String的值是不可变的,这就导致每次对String的操作都会生成新的String对象,不仅效率低下,而且大量浪费有限的内存空间。
String a = "a"; //假设a指向地址0x0001
a = "b";//重新赋值后a指向地址0x0002,但0x0001地址中保存的"a"依旧存在,但已经不再是a所指向的,a 已经指向了其它地址。
因此String的操作都是改变赋值地址而不是改变值操作。
2. StringBuffer是可变类,和线程安全的字符串操作类,任何对它指向的字符串的操作都不会产生新的对象。 每个StringBuffer对象都有一定的缓冲区容量,当字符串大小没有超过容量时,不会分配新的容量,当字符串大小超过容量时,会自动增加容量。
StringBuffer buf=new StringBuffer(); //分配长16字节的字符缓冲区
StringBuffer buf=new StringBuffer(512); //分配长512字节的字符缓冲区
StringBuffer buf=new StringBuffer("this is a test")//在缓冲区中存放了字符串,并在后面预留了16字节的空缓冲区。
3.StringBuilder( 内部有维护ArrayList )
StringBuffer和StringBuilder类功能基本相似,主要区别在于StringBuffer类的方法是多线程、安全的,而StringBuilder不是线程安全的,相比而言,StringBuilder类会略微快一点。对于经常要改变值的字符串应该使用StringBuffer和StringBuilder类。
4.线程安全
StringBuffer 线程安全
StringBuilder 线程不安全
5.速度
一般情况下,速度从快到慢:StringBuilder>StringBuffer>String,这种比较是相对的,不是绝对的。
6.总结
(1).如果要操作少量的数据用 = String
(2).单线程操作字符串缓冲区 下操作大量数据 = StringBuilder
(3).多线程操作字符串缓冲区 下操作大量数据 = StringBuffer
以下是代码与演示说明:
public class TestCharacter {
final static int time = 50000; //循环次数
public TestCharacter(){
}
public void test(String s){
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0; i<time; i++){
s += “add”;
}
long over = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(“操作”+s.getClass().getName()+”类型使用的时间为:”+(over-begin)+”毫秒”);
}
public void test(StringBuffer s){
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0; i<time; i++){
s.append(“add”);
}
long over = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(“操作”+s.getClass().getCanonicalName()+”类型使用的时间为:”+(over-begin)+”毫秒”);
}
public void test(StringBuilder s){
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0; i<time; i++){
s.append(“add”);
}
long over = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(“操作”+s.getClass().getName()+”类型使用的时间为:”+(over-begin)+”毫秒”);
}
/*对 String 直接进行字符串拼接的测试*/
public void test2(){
String s2 = “abcd”;
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0; i<time; i++){
String s = s2 + s2 +s2;
}
long over = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(“操作字符串对象引用相加类型使用的时间为:”+(over-begin)+”毫秒”);
}
public void test3(){
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0; i<time; i++){
String s =”abcd” + “abcd” + “abcd”;
}
long over = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(“操作字符串相加使用的时间为:”+(over-begin)+”毫秒”);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String s1 = “abcd”;
StringBuffer st1 = new StringBuffer(“abcd”);
StringBuilder st2 = new StringBuilder(“abcd”);
TestCharacter tc = new TestCharacter();
tc.test(s1);
tc.test(st1);
tc.test(st2);
tc.test2();
tc.test3();
}
}
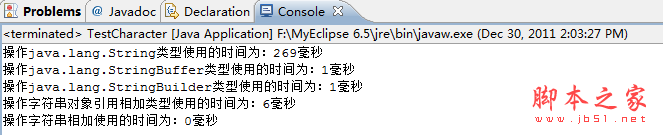
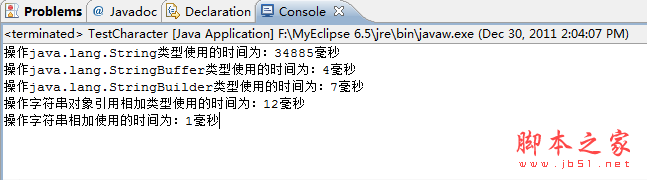
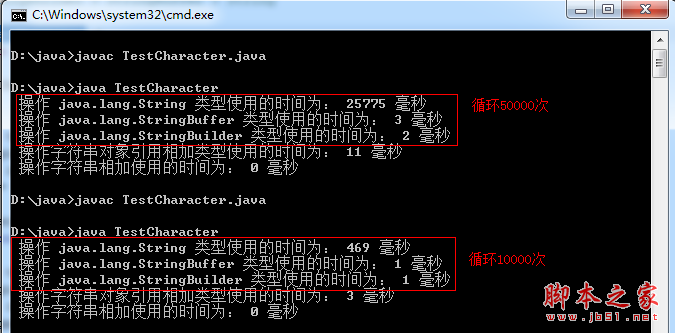
我在myeclipse和dos下都运行了这段代码,各自打印出的时间有些不同,运行结果如下:
1)myeclipse下循环10000次时:
参考:http://www.jb51.net/article/33398.htm
三种形式源码解析:
长久以来,我们被教导字符串的连接最好用StringBuffer、StringBuilder,但是我们却不知道这两者之间的区别.跟字符串相关的一些方法中总是有CharSequence、StringBuffer、StringBuilder、String,他们之间到底有什么联系呢?
