一、使用场景举例
在了解@Transactional怎么用之前我们必须要先知道@Transactional有什么用。下面举个栗子:比如一个部门里面有很多成员,这两者分别保存在部门表和成员表里面,在删除某个部门的时候,假设我们默认删除对应的成员。但是在执行的时候可能会出现这种情况,我们先删除部门,再删除成员,但是部门删除成功了,删除成员的时候出异常了。这时候我们希望如果成员删除失败了,之前删除的部门也取消删除。这种场景就可以使用@Transactional事物回滚。
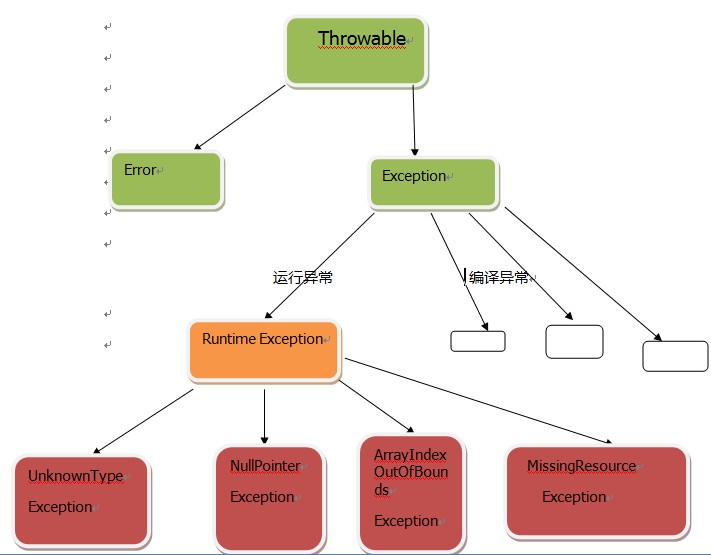
二、checked异常和unchecked异常
这里之所以让大家清楚checked异常和unchecked异常概念,是因为:
Spring使用声明式事务处理,默认情况下,如果被注解的数据库操作方法中发生了unchecked异常,所有的数据库操作将rollback;如果发生的异常是checked异常,默认情况下数据库操作还是会提交的。
checked异常:
表示无效,不是程序中可以预测的。比如无效的用户输入,文件不存在,网络或者数据库链接错误。这些都是外在的原因,都不是程序内部可以控制的。
必须在代码中显式地处理。比如try-catch块处理,或者给所在的方法加上throws说明,将异常抛到调用栈的上一层。
继承自java.lang.Exception(java.lang.RuntimeException除外)。
unchecked异常:
表示错误,程序的逻辑错误。是RuntimeException的子类,比如IllegalArgumentException, NullPointerException和IllegalStateException。
不需要在代码中显式地捕获unchecked异常做处理。
继承自java.lang.RuntimeException(而java.lang.RuntimeException继承自java.lang.Exception)。
看下面的异常结构图或许层次感更加深些:
三、@Transactional的使用实例
本实例采用的是Eclipse+maven,maven只是作为jar管理,即便不了解的maven的猿友也可以读懂。
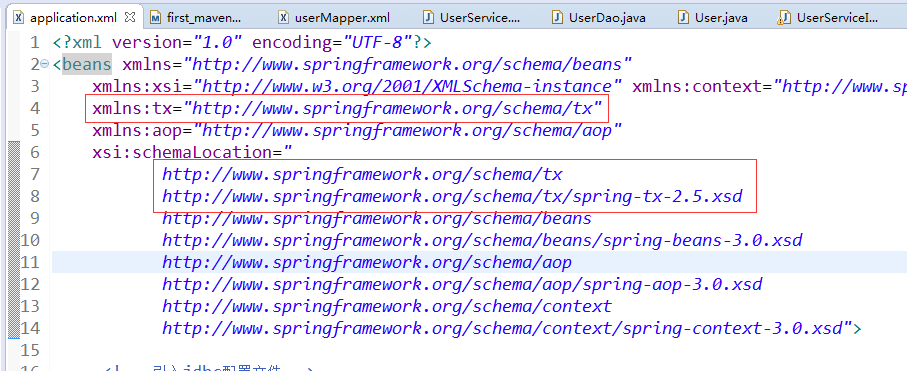
3.1、spring的配置文件
里面必须先配置tx名字空间如下:
为了使用基于@Transactional的事务管理,需要在Spring中进行如下的配置:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<bean id=
"appTransactionManager"
class
=
"org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"
>
<property name=
"dataSource"
ref=
"dataSource"
/>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven proxy-target-
class
=
"false"
transaction-manager=
"appTransactionManager"
/>
|
博主的整个spring配置文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
|
<?xml version=
"1.0"
encoding=
"UTF-8"
?>
<beans xmlns=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi=
"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/context
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<!-- 引入jdbc配置文件 -->
<bean id=
"propertyConfigurer"
class
=
"org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"
>
<property name=
"locations"
>
<list>
<value>classpath:properties/*.properties</value>
<!--要是有多个配置文件,只需在这里继续添加即可 -->
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id=
"dataSource"
class
=
"org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"
>
<!-- 不使用properties来配置 -->
<!-- <property name=
"driverClassName"
value=
"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
/>
<property name=
"url"
value=
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/learning"
/>
<property name=
"username"
value=
"root"
/>
