AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient(); client.get("http://www.google.com", new AsyncHttpResponseHandler() { @Override public void onSuccess(String response) { System.out.println(response); } });
通过AsyncHttpClient类的实例就可以执行网络请求,包括get、put、post、head、delete。并指定一个ResponseHandlerInterface的实例接收请求结果。(onSuccess参数不对,此处只说明基本用法,详细参数看源码)
主要类介绍
- AsyncHttpRequest
继承自Runnabler,被submit至线程池执行网络请求并发送start,success等消息
- AsyncHttpResponseHandler
接收请求结果,一般重写onSuccess及onFailure接收请求成功或失败的消息,还有onStart,onFinish等消息
- TextHttpResponseHandler
继承自AsyncHttpResponseHandler,只是重写了AsyncHttpResponseHandler的onSuccess和onFailure方法,将请求结果由byte数组转换为String
- JsonHttpResponseHandler
继承自TextHttpResponseHandler,同样是重写onSuccess和onFailure方法,将请求结果由String转换为JSONObject或JSONArray
- BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler
继承自TextHttpResponseHandler,是一个泛型类,提供了parseResponse方法,子类需要提供实现,将请求结果解析成需要的类型,子类可以灵活地使用解析方法,可以直接原始解析,使用gson等。
- RequestParams
请求参数,可以添加普通的字符串参数,并可添加File,InputStream上传文件
- AsyncHttpClient
核心类,使用HttpClient执行网络请求,提供了get,put,post,delete,head等请求方法,使用起来很简单,只需以url及RequestParams调用相应的方法即可,还可以选择性地传入Context,用于取消Content相关的请求,同时必须提供ResponseHandlerInterface(AsyncHttpResponseHandler继承自ResponseHandlerInterface)的实现类,一般为AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类,AsyncHttpClient内部有一个线程池,当使用AsyncHttpClient执行网络请求时,最终都会调用sendRequest方法,在这个方法内部将请求参数封装成AsyncHttpRequest(继承自Runnable)交由内部的线程池执行。
- SyncHttpClient
继承自AsyncHttpClient,同步执行网络请求,AsyncHttpClient把请求封装成AsyncHttpRequest后提交至线程池,SyncHttpClient把请求封装成AsyncHttpRequest后直接调用它的run方法。
请求流程

- 调用AsyncHttpClient的get或post等方法发起网络请求
- 所有的请求都走了sendRequest,在sendRequest中把请求封装为了AsyncHttpRequest,并添加到线程池执行
- 当请求被执行时(即AsyncHttpRequest的run方法),执行AsyncHttpRequest的makeRequestWithRetries方法执行实际的请求,当请求失败时可以重试。并在请求开始,结束,成功或失败时向请求时传的ResponseHandlerInterface实例发送消息
- 基本上使用的都是AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类,调用其onStart,onSuccess等方法返回请求结果
详细使用方法
官方建议使用一个静态的AsyncHttpClient,像下面的这样:
public class TwitterRestClient { private static final String BASE_URL = "http://api.twitter.com/1/"; private static AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient(); public static void get(String url, RequestParams params, AsyncHttpResponseHandler responseHandler) { client.get(getAbsoluteUrl(url), params, responseHandler); } public static void post(String url, RequestParams params, AsyncHttpResponseHandler responseHandler) { client.post(getAbsoluteUrl(url), params, responseHandler); } private static String getAbsoluteUrl(String relativeUrl) { return BASE_URL + relativeUrl; } }
封装的方法建议都加上Context参数,以在Activity pause或stop时取消掉没用的请求。
详细使用方法就不说了,直接看官方文档
其他说明及总结
Android-Async-Http的使用非常简单,通过AsyncHttpClient发起请求就可以了,如果需要添加参数,直接传一个RequestParams过去,而且参数可以是String、File和InputStream,可以很方便地上传文件。
每个请求都需要传一个ResponseHandlerInterface的实例用以接收请求结果或请求失败,请求结束等通知,一般是AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类。
通过BinaryHttpResponseHandler可以发起二进制请求,如请求图片。
通过TextHttpResponseHandler可以发起返回结果为字符串的请求,一般这个使用较多。
也可以使用它的子类JsonHttpResponseHandler,返回结果是一个JSONObject或JSONArray。不过感觉这个类作用不大,一是有另一个类BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler,可以直接解析返回的JSON数据,二是JsonHttpResponseHandler的方法太复杂了,有太多的onSuccess和onFailure方法,都不知道重写哪个了。

如上图所示,每个子类有太多的onSuccess和onFailure了,尤其是JsonHttpResponseHandler,这应该算是这个类库的不足吧。所以平时使用时基本不使用JsonHttpResponseHandler,而是直接使用TextHttpResponseHandler,当然也可以使用BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler。
这个类库还有一点不足,就是onSuccess等方法一般会在主线程执行,其实这么说不严谨,看代码吧:
public AsyncHttpResponseHandler() { boolean missingLooper = null == Looper.myLooper(); // Try to create handler if (!missingLooper) handler = new ResponderHandler(this); else { // There is no Looper on this thread so synchronous mode should be used. handler = null; setUseSynchronousMode(true); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Current thread has not called Looper.prepare(). Forcing synchronous mode."); } // Init Looper by calling postRunnable without an argument. postRunnable(null); }
可以看到,内部使用了Handler,当新建AsyncHttpResponseHandler的实例的时候会获取当前线程的Looper,如果为空就启用同步模式,即所有的回调都会在执行请求的线程中执行,当在一个普通的后台线程时这样执行是正常的,而我们一般都会在主线程发请请求,结果就是所有的回调都会在主线程中执行,这就限制了我们在onSuccess中执行耗时操作,比如请求成功后将数据持久化到数据库。
不过可以看到创建Handler的时候使用了Looper对象,所以我们就可以改进一下其构造函数,添加一个Looper参数(同步修改子类),这样所有的回调就都会在Looper所在线程执行,这样我们只需要开启一个HandlerThread就行了。但这样和Looper为空时一样有一个弊端,如果要更新UI操作的话,还需要向一个主线程的Handler发送消息让UI更新。还有第二个弊端,所有回调都在同一个HandlerThread中执行,如果一个处理耗时太久会阻塞后面的请求结果处理,如果只是简单地写个数据库影响应该不大,如果真耗时太久,为这个耗时处理再开个线程吧。
android-async-http开源项目可以是我们轻松的获取网络数据或者向服务器发送数据,使用起来非常简单,关于android-async-http开源项目的介绍内容来自于官方:http://loopj.com/android-async-http/.下面我对此主页上内容进行大体上的翻译,希望能够对你理解android-async-http开源项目有所帮助
1.1 Overview(概况)
An asynchronous callback-based Http client for Android built on top of Apache’s HttpClient libraries. All requests are made outside of your app’s main UI thread, but any callback logic will be executed on the same thread as the callback was created using Android’s Handler message passing.