1、从类的定义看CharSequence、StringBuffer、StringBuilder、String的关系
下面先贴上这四者的定义(来自JDK1.6)
CharSequence是一个定义字符串操作的接口,StringBuffer、StringBuilder、String中都实现了这个接口.
//CharSequence定义 public interface CharSequence //StringBuffer定义 public final class StringBuffer extends AbstractStringBuilder implements java.io.Serializable, CharSequence //StringBuilder定义 public final class StringBuilder extends AbstractStringBuilder implements java.io.Serializable, CharSequence //String定义 public final class String implementsjava.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence
String 是java中的字符串,它继承于CharSequence。
String类所包含的API接口非常多。为了便于今后的使用,我对String的API进行了分类,并都给出的演示程序。
String 和 CharSequence 关系
String 继承于CharSequence,也就是说String也是CharSequence类型。
CharSequence是一个接口,它只包括length(), charAt(int index), subSequence(int start, int end)这几个API接口。除了String实现了CharSequence之外,StringBuffer和StringBuilder也实现了CharSequence接口。
也就是说,CharSequence其实也就是定义了字符串操作的接口,其他具体的实现是由String、StringBuilder、StringBuffer完成的,String、StringBuilder、StringBuffer都可以转化为CharSequence类型。
StringBuilder 和 StringBuffer 的区别
StringBuilder 和 StringBuffer都是可变的字符序列。它们都继承于AbstractStringBuilder,实现了CharSequence接口。
但是,StringBuilder是非线程安全的,而StringBuffer是线程安全的。
它们之间的关系图如下:

2、从构造函数到具体的字符串拼接操作看看String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder的区别
下面我们来分析一下String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder具体的构造函数,了解他们是怎么构造出来的,再看看具体的字符串连接操作。
(1)String
String的构造函数(几个常见的构造函数)
public String() { this.offset = 0; this.count = 0; this.value = new char[0]; } /** * Initializes a newly created {@code String} object so that it represents * the same sequence of characters as the argument; in other words, the * newly created string is a copy of the argument string. Unless an * explicit copy of {@code original} is needed, use of this constructor is * unnecessary since Strings are immutable. * * @param original * A {@code String} */ public String(String original) { int size = original.count; char[] originalValue = original.value; char[] v; if (originalValue.length > size) { // The array representing the String is bigger than the new // String itself. Perhaps this constructor is being called // in order to trim the baggage, so make a copy of the array. int off = original.offset; v = Arrays.copyOfRange(originalValue, off, off + size); } else { // The array representing the String is the same // size as the String, so no point in making a copy. v = originalValue; } this.offset = 0; this.count = size; this.value = v; } /** * Allocates a new {@code String} so that it represents the sequence of * characters currently contained in the character array argument. The * contents of the character array are copied; subsequent modification of * the character array does not affect the newly created string. * * @param value * The initial value of the string */ public String(char[] value) { this.offset = 0; this.count = value.length; this.value = StringValue.from(value); }
再看看String中具体的Concat函数
public String concat(String str) { int otherLen = str.length(); if (otherLen == 0) { return this; } char[] buf = new char[count + otherLen]; getChars(0, count, buf, 0); str.getChars(0, otherLen, buf, count); return new String(0, count + otherLen, buf);//注意:这里返回一个新的字符串 }
从Concat函数中,我们可以知道在对字符串使用concat操作后,具体的操作new出一个等同于两个字符串连接总长度的新的char数组,然后将两个字符串复制到新的char数组中,然后返回一个新的String对象。
(2)StringBuilder
StringBuilder常见构造函数
public StringBuffer() { super(16);//默认16字节 } public StringBuffer(int capacity) { super(capacity); }
从StringBuilder的构造函数中,我们可以看见StringBuilder直接调用父类(AbstractStringBuilder)的构造函数,我们再看看AbstractStringBuilder的构造函数
abstract class AbstractStringBuilder implements Appendable, CharSequence { final static int[] sizeTable = { 9, 99, 999, 9999, 99999, 999999, 9999999, 99999999, 999999999, Integer.MAX_VALUE }; /** * The value is used for character storage. */ char[] value; /** * The count is the number of characters used. */ int count; /** * This no-arg constructor is necessary for serialization of subclasses. */ AbstractStringBuilder() { } /** * Creates an AbstractStringBuilder of the specified capacity. */ AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity) { value = new char[capacity]; } //其他的一些逻辑 }
