethods);
if (!destroyMethodsToUse.isEmpty()) {
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (LifecycleElement element : destroyMethodsToUse) { //循环遍历所有被PreDestory注解的方法
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Invoking destroy method on bean '" + beanName + "': " + element.getMethod());
}
element.invoke(target);//反射执行,tagret是bean实例对象
}
}
}到此bean销毁过程全部结束
PreDestory和PostConstruct的问题之findLifecycleMetadata方法
关于InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类中findLifecycleMetadata方法。
如何获得前Bean所有注解了PreDestory和PostConstruct的方法的问题。
private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {
if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) {
// Happens after deserialization, during destruction...
return buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
}
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata);
}
return metadata;
}
}
return metadata;
}private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
LinkedList<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>();
LinkedList<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final LinkedList<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>();
final LinkedList<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() {
@Override
public void doWith(Method method) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (initAnnotationType != null) {
//获得此Bean所有带有initAnnotationType注解的方法(其实就是PostConstruct注解)
if (method.getAnnotation(initAnnotationType) != null) {
LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method);
currInitMethods.add(element);
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
}
if (destroyAnnotationType != null) {
获得此Bean所有带有destroyAnnotationType注解的方法(其实就是PreDestory注解)
if (method.getAnnotation(destroyAnnotationType) != null) {
currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method));
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
}
}
});
initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods);
destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods);
}
关于initAnnotationType和destroyAnnotationType到底是什么,在InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类中有两个方法
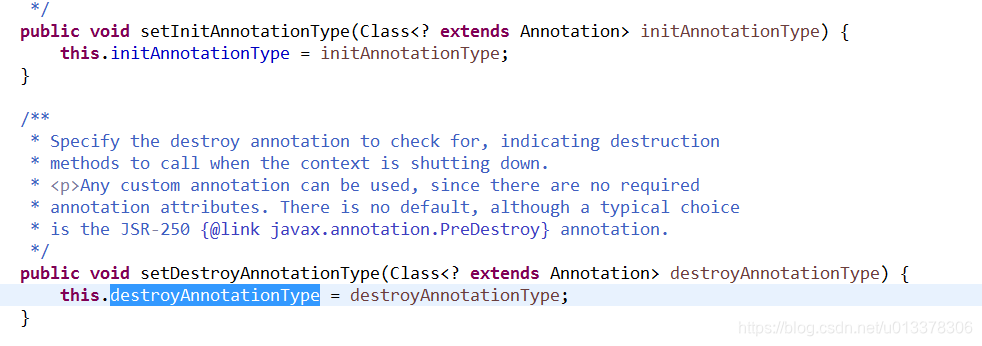
上述这两个方法在CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor初始化构造函数的时候会被调用,代码如下。
public CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 3);
setInitAnnotationType(PostConstruct.class);
setDestroyAnnotationType(PreDestroy.class);
ignoreResourceType("javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext");
}而CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor继承InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,在容器启动或者刷新时 会实例化 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,就会触发构造方法。






















 564
564











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