译文:
异步基于回调的Http客户端为Android构建,是基于Apache HttpClient库的。所有的请求都是位于应用程序主线程 UI 之外,但任何回调逻辑将相同的线程上执行回调,使用Android的处理程序创建消息传递。
1.2 Features(特征)
- Make asynchronous HTTP requests, handle responses in anonymous callbacks
- 进行异步HTTP请求,处理响应在匿名回调中完成
- HTTP requests happen outside the UI thread
- HTTP请求发生在UI线程之外
- Requests use a threadpool to cap concurrent resource usage
- 请求使用threadpool,限制并发资源使用情况
- GET/POST params builder (RequestParams)
- GET / POST参数构建使用(RequestParams)
- Multipart file uploads with no additional third party libraries
- Multipart 文件上传,没有额外的第三方库
- Tiny size overhead to your application, only 25kb for everything
- 在你的应用程序上利用很小的开销,仅仅25 kb就可以做一切
- Automatic smart request retries optimized for spotty mobile connections
- 自动智能请求重试,优化了质量不一的移动连接
- Automatic gzip response decoding support for super-fast requests
- 自动解码支持gzip反应速度超快的请求
- Binary file (images etc) downloading with
BinaryHttpResponseHandler -
二进制文件(图片等)的下载,使用BinaryHttpResponseHandler
- Built-in response parsing into JSON with
JsonHttpResponseHandler -
内置响应解析成JSON,使用JsonHttpResponseHandler
- Persistent cookie store, saves cookies into your app’s SharedPreferences
- 持久化cookie存储,保存cookie到你的应用程序的SharedPreferences
2. Installation & Basic Usage( 安装和基本用法)
Download the latest .jar file from github and place it in your Android app’s libs/ folder.
从github上下载最新的最新的jar文件.并将其放置在你的Android应用程序的libs /文件夹.
2.1下载方式:
1.从http://loopj.com/android-async-http/的页面下载
点击DownLoad即可下载最新的jar文件
2.从https://github.com/loopj/android-async-http的页面下载
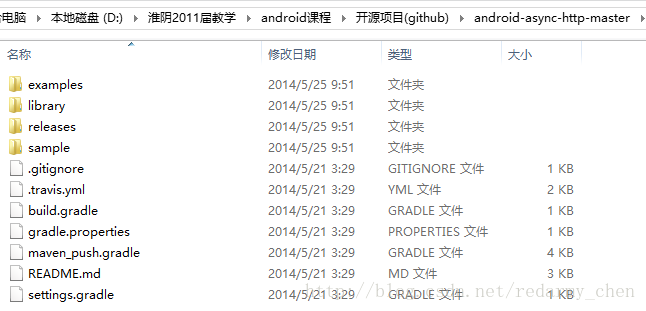
找到DownLoad ZIP进行下载文件,解压后的目录如下
examples:里面有简单的例子
library:里面存放的是android-async-http开源项目的源码(方法一:可以把library\src\main\java文件下面的文件拷贝到,你应用的src下也可以直接使用)
releases:里面存放的是各个版本的jar文件,(方法二:只需把最新的jar文件拷贝到你应用的libs目录下即可.)
samples:里面存放的也是例子(可供参考)
备注:方法一和方法二只能采用其中之一,建议采用方法二
2.2使用方法
Import the http package.
Create a new AsyncHttpClient instance and make a request:
Adding GET/POST Parameters with RequestParams
The RequestParams class is used to add optional GET or POST parameters to your requests.RequestParams can be built and constructed in various ways:
Create empty RequestParams and immediately add some parameters:
Create RequestParams for a single parameter:
Create RequestParams from an existing Map of key/value strings:
See the RequestParams Javadoc for more information.
Add an InputStream to the RequestParams to upload:
Add a File object to the RequestParams to upload:
Add a byte array to the RequestParams to upload:
See the RequestParams Javadoc for more information.
Downloading Binary Data with BinaryHttpResponseHandler
The BinaryHttpResponseHandler class can be used to fetch binary data such as images and other files. For example:
See the BinaryHttpResponseHandler Javadoc for more information.
AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient(); client.get("http://www.google.com", new AsyncHttpResponseHandler() { @Override public void onSuccess(String response) { System.out.println(response); } });
通过AsyncHttpClient类的实例就可以执行网络请求,包括get、put、post、head、delete。并指定一个ResponseHandlerInterface的实例接收请求结果。(onSuccess参数不对,此处只说明基本用法,详细参数看源码)
主要类介绍
- AsyncHttpRequest
继承自Runnabler,被submit至线程池执行网络请求并发送start,success等消息
- AsyncHttpResponseHandler
接收请求结果,一般重写onSuccess及onFailure接收请求成功或失败的消息,还有onStart,onFinish等消息
- TextHttpResponseHandler
继承自AsyncHttpResponseHandler,只是重写了AsyncHttpResponseHandler的onSuccess和onFailure方法,将请求结果由byte数组转换为String
- JsonHttpResponseHandler
继承自TextHttpResponseHandler,同样是重写onSuccess和onFailure方法,将请求结果由String转换为JSONObject或JSONArray
- BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler
继承自TextHttpResponseHandler,是一个泛型类,提供了parseResponse方法,子类需要提供实现,将请求结果解析成需要的类型,子类可以灵活地使用解析方法,可以直接原始解析,使用gson等。
- RequestParams
请求参数,可以添加普通的字符串参数,并可添加File,InputStream上传文件
- AsyncHttpClient
核心类,使用HttpClient执行网络请求,提供了get,put,post,delete,head等请求方法,使用起来很简单,只需以url及RequestParams调用相应的方法即可,还可以选择性地传入Context,用于取消Content相关的请求,同时必须提供ResponseHandlerInterface(AsyncHttpResponseHandler继承自ResponseHandlerInterface)的实现类,一般为AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类,AsyncHttpClient内部有一个线程池,当使用AsyncHttpClient执行网络请求时,最终都会调用sendRequest方法,在这个方法内部将请求参数封装成AsyncHttpRequest(继承自Runnable)交由内部的线程池执行。
- SyncHttpClient
继承自AsyncHttpClient,同步执行网络请求,AsyncHttpClient把请求封装成AsyncHttpRequest后提交至线程池,SyncHttpClient把请求封装成AsyncHttpRequest后直接调用它的run方法。
请求流程

- 调用AsyncHttpClient的get或post等方法发起网络请求
- 所有的请求都走了sendRequest,在sendRequest中把请求封装为了AsyncHttpRequest,并添加到线程池执行
- 当请求被执行时(即AsyncHttpRequest的run方法),执行AsyncHttpRequest的makeRequestWithRetries方法执行实际的请求,当请求失败时可以重试。并在请求开始,结束,成功或失败时向请求时传的ResponseHandlerInterface实例发送消息
