一、数据库的分页语句
在编写Web应用程序等系统时,会涉及到与数据库的交互,如果数据库中数据量很大的话,一次检索所有的记录,会占用系统很大的资源,因此常常采用分页语句:需要多少数据就只从数据库中取多少条记录。以下是Sql Server,Oracle和MySQL的分页语句(从数据库表中的第M条数据开始取N条记录):
SQL Server
从数据库表中的第M条记录开始取N条记录,利用Top关键字(如果Select语句中既有top,又有order by,则是从排序好的结果集中选择):
SELECT *
FROM ( SELECT Top N * FROM (SELECT Top (M + N - 1) * FROM 表名称 Order by 主键 desc) t1 ) t2
Order by 主键 asc例如从表Sys_option(主键为sys_id)中从10条记录还是检索20条记录,语句如下:
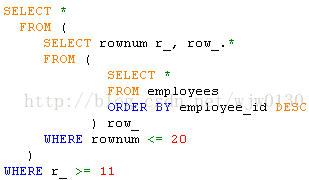
SELECT * FROM ( SELECT TOP 20 *
FROM (SELECT TOP 29 * FROM Sys_option order by sys_id desc) t1) t2
Order by sys_id ascOralce数据库
从数据库表中第M条记录 开始检索N条记录
例如从表employees(主键为employee_id)中从11条记录还是检索20条记录,语句如下:
MySQL数据库
My sql数据库最简单,是利用mySQL的LIMIT函数,LIMIT [offset,] rows从数据库表中M条记录开始检索N条记录的语句为:
SELECT [列名列表] FROM 表名称 LIMIT M,N 例如从表Sys_option(主键为sys_id)中从10条记录还是检索20条记录,语句如下:
select * from sys_option limit 10,20 二、调用存储函数 和 存储过程
创建函数
获取指定部门的工资和员工人数
create or replace function get_dept_salary(v_dept number , v_num out number)
return number
is
v_sal number(20,2) := 0;
cursor salary_cursor is select salary from employees where department_id = v_dept;
begin
v_num := 0;
for c in salary_cursor loop
v_sal := v_sal + c.salary;
v_num := v_num + 1;
end loop;
return v_sal;
end;创建存储过程
获取指定部门的工资
create or replace procedure get_salary(v_dept number , v_num out number)
is
cursor salary_cursor is select salary from employees where department_id = v_dept;
begin
v_num := 0;
for c in salary_cursor loop
v_num := v_num + c.salary;
end loop;
dbms_output.put_line(v_num);
end;调用函数:
/**
* 使用JDBC 调用函数
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
Connection conn = null;
CallableStatement callableStatement = null;
try {
conn = JDBC_Tools.getConnection();
//1.用Connection 对象的 prepareCall() 方法获取CallableStatement 实例
//prepareCall() 方法需要传入 SQL 字符串,严格书写格式
String sql = "{?= call get_dept_salary(?,?)}";
callableStatement = conn.prepareCall(sql);
//2.通过CallableStatement 的 registerOutParameter() 方法设置OUT 参数
callableStatement.registerOutParameter(1, Types.NUMERIC);
callableStatement.registerOutParameter(3, Types.NUMERIC);
//3.通过 CallableStatement 的 setXxx() 方法设置IN 或 IN OUT 参数的值,若为空,setNull()方法
callableStatement.setInt(2, 80);
//4.调用 execute() 方法执行
callableStatement.execute();
//5.如果调用的是带返回值
double salary = callableStatement.getDouble(1);
long nums = callableStatement.getLong(3);
System.out.println("salary : "+salary+" nums : "+nums);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBC_Tools.relaseSource(conn, callableStatement);
}
}/**
* 使用JDBC 调用存储过程
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
Connection conn = null;
CallableStatement callableStatement = null;
try {
conn = JDBC_Tools.getConnection();
String sql = "{call get_salary(?,?)}";
callableStatement = conn.prepareCall(sql);
callableStatement.registerOutParameter(2, Types.NUMERIC);
callableStatement.setInt(1, 80);
callableStatement.execute();
double salary = callableStatement.getDouble(2);
System.out.println("salary : "+salary);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBC_Tools.relaseSource(conn, callableStatement);
}
}

























 1204
1204

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