<property name=
"password"
value=
"christmas258@"
/> -->
<!-- 使用properties来配置 -->
<property name=
"driverClassName"
>
<value>${jdbc_driverClassName}</value>
</property>
<property name=
"url"
>
<value>${jdbc_url}</value>
</property>
<property name=
"username"
>
<value>${jdbc_username}</value>
</property>
<property name=
"password"
>
<value>${jdbc_password}</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id=
"appTransactionManager"
class
=
"org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"
>
<property name=
"dataSource"
ref=
"dataSource"
/>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven proxy-target-
class
=
"false"
transaction-manager=
"appTransactionManager"
/>
<!-- 自动扫描了所有的XxxxMapper.xml对应的mapper接口文件,这样就不用一个一个手动配置Mpper的映射了,只要Mapper接口类和Mapper映射文件对应起来就可以了。 -->
<bean
class
=
"org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"
>
<property name=
"basePackage"
value=
"com.luo.dao"
/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置Mybatis的文件 ,mapperLocations配置**Mapper.xml文件位置,configLocation配置mybatis-config文件位置-->
<bean id=
"sqlSessionFactory"
class
=
"org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"
>
<property name=
"dataSource"
ref=
"dataSource"
/>
<property name=
"mapperLocations"
value=
"classpath:mapper/*.xml"
/>
<property name=
"configLocation"
value=
"classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml"
/>
<!-- <property name=
"typeAliasesPackage"
value=
"com.tiantian.ckeditor.model"
/> -->
</bean>
<!-- 自动扫描注解的bean -->
<context:component-scan base-
package
=
"com.luo.service"
/>
</beans>
|
3.2、使用@Transactional,在添加用户实现类方法加上注解
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Transactional
(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
public
void
addUser(User user) {
userDao.addUser(user);
String string =
null
;
if
(string.equals(
""
)) {
int
i =
0
;
}
}
|
上面的方法我故意让其出现空指针异常,会事物回滚
3.3、运行单元测试类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@Test
public
void
addUserTest(){
User user =
new
User();
user.setUserName(
"luoguohui1"
);
user.setUserPassword(
"luoguohui1"
);
userService.addUser(user);
}
|
发现无法插入进去,但是如果把@Transactional去掉,即代码如下,虽然出现异常,但是数据库中还是有添加对应数据的:
3.4、源码下载
本文的工程是在mybatis入门(含实例教程和源码)的基础上修改的,该文包含了数据库脚本及工程搭建的详细流程。
本文最终源码下载:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/u013142781/9381184
四、Spring中的@Transactional必须要了解的概念
Spring中的@Transactional基于动态代理的机制,提供了一种透明的事务管理机制,方便快捷解决在开发中碰到的问题。