- 基本上使用的都是AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类,调用其onStart,onSuccess等方法返回请求结果
详细使用方法
官方建议使用一个静态的AsyncHttpClient,像下面的这样:
public class TwitterRestClient { private static final String BASE_URL = "http://api.twitter.com/1/"; private static AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient(); public static void get(String url, RequestParams params, AsyncHttpResponseHandler responseHandler) { client.get(getAbsoluteUrl(url), params, responseHandler); } public static void post(String url, RequestParams params, AsyncHttpResponseHandler responseHandler) { client.post(getAbsoluteUrl(url), params, responseHandler); } private static String getAbsoluteUrl(String relativeUrl) { return BASE_URL + relativeUrl; } }
封装的方法建议都加上Context参数,以在Activity pause或stop时取消掉没用的请求。
详细使用方法就不说了,直接看官方文档
其他说明及总结
Android-Async-Http的使用非常简单,通过AsyncHttpClient发起请求就可以了,如果需要添加参数,直接传一个RequestParams过去,而且参数可以是String、File和InputStream,可以很方便地上传文件。
每个请求都需要传一个ResponseHandlerInterface的实例用以接收请求结果或请求失败,请求结束等通知,一般是AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类。
通过BinaryHttpResponseHandler可以发起二进制请求,如请求图片。
通过TextHttpResponseHandler可以发起返回结果为字符串的请求,一般这个使用较多。
也可以使用它的子类JsonHttpResponseHandler,返回结果是一个JSONObject或JSONArray。不过感觉这个类作用不大,一是有另一个类BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler,可以直接解析返回的JSON数据,二是JsonHttpResponseHandler的方法太复杂了,有太多的onSuccess和onFailure方法,都不知道重写哪个了。

如上图所示,每个子类有太多的onSuccess和onFailure了,尤其是JsonHttpResponseHandler,这应该算是这个类库的不足吧。所以平时使用时基本不使用JsonHttpResponseHandler,而是直接使用TextHttpResponseHandler,当然也可以使用BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler。
这个类库还有一点不足,就是onSuccess等方法一般会在主线程执行,其实这么说不严谨,看代码吧:
public AsyncHttpResponseHandler() { boolean missingLooper = null == Looper.myLooper(); // Try to create handler if (!missingLooper) handler = new ResponderHandler(this); else { // There is no Looper on this thread so synchronous mode should be used. handler = null; setUseSynchronousMode(true); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Current thread has not called Looper.prepare(). Forcing synchronous mode."); } // Init Looper by calling postRunnable without an argument. postRunnable(null); }
可以看到,内部使用了Handler,当新建AsyncHttpResponseHandler的实例的时候会获取当前线程的Looper,如果为空就启用同步模式,即所有的回调都会在执行请求的线程中执行,当在一个普通的后台线程时这样执行是正常的,而我们一般都会在主线程发请请求,结果就是所有的回调都会在主线程中执行,这就限制了我们在onSuccess中执行耗时操作,比如请求成功后将数据持久化到数据库。
不过可以看到创建Handler的时候使用了Looper对象,所以我们就可以改进一下其构造函数,添加一个Looper参数(同步修改子类),这样所有的回调就都会在Looper所在线程执行,这样我们只需要开启一个HandlerThread就行了。但这样和Looper为空时一样有一个弊端,如果要更新UI操作的话,还需要向一个主线程的Handler发送消息让UI更新。还有第二个弊端,所有回调都在同一个HandlerThread中执行,如果一个处理耗时太久会阻塞后面的请求结果处理,如果只是简单地写个数据库影响应该不大,如果真耗时太久,为这个耗时处理再开个线程吧。
android-async-http开源项目可以是我们轻松的获取网络数据或者向服务器发送数据,使用起来非常简单,关于android-async-http开源项目的介绍内容来自于官方:http://loopj.com/android-async-http/.下面我对此主页上内容进行大体上的翻译,希望能够对你理解android-async-http开源项目有所帮助
1.1 Overview(概况)
An asynchronous callback-based Http client for Android built on top of Apache’s HttpClient libraries. All requests are made outside of your app’s main UI thread, but any callback logic will be executed on the same thread as the callback was created using Android’s Handler message passing.
译文:
异步基于回调的Http客户端为Android构建,是基于Apache HttpClient库的。所有的请求都是位于应用程序主线程 UI 之外,但任何回调逻辑将相同的线程上执行回调,使用Android的处理程序创建消息传递。
1.2 Features(特征)
- Make asynchronous HTTP requests, handle responses in anonymous callbacks
- 进行异步HTTP请求,处理响应在匿名回调中完成
- HTTP requests happen outside the UI thread
- HTTP请求发生在UI线程之外
- Requests use a threadpool to cap concurrent resource usage
- 请求使用threadpool,限制并发资源使用情况
- GET/POST params builder (RequestParams)
- GET / POST参数构建使用(RequestParams)
- Multipart file uploads with no additional third party libraries
- Multipart 文件上传,没有额外的第三方库
- Tiny size overhead to your application, only 25kb for everything
- 在你的应用程序上利用很小的开销,仅仅25 kb就可以做一切
- Automatic smart request retries optimized for spotty mobile connections
- 自动智能请求重试,优化了质量不一的移动连接
- Automatic gzip response decoding support for super-fast requests
- 自动解码支持gzip反应速度超快的请求
- Binary file (images etc) downloading with
BinaryHttpResponseHandler -
二进制文件(图片等)的下载,使用BinaryHttpResponseHandler
- Built-in response parsing into JSON with
JsonHttpResponseHandler -
内置响应解析成JSON,使用JsonHttpResponseHandler
- Persistent cookie store, saves cookies into your app’s SharedPreferences
- 持久化cookie存储,保存cookie到你的应用程序的SharedPreferences
2. Installation & Basic Usage( 安装和基本用法)
Download the latest .jar file from github and place it in your Android app’s libs/ folder.