从AbstractStringBuilder的构造函数中,我们可以看出StringBuilder中存储字符串其实用的是一个char数组,capacity其实就是指定这个char数组的大小。
下面我们再从StringBuilder中的append函数看看他具体是怎么做的(以 append(String str) 为例看看)。
public StringBuilder append(String str) { super.append(str); return this; }
又是直接调用父类(AbstractStringBuilder)的append方法,再跟到父类中去看看。
/** * value 用来存储字符串. */ char value[]; /** * 有效字符串的数目. */ int count; public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) { if (str == null) { str = "null"; } int len = str.length(); if (len == 0) { return this; } int newCount = count + len; if (newCount > value.length) { expandCapacity(newCount); } //getChars将字符串复制到指定的位置 str.getChars(0, len, value, count); count = newCount; return this;//没有创建新对象 }
上面的逻辑还是比较简单的,在append(str)函数调用的时候,首先会判断原来用于存储字符串的values的字符串数组有没有足够的大小来存储将要新添加入StringBuilder的字符串。如果不够用,那么就调用expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity)让容量翻两倍(一般是扩大两倍,特殊情况见代码),如果够用,那么就直接添加进去。
/** * This implements the expansion semantics of ensureCapacity with no * size check or synchronization. */ void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) { int newCapacity = (value.length + 1) * 2; if (newCapacity < 0) { newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE; } else if (minimumCapacity > newCapacity) { newCapacity = minimumCapacity; } value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity); }
(3)StringBuffer
StringBuffer的构造函数
/** * Constructs a string buffer with no characters in it and an * initial capacity of 16 characters. */ public StringBuffer() { super(16); } /** * Constructs a string buffer with no characters in it and * the specified initial capacity. * * @param capacity the initial capacity. * @exception NegativeArraySizeException if the <code>capacity</code> * argument is less than <code>0</code>. */ public StringBuffer(int capacity) { super(capacity); }
StringBuffer也是直接调用父类(AbstractStringBuilder)的构造函数,那么我们从上面的分析中,就可以知道StringBuffer其实也是利用char[]类型的数组来保存字符串数组的。
再看看StringBuffer的append函数
public synchronized StringBuffer append(String str) { super.append(str); return this; }
还是调用父类的append函数,但是在这里有值得注意的地方,StringBuffer的append函数有一个synchronized标识符,也就是说StringBuffer中的append函数是线程安全的,通过继续查阅其他StringBuffer中的函数,我们也可以发现他们有synchronized标识符,这就不难理解为什么StringBuffer是线程安全的,但是很明显加上线程控制会拖慢程序运行的速度,所以如果不需要线程控制,那么最好就用StringBuilder。
//下面只是节选一些StringBuffer中的函数 synchronized StringBuffer append(char ch) synchronized StringBuffer append(char[] chars) synchronized StringBuffer append(char[] chars, int start, int length) synchronized StringBuffer append(Object obj) synchronized StringBuffer append(String string) synchronized StringBuffer append(StringBuffer sb) synchronized StringBuffer append(CharSequence s) synchronized StringBuffer append(CharSequence s, int start, int end) synchronized StringBuffer insert(int index, char ch) synchronized StringBuffer insert(int index, char[] chars) synchronized StringBuffer insert(int index, char[] chars, int start, int length) synchronized StringBuffer insert(int index, String string) StringBuffer insert(int index, Object obj)
后记:
String x = "a1" + "a2"
其实在编译后,代码变为
String x = (new StringBuilder(String.valueOf("a1"))).append("a2").toString();
这就是为什么在操作String时建议采用StringBuffer了,上面的操作显然对多次String的相加不利。
可能很多同学会想了解String中的+和StringBuilder.append的效率,以及纠结要用哪个。我在网上发现有人已经写了一篇文章,分享给大家在Java中连接字符串时是使用+号还是使用StringBuilder。
参考链接
在Java中连接字符串时是使用+号还是使用StringBuilder
String详解, String和CharSequence区别, StringBuilder和StringBuffer的区别 (String系列之1)
http://www.cnblogs.com/kissazi2/p/3648671.html























 7394
7394











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