从github上下载最新的最新的jar文件.并将其放置在你的Android应用程序的libs /文件夹.
2.1下载方式:
1.从http://loopj.com/android-async-http/的页面下载
点击DownLoad即可下载最新的jar文件
2.从https://github.com/loopj/android-async-http的页面下载
找到DownLoad ZIP进行下载文件,解压后的目录如下
examples:里面有简单的例子
library:里面存放的是android-async-http开源项目的源码(方法一:可以把library\src\main\java文件下面的文件拷贝到,你应用的src下也可以直接使用)
releases:里面存放的是各个版本的jar文件,(方法二:只需把最新的jar文件拷贝到你应用的libs目录下即可.)
samples:里面存放的也是例子(可供参考)
备注:方法一和方法二只能采用其中之一,建议采用方法二
2.2使用方法
Import the http package.
Create a new AsyncHttpClient instance and make a request:
Adding GET/POST Parameters with RequestParams
The RequestParams class is used to add optional GET or POST parameters to your requests.RequestParams can be built and constructed in various ways:
Create empty RequestParams and immediately add some parameters:
Create RequestParams for a single parameter:
Create RequestParams from an existing Map of key/value strings:
See the RequestParams Javadoc for more information.
Add an InputStream to the RequestParams to upload:
Add a File object to the RequestParams to upload:
Add a byte array to the RequestParams to upload:
See the RequestParams Javadoc for more information.
Downloading Binary Data with BinaryHttpResponseHandler
The BinaryHttpResponseHandler class can be used to fetch binary data such as images and other files. For example:
See the BinaryHttpResponseHandler Javadoc for more information.
AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient(); client.get("http://www.google.com", new AsyncHttpResponseHandler() { @Override public void onSuccess(String response) { System.out.println(response); } });
通过AsyncHttpClient类的实例就可以执行网络请求,包括get、put、post、head、delete。并指定一个ResponseHandlerInterface的实例接收请求结果。(onSuccess参数不对,此处只说明基本用法,详细参数看源码)
主要类介绍
- AsyncHttpRequest
继承自Runnabler,被submit至线程池执行网络请求并发送start,success等消息
- AsyncHttpResponseHandler
接收请求结果,一般重写onSuccess及onFailure接收请求成功或失败的消息,还有onStart,onFinish等消息
- TextHttpResponseHandler
继承自AsyncHttpResponseHandler,只是重写了AsyncHttpResponseHandler的onSuccess和onFailure方法,将请求结果由byte数组转换为String
- JsonHttpResponseHandler
继承自TextHttpResponseHandler,同样是重写onSuccess和onFailure方法,将请求结果由String转换为JSONObject或JSONArray
- BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler
继承自TextHttpResponseHandler,是一个泛型类,提供了parseResponse方法,子类需要提供实现,将请求结果解析成需要的类型,子类可以灵活地使用解析方法,可以直接原始解析,使用gson等。
- RequestParams
请求参数,可以添加普通的字符串参数,并可添加File,InputStream上传文件
- AsyncHttpClient
核心类,使用HttpClient执行网络请求,提供了get,put,post,delete,head等请求方法,使用起来很简单,只需以url及RequestParams调用相应的方法即可,还可以选择性地传入Context,用于取消Content相关的请求,同时必须提供ResponseHandlerInterface(AsyncHttpResponseHandler继承自ResponseHandlerInterface)的实现类,一般为AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类,AsyncHttpClient内部有一个线程池,当使用AsyncHttpClient执行网络请求时,最终都会调用sendRequest方法,在这个方法内部将请求参数封装成AsyncHttpRequest(继承自Runnable)交由内部的线程池执行。
- SyncHttpClient
继承自AsyncHttpClient,同步执行网络请求,AsyncHttpClient把请求封装成AsyncHttpRequest后提交至线程池,SyncHttpClient把请求封装成AsyncHttpRequest后直接调用它的run方法。
请求流程

- 调用AsyncHttpClient的get或post等方法发起网络请求
- 所有的请求都走了sendRequest,在sendRequest中把请求封装为了AsyncHttpRequest,并添加到线程池执行
- 当请求被执行时(即AsyncHttpRequest的run方法),执行AsyncHttpRequest的makeRequestWithRetries方法执行实际的请求,当请求失败时可以重试。并在请求开始,结束,成功或失败时向请求时传的ResponseHandlerInterface实例发送消息
- 基本上使用的都是AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类,调用其onStart,onSuccess等方法返回请求结果
详细使用方法
官方建议使用一个静态的AsyncHttpClient,像下面的这样:
public class TwitterRestClient { private static final String BASE_URL = "http://api.twitter.com/1/"; private static AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient(); public static void get(String url, RequestParams params, AsyncHttpResponseHandler responseHandler) { client.get(getAbsoluteUrl(url), params, responseHandler); } public static void post(String url, RequestParams params, AsyncHttpResponseHandler responseHandler) { client.post(getAbsoluteUrl(url), params, responseHandler); } private static String getAbsoluteUrl(String relativeUrl) { return BASE_URL + relativeUrl; } }
封装的方法建议都加上Context参数,以在Activity pause或stop时取消掉没用的请求。
详细使用方法就不说了,直接看官方文档
其他说明及总结
Android-Async-Http的使用非常简单,通过AsyncHttpClient发起请求就可以了,如果需要添加参数,直接传一个RequestParams过去,而且参数可以是String、File和InputStream,可以很方便地上传文件。
每个请求都需要传一个ResponseHandlerInterface的实例用以接收请求结果或请求失败,请求结束等通知,一般是AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类。
通过BinaryHttpResponseHandler可以发起二进制请求,如请求图片。
通过TextHttpResponseHandler可以发起返回结果为字符串的请求,一般这个使用较多。
也可以使用它的子类JsonHttpResponseHandler,返回结果是一个JSONObject或JSONArray。不过感觉这个类作用不大,一是有另一个类BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler,可以直接解析返回的JSON数据,二是JsonHttpResponseHandler的方法太复杂了,有太多的onSuccess和onFailure方法,都不知道重写哪个了。

如上图所示,每个子类有太多的onSuccess和onFailure了,尤其是JsonHttpResponseHandler,这应该算是这个类库的不足吧。所以平时使用时基本不使用JsonHttpResponseHandler,而是直接使用TextHttpResponseHandler,当然也可以使用BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler。
这个类库还有一点不足,就是onSuccess等方法一般会在主线程执行,其实这么说不严谨,看代码吧:
public AsyncHttpResponseHandler() { boolean missingLooper = null == Looper.myLooper(); // Try to create handler if (!missingLooper) handler = new ResponderHandler(this); else { // There is no Looper on this thread so synchronous mode should be used. handler = null; setUseSynchronousMode(true); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Current thread has not called Looper.prepare(). Forcing synchronous mode."); } // Init Looper by calling postRunnable without an argument. postRunnable(null); }
可以看到,内部使用了Handler,当新建AsyncHttpResponseHandler的实例的时候会获取当前线程的Looper,如果为空就启用同步模式,即所有的回调都会在执行请求的线程中执行,当在一个普通的后台线程时这样执行是正常的,而我们一般都会在主线程发请请求,结果就是所有的回调都会在主线程中执行,这就限制了我们在onSuccess中执行耗时操作,比如请求成功后将数据持久化到数据库。
不过可以看到创建Handler的时候使用了Looper对象,所以我们就可以改进一下其构造函数,添加一个Looper参数(同步修改子类),这样所有的回调就都会在Looper所在线程执行,这样我们只需要开启一个HandlerThread就行了。但这样和Looper为空时一样有一个弊端,如果要更新UI操作的话,还需要向一个主线程的Handler发送消息让UI更新。还有第二个弊端,所有回调都在同一个HandlerThread中执行,如果一个处理耗时太久会阻塞后面的请求结果处理,如果只是简单地写个数据库影响应该不大,如果真耗时太久,为这个耗时处理再开个线程吧。
android-async-http开源项目可以是我们轻松的获取网络数据或者向服务器发送数据,使用起来非常简单,关于android-async-http开源项目的介绍内容来自于官方:http://loopj.com/android-async-http/.下面我对此主页上内容进行大体上的翻译,希望能够对你理解android-async-http开源项目有所帮助
1.1 Overview(概况)
An asynchronous callback-based Http client for Android built on top of Apache’s HttpClient libraries. All requests are made outside of your app’s main UI thread, but any callback logic will be executed on the same thread as the callback was created using Android’s Handler message passing.
译文:
异步基于回调的Http客户端为Android构建,是基于Apache HttpClient库的。所有的请求都是位于应用程序主线程 UI 之外,但任何回调逻辑将相同的线程上执行回调,使用Android的处理程序创建消息传递。
1.2 Features(特征)
- Make asynchronous HTTP requests, handle responses in anonymous callbacks
- 进行异步HTTP请求,处理响应在匿名回调中完成
- HTTP requests happen outside the UI thread
- HTTP请求发生在UI线程之外
- Requests use a threadpool to cap concurrent resource usage
- 请求使用threadpool,限制并发资源使用情况
- GET/POST params builder (RequestParams)
- GET / POST参数构建使用(RequestParams)
- Multipart file uploads with no additional third party libraries
- Multipart 文件上传,没有额外的第三方库
- Tiny size overhead to your application, only 25kb for everything
- 在你的应用程序上利用很小的开销,仅仅25 kb就可以做一切
- Automatic smart request retries optimized for spotty mobile connections
- 自动智能请求重试,优化了质量不一的移动连接
- Automatic gzip response decoding support for super-fast requests
- 自动解码支持gzip反应速度超快的请求
- Binary file (images etc) downloading with
BinaryHttpResponseHandler -
二进制文件(图片等)的下载,使用BinaryHttpResponseHandler
- Built-in response parsing into JSON with
JsonHttpResponseHandler -
内置响应解析成JSON,使用JsonHttpResponseHandler
- Persistent cookie store, saves cookies into your app’s SharedPreferences
- 持久化cookie存储,保存cookie到你的应用程序的SharedPreferences
2. Installation & Basic Usage( 安装和基本用法)
Download the latest .jar file from github and place it in your Android app’s libs/ folder.
从github上下载最新的最新的jar文件.并将其放置在你的Android应用程序的libs /文件夹.
2.1下载方式:
1.从http://loopj.com/android-async-http/的页面下载
点击DownLoad即可下载最新的jar文件
2.从https://github.com/loopj/android-async-http的页面下载
找到DownLoad ZIP进行下载文件,解压后的目录如下
examples:里面有简单的例子
library:里面存放的是android-async-http开源项目的源码(方法一:可以把library\src\main\java文件下面的文件拷贝到,你应用的src下也可以直接使用)
releases:里面存放的是各个版本的jar文件,(方法二:只需把最新的jar文件拷贝到你应用的libs目录下即可.)
samples:里面存放的也是例子(可供参考)
备注:方法一和方法二只能采用其中之一,建议采用方法二
2.2使用方法
Import the http package.
Create a new AsyncHttpClient instance and make a request:
Adding GET/POST Parameters with RequestParams
The RequestParams class is used to add optional GET or POST parameters to your requests.RequestParams can be built and constructed in various ways:
Create empty RequestParams and immediately add some parameters:
Create RequestParams for a single parameter:
Create RequestParams from an existing Map of key/value strings:
See the RequestParams Javadoc for more information.
Add an InputStream to the RequestParams to upload:
Add a File object to the RequestParams to upload:
Add a byte array to the RequestParams to upload:
See the RequestParams Javadoc for more information.
Downloading Binary Data with BinaryHttpResponseHandler
The BinaryHttpResponseHandler class can be used to fetch binary data such as images and other files. For example:
See the BinaryHttpResponseHandler Javadoc for more information.
AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient(); client.get("http://www.google.com", new AsyncHttpResponseHandler() { @Override public void onSuccess(String response) { System.out.println(response); } });
通过AsyncHttpClient类的实例就可以执行网络请求,包括get、put、post、head、delete。并指定一个ResponseHandlerInterface的实例接收请求结果。(onSuccess参数不对,此处只说明基本用法,详细参数看源码)
主要类介绍
- AsyncHttpRequest
继承自Runnabler,被submit至线程池执行网络请求并发送start,success等消息
- AsyncHttpResponseHandler
接收请求结果,一般重写onSuccess及onFailure接收请求成功或失败的消息,还有onStart,onFinish等消息
- TextHttpResponseHandler
继承自AsyncHttpResponseHandler,只是重写了AsyncHttpResponseHandler的onSuccess和onFailure方法,将请求结果由byte数组转换为String
- JsonHttpResponseHandler
继承自TextHttpResponseHandler,同样是重写onSuccess和onFailure方法,将请求结果由String转换为JSONObject或JSONArray
- BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler
继承自TextHttpResponseHandler,是一个泛型类,提供了parseResponse方法,子类需要提供实现,将请求结果解析成需要的类型,子类可以灵活地使用解析方法,可以直接原始解析,使用gson等。
- RequestParams
请求参数,可以添加普通的字符串参数,并可添加File,InputStream上传文件
- AsyncHttpClient
核心类,使用HttpClient执行网络请求,提供了get,put,post,delete,head等请求方法,使用起来很简单,只需以url及RequestParams调用相应的方法即可,还可以选择性地传入Context,用于取消Content相关的请求,同时必须提供ResponseHandlerInterface(AsyncHttpResponseHandler继承自ResponseHandlerInterface)的实现类,一般为AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类,AsyncHttpClient内部有一个线程池,当使用AsyncHttpClient执行网络请求时,最终都会调用sendRequest方法,在这个方法内部将请求参数封装成AsyncHttpRequest(继承自Runnable)交由内部的线程池执行。
- SyncHttpClient
继承自AsyncHttpClient,同步执行网络请求,AsyncHttpClient把请求封装成AsyncHttpRequest后提交至线程池,SyncHttpClient把请求封装成AsyncHttpRequest后直接调用它的run方法。
请求流程

- 调用AsyncHttpClient的get或post等方法发起网络请求
- 所有的请求都走了sendRequest,在sendRequest中把请求封装为了AsyncHttpRequest,并添加到线程池执行
- 当请求被执行时(即AsyncHttpRequest的run方法),执行AsyncHttpRequest的makeRequestWithRetries方法执行实际的请求,当请求失败时可以重试。并在请求开始,结束,成功或失败时向请求时传的ResponseHandlerInterface实例发送消息
- 基本上使用的都是AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类,调用其onStart,onSuccess等方法返回请求结果
详细使用方法
官方建议使用一个静态的AsyncHttpClient,像下面的这样:
public class TwitterRestClient { private static final String BASE_URL = "http://api.twitter.com/1/"; private static AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient(); public static void get(String url, RequestParams params, AsyncHttpResponseHandler responseHandler) { client.get(getAbsoluteUrl(url), params, responseHandler); } public static void post(String url, RequestParams params, AsyncHttpResponseHandler responseHandler) { client.post(getAbsoluteUrl(url), params, responseHandler); } private static String getAbsoluteUrl(String relativeUrl) { return BASE_URL + relativeUrl; } }
封装的方法建议都加上Context参数,以在Activity pause或stop时取消掉没用的请求。
详细使用方法就不说了,直接看官方文档
其他说明及总结
Android-Async-Http的使用非常简单,通过AsyncHttpClient发起请求就可以了,如果需要添加参数,直接传一个RequestParams过去,而且参数可以是String、File和InputStream,可以很方便地上传文件。
每个请求都需要传一个ResponseHandlerInterface的实例用以接收请求结果或请求失败,请求结束等通知,一般是AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类。
通过BinaryHttpResponseHandler可以发起二进制请求,如请求图片。
通过TextHttpResponseHandler可以发起返回结果为字符串的请求,一般这个使用较多。
也可以使用它的子类JsonHttpResponseHandler,返回结果是一个JSONObject或JSONArray。不过感觉这个类作用不大,一是有另一个类BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler,可以直接解析返回的JSON数据,二是JsonHttpResponseHandler的方法太复杂了,有太多的onSuccess和onFailure方法,都不知道重写哪个了。

如上图所示,每个子类有太多的onSuccess和onFailure了,尤其是JsonHttpResponseHandler,这应该算是这个类库的不足吧。所以平时使用时基本不使用JsonHttpResponseHandler,而是直接使用TextHttpResponseHandler,当然也可以使用BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler。
这个类库还有一点不足,就是onSuccess等方法一般会在主线程执行,其实这么说不严谨,看代码吧:
public AsyncHttpResponseHandler() { boolean missingLooper = null == Looper.myLooper(); // Try to create handler if (!missingLooper) handler = new ResponderHandler(this); else { // There is no Looper on this thread so synchronous mode should be used. handler = null; setUseSynchronousMode(true); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Current thread has not called Looper.prepare(). Forcing synchronous mode."); } // Init Looper by calling postRunnable without an argument. postRunnable(null); }
可以看到,内部使用了Handler,当新建AsyncHttpResponseHandler的实例的时候会获取当前线程的Looper,如果为空就启用同步模式,即所有的回调都会在执行请求的线程中执行,当在一个普通的后台线程时这样执行是正常的,而我们一般都会在主线程发请请求,结果就是所有的回调都会在主线程中执行,这就限制了我们在onSuccess中执行耗时操作,比如请求成功后将数据持久化到数据库。
不过可以看到创建Handler的时候使用了Looper对象,所以我们就可以改进一下其构造函数,添加一个Looper参数(同步修改子类),这样所有的回调就都会在Looper所在线程执行,这样我们只需要开启一个HandlerThread就行了。但这样和Looper为空时一样有一个弊端,如果要更新UI操作的话,还需要向一个主线程的Handler发送消息让UI更新。还有第二个弊端,所有回调都在同一个HandlerThread中执行,如果一个处理耗时太久会阻塞后面的请求结果处理,如果只是简单地写个数据库影响应该不大,如果真耗时太久,为这个耗时处理再开个线程吧。
android-async-http开源项目可以是我们轻松的获取网络数据或者向服务器发送数据,使用起来非常简单,关于android-async-http开源项目的介绍内容来自于官方:http://loopj.com/android-async-http/.下面我对此主页上内容进行大体上的翻译,希望能够对你理解android-async-http开源项目有所帮助
1.1 Overview(概况)
An asynchronous callback-based Http client for Android built on top of Apache’s HttpClient libraries. All requests are made outside of your app’s main UI thread, but any callback logic will be executed on the same thread as the callback was created using Android’s Handler message passing.
译文:
异步基于回调的Http客户端为Android构建,是基于Apache HttpClient库的。所有的请求都是位于应用程序主线程 UI 之外,但任何回调逻辑将相同的线程上执行回调,使用Android的处理程序创建消息传递。
1.2 Features(特征)
- Make asynchronous HTTP requests, handle responses in anonymous callbacks
- 进行异步HTTP请求,处理响应在匿名回调中完成
- HTTP requests happen outside the UI thread
- HTTP请求发生在UI线程之外
- Requests use a threadpool to cap concurrent resource usage
- 请求使用threadpool,限制并发资源使用情况
- GET/POST params builder (RequestParams)
- GET / POST参数构建使用(RequestParams)
- Multipart file uploads with no additional third party libraries
- Multipart 文件上传,没有额外的第三方库
- Tiny size overhead to your application, only 25kb for everything
- 在你的应用程序上利用很小的开销,仅仅25 kb就可以做一切
- Automatic smart request retries optimized for spotty mobile connections
- 自动智能请求重试,优化了质量不一的移动连接
- Automatic gzip response decoding support for super-fast requests
- 自动解码支持gzip反应速度超快的请求
- Binary file (images etc) downloading with
BinaryHttpResponseHandler -
二进制文件(图片等)的下载,使用BinaryHttpResponseHandler
- Built-in response parsing into JSON with
JsonHttpResponseHandler -
内置响应解析成JSON,使用JsonHttpResponseHandler
- Persistent cookie store, saves cookies into your app’s SharedPreferences
- 持久化cookie存储,保存cookie到你的应用程序的SharedPreferences
2. Installation & Basic Usage( 安装和基本用法)
Download the latest .jar file from github and place it in your Android app’s libs/ folder.
从github上下载最新的最新的jar文件.并将其放置在你的Android应用程序的libs /文件夹.
2.1下载方式:
1.从http://loopj.com/android-async-http/的页面下载
点击DownLoad即可下载最新的jar文件
2.从https://github.com/loopj/android-async-http的页面下载
找到DownLoad ZIP进行下载文件,解压后的目录如下
examples:里面有简单的例子
library:里面存放的是android-async-http开源项目的源码(方法一:可以把library\src\main\java文件下面的文件拷贝到,你应用的src下也可以直接使用)
releases:里面存放的是各个版本的jar文件,(方法二:只需把最新的jar文件拷贝到你应用的libs目录下即可.)
samples:里面存放的也是例子(可供参考)
备注:方法一和方法二只能采用其中之一,建议采用方法二
2.2使用方法
Import the http package.
Create a new AsyncHttpClient instance and make a request:
Adding GET/POST Parameters with RequestParams
The RequestParams class is used to add optional GET or POST parameters to your requests.RequestParams can be built and constructed in various ways:
Create empty RequestParams and immediately add some parameters:
Create RequestParams for a single parameter:
Create RequestParams from an existing Map of key/value strings:
See the RequestParams Javadoc for more information.
Add an InputStream to the RequestParams to upload:
Add a File object to the RequestParams to upload:
Add a byte array to the RequestParams to upload:
See the RequestParams Javadoc for more information.
Downloading Binary Data with BinaryHttpResponseHandler
The BinaryHttpResponseHandler class can be used to fetch binary data such as images and other files. For example:
See the BinaryHttpResponseHandler Javadoc for more information.
AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient(); client.get("http://www.google.com", new AsyncHttpResponseHandler() { @Override public void onSuccess(String response) { System.out.println(response); } });
通过AsyncHttpClient类的实例就可以执行网络请求,包括get、put、post、head、delete。并指定一个ResponseHandlerInterface的实例接收请求结果。(onSuccess参数不对,此处只说明基本用法,详细参数看源码)
主要类介绍
- AsyncHttpRequest
继承自Runnabler,被submit至线程池执行网络请求并发送start,success等消息
- AsyncHttpResponseHandler
接收请求结果,一般重写onSuccess及onFailure接收请求成功或失败的消息,还有onStart,onFinish等消息
- TextHttpResponseHandler
继承自AsyncHttpResponseHandler,只是重写了AsyncHttpResponseHandler的onSuccess和onFailure方法,将请求结果由byte数组转换为String
- JsonHttpResponseHandler
继承自TextHttpResponseHandler,同样是重写onSuccess和onFailure方法,将请求结果由String转换为JSONObject或JSONArray
- BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler
继承自TextHttpResponseHandler,是一个泛型类,提供了parseResponse方法,子类需要提供实现,将请求结果解析成需要的类型,子类可以灵活地使用解析方法,可以直接原始解析,使用gson等。
- RequestParams
请求参数,可以添加普通的字符串参数,并可添加File,InputStream上传文件
- AsyncHttpClient
核心类,使用HttpClient执行网络请求,提供了get,put,post,delete,head等请求方法,使用起来很简单,只需以url及RequestParams调用相应的方法即可,还可以选择性地传入Context,用于取消Content相关的请求,同时必须提供ResponseHandlerInterface(AsyncHttpResponseHandler继承自ResponseHandlerInterface)的实现类,一般为AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类,AsyncHttpClient内部有一个线程池,当使用AsyncHttpClient执行网络请求时,最终都会调用sendRequest方法,在这个方法内部将请求参数封装成AsyncHttpRequest(继承自Runnable)交由内部的线程池执行。
- SyncHttpClient
继承自AsyncHttpClient,同步执行网络请求,AsyncHttpClient把请求封装成AsyncHttpRequest后提交至线程池,SyncHttpClient把请求封装成AsyncHttpRequest后直接调用它的run方法。
请求流程

- 调用AsyncHttpClient的get或post等方法发起网络请求
- 所有的请求都走了sendRequest,在sendRequest中把请求封装为了AsyncHttpRequest,并添加到线程池执行
- 当请求被执行时(即AsyncHttpRequest的run方法),执行AsyncHttpRequest的makeRequestWithRetries方法执行实际的请求,当请求失败时可以重试。并在请求开始,结束,成功或失败时向请求时传的ResponseHandlerInterface实例发送消息
- 基本上使用的都是AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类,调用其onStart,onSuccess等方法返回请求结果
详细使用方法
官方建议使用一个静态的AsyncHttpClient,像下面的这样:
public class TwitterRestClient { private static final String BASE_URL = "http://api.twitter.com/1/"; private static AsyncHttpClient client = new AsyncHttpClient(); public static void get(String url, RequestParams params, AsyncHttpResponseHandler responseHandler) { client.get(getAbsoluteUrl(url), params, responseHandler); } public static void post(String url, RequestParams params, AsyncHttpResponseHandler responseHandler) { client.post(getAbsoluteUrl(url), params, responseHandler); } private static String getAbsoluteUrl(String relativeUrl) { return BASE_URL + relativeUrl; } }
封装的方法建议都加上Context参数,以在Activity pause或stop时取消掉没用的请求。
详细使用方法就不说了,直接看官方文档
其他说明及总结
Android-Async-Http的使用非常简单,通过AsyncHttpClient发起请求就可以了,如果需要添加参数,直接传一个RequestParams过去,而且参数可以是String、File和InputStream,可以很方便地上传文件。
每个请求都需要传一个ResponseHandlerInterface的实例用以接收请求结果或请求失败,请求结束等通知,一般是AsyncHttpResponseHandler的子类。
通过BinaryHttpResponseHandler可以发起二进制请求,如请求图片。
通过TextHttpResponseHandler可以发起返回结果为字符串的请求,一般这个使用较多。
也可以使用它的子类JsonHttpResponseHandler,返回结果是一个JSONObject或JSONArray。不过感觉这个类作用不大,一是有另一个类BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler,可以直接解析返回的JSON数据,二是JsonHttpResponseHandler的方法太复杂了,有太多的onSuccess和onFailure方法,都不知道重写哪个了。

如上图所示,每个子类有太多的onSuccess和onFailure了,尤其是JsonHttpResponseHandler,这应该算是这个类库的不足吧。所以平时使用时基本不使用JsonHttpResponseHandler,而是直接使用TextHttpResponseHandler,当然也可以使用BaseJsonHttpResponseHandler。
这个类库还有一点不足,就是onSuccess等方法一般会在主线程执行,其实这么说不严谨,看代码吧:
public AsyncHttpResponseHandler() { boolean missingLooper = null == Looper.myLooper(); // Try to create handler if (!missingLooper) handler = new ResponderHandler(this); else { // There is no Looper on this thread so synchronous mode should be used. handler = null; setUseSynchronousMode(true); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Current thread has not called Looper.prepare(). Forcing synchronous mode."); } // Init Looper by calling postRunnable without an argument. postRunnable(null); }
可以看到,内部使用了Handler,当新建AsyncHttpResponseHandler的实例的时候会获取当前线程的Looper,如果为空就启用同步模式,即所有的回调都会在执行请求的线程中执行,当在一个普通的后台线程时这样执行是正常的,而我们一般都会在主线程发请请求,结果就是所有的回调都会在主线程中执行,这就限制了我们在onSuccess中执行耗时操作,比如请求成功后将数据持久化到数据库。
不过可以看到创建Handler的时候使用了Looper对象,所以我们就可以改进一下其构造函数,添加一个Looper参数(同步修改子类),这样所有的回调就都会在Looper所在线程执行,这样我们只需要开启一个HandlerThread就行了。但这样和Looper为空时一样有一个弊端,如果要更新UI操作的话,还需要向一个主线程的Handler发送消息让UI更新。还有第二个弊端,所有回调都在同一个HandlerThread中执行,如果一个处理耗时太久会阻塞后面的请求结果处理,如果只是简单地写个数据库影响应该不大,如果真耗时太久,为这个耗时处理再开个线程吧。
android-async-http开源项目可以是我们轻松的获取网络数据或者向服务器发送数据,使用起来非常简单,关于android-async-http开源项目的介绍内容来自于官方:http://loopj.com/android-async-http/.下面我对此主页上内容进行大体上的翻译,希望能够对你理解android-async-http开源项目有所帮助
1.1 Overview(概况)
An asynchronous callback-based Http client for Android built on top of Apache’s HttpClient libraries. All requests are made outside of your app’s main UI thread, but any callback logic will be executed on the same thread as the callback was created using Android’s Handler message passing.
译文:
异步基于回调的Http客户端为Android构建,是基于Apache HttpClient库的。所有的请求都是位于应用程序主线程 UI 之外,但任何回调逻辑将相同的线程上执行回调,使用Android的处理程序创建消息传递。
1.2 Features(特征)
- Make asynchronous HTTP requests, handle responses in anonymous callbacks
- 进行异步HTTP请求,处理响应在匿名回调中完成
- HTTP requests happen outside the UI thread
- HTTP请求发生在UI线程之外
- Requests use a threadpool to cap concurrent resource usage
- 请求使用threadpool,限制并发资源使用情况
- GET/POST params builder (RequestParams)
- GET / POST参数构建使用(RequestParams)
- Multipart file uploads with no additional third party libraries
- Multipart 文件上传,没有额外的第三方库
- Tiny size overhead to your application, only 25kb for everything
- 在你的应用程序上利用很小的开销,仅仅25 kb就可以做一切
- Automatic smart request retries optimized for spotty mobile connections
- 自动智能请求重试,优化了质量不一的移动连接
- Automatic gzip response decoding support for super-fast requests
- 自动解码支持gzip反应速度超快的请求
- Binary file (images etc) downloading with
BinaryHttpResponseHandler -
二进制文件(图片等)的下载,使用BinaryHttpResponseHandler
- Built-in response parsing into JSON with
JsonHttpResponseHandler -
内置响应解析成JSON,使用JsonHttpResponseHandler
- Persistent cookie store, saves cookies into your app’s SharedPreferences
- 持久化cookie存储,保存cookie到你的应用程序的SharedPreferences
2. Installation & Basic Usage( 安装和基本用法)
Download the latest .jar file from github and place it in your Android app’s libs/ folder.
从github上下载最新的最新的jar文件.并将其放置在你的Android应用程序的libs /文件夹.
2.1下载方式:
1.从http://loopj.com/android-async-http/的页面下载
点击DownLoad即可下载最新的jar文件
2.从https://github.com/loopj/android-async-http的页面下载
找到DownLoad ZIP进行下载文件,解压后的目录如下
examples:里面有简单的例子
library:里面存放的是android-async-http开源项目的源码(方法一:可以把library\src\main\java文件下面的文件拷贝到,你应用的src下也可以直接使用)
releases:里面存放的是各个版本的jar文件,(方法二:只需把最新的jar文件拷贝到你应用的libs目录下即可.)
samples:里面存放的也是例子(可供参考)
备注:方法一和方法二只能采用其中之一,建议采用方法二
2.2使用方法
Import the http package.
Create a new AsyncHttpClient instance and make a request:
Adding GET/POST Parameters with RequestParams
The RequestParams class is used to add optional GET or POST parameters to your requests.RequestParams can be built and constructed in various ways:
Create empty RequestParams and immediately add some parameters:
Create RequestParams for a single parameter:
Create RequestParams from an existing Map of key/value strings:
See the RequestParams Javadoc for more information.
Add an InputStream to the RequestParams to upload:
Add a File object to the RequestParams to upload:
Add a byte array to the RequestParams to upload:
See the RequestParams Javadoc for more information.
Downloading Binary Data with BinaryHttpResponseHandler
The BinaryHttpResponseHandler class can be used to fetch binary data such as images and other files. For example:
See the BinaryHttpResponseHandler Javadoc for more information.


























 3975
3975

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