一般使用是通过如下代码对方法或接口或类注释:
|
1
|
@Transactional
(propagation=Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED)
|
Propagation支持7种不同的传播机制:
REQUIRED:如果存在一个事务,则支持当前事务。如果没有事务则开启一个新的事务。
SUPPORTS: 如果存在一个事务,支持当前事务。如果没有事务,则非事务的执行。但是对于事务同步的事务管理器,PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS与不使用事务有少许不同。
NOT_SUPPORTED:总是非事务地执行,并挂起任何存在的事务。
REQUIRESNEW:总是开启一个新的事务。如果一个事务已经存在,则将这个存在的事务挂起。
MANDATORY:如果已经存在一个事务,支持当前事务。如果没有一个活动的事务,则抛出异常。
NEVER:总是非事务地执行,如果存在一个活动事务,则抛出异常
NESTED:如果一个活动的事务存在,则运行在一个嵌套的事务中。如果没有活动事务,则按REQUIRED属性执行。
下面是一些需要注意的事项,必须必须必须要看,不然遇到各种坑别说博主没有提醒你哦:
下面是一些需要注意的事项,必须必须必须要看,不然遇到各种坑别说博主没有提醒你哦:
下面是一些需要注意的事项,必须必须必须要看,不然遇到各种坑别说博主没有提醒你哦:
- 在需要事务管理的地方加@Transactional 注解。@Transactional 注解可以被应用于接口定义和接口方法、类定义和类的 public 方法上。
- @Transactional 注解只能应用到 public 可见度的方法上。 如果你在 protected、private 或者 package-visible 的方法上使用 @Transactional 注解,它也不会报错, 但是这个被注解的方法将不会展示已配置的事务设置。
- 注意仅仅 @Transactional 注解的出现不足于开启事务行为,它仅仅 是一种元数据。必须在配置文件中使用配置元素,才真正开启了事务行为。
- 通过 元素的 “proxy-target-class” 属性值来控制是基于接口的还是基于类的代理被创建。如果 “proxy-target-class” 属值被设置为 “true”,那么基于类的代理将起作用(这时需要CGLIB库cglib.jar在CLASSPATH中)。如果 “proxy-target-class” 属值被设置为 “false” 或者这个属性被省略,那么标准的JDK基于接口的代理将起作用。
- Spring团队建议在具体的类(或类的方法)上使用 @Transactional 注解,而不要使用在类所要实现的任何接口上。在接口上使用 @Transactional 注解,只能当你设置了基于接口的代理时它才生效。因为注解是 不能继承 的,这就意味着如果正在使用基于类的代理时,那么事务的设置将不能被基于类的代理所识别,而且对象也将不会被事务代理所包装。
- @Transactional 的事务开启 ,或者是基于接口的 或者是基于类的代理被创建。所以在同一个类中一个方法调用另一个方法有事务的方法,事务是不会起作用的。
1. 在需要事务管理的地方加@Transactional 注解。@Transactional 注解可以被应用于接口定义和接口方法、类定义和类的 public 方法上。
2. @Transactional 注解只能应用到 public 可见度的方法上。 如果你在 protected、private 或者 package-visible 的方法上使用 @Transactional 注解,它也不会报错, 但是这个被注解的方法将不会展示已配置的事务设置。
3. 注意仅仅 @Transactional 注解的出现不足于开启事务行为,它仅仅 是一种元数据。必须在配置文件中使用配置元素,才真正开启了事务行为。
4. 通过 元素的 "proxy-target-class" 属性值来控制是基于接口的还是基于类的代理被创建。如果 "proxy-target-class" 属值被设置为 "true",那么基于类的代理将起作用(这时需要CGLIB库cglib.jar在CLASSPATH中)。如果 "proxy-target-class" 属值被设置为 "false" 或者这个属性被省略,那么标准的JDK基于接口的代理将起作用。
标准的JDK基于接口的代理将起作用-->
proxy-target-class="false"/>
基于类的代理将起作用 ,同时 cglib.jar必须在CLASSPATH中
proxy-target-class="true"/>
-->
非JTA事务(即非分布式事务), 事务配置的时候 ,需要指定dataSource属性(非分布式事务,事务是在数据库创建的链接上开启。)-->
JTA事务(非分布式事务), 事务配置的时候 ,不能指定dataSource属性(分布式事务,是有全局事务来管理数据库链接的)-->
注解@Transactional cglib与java动态代理最大区别是代理目标对象不用实现接口,那么注解要是写到接口方法上,要是使用cglib代理,这是注解事物就失效了,为了保持兼容注解最好都写到实现类方法上。
5. Spring团队建议在具体的类(或类的方法)上使用 @Transactional 注解,而不要使用在类所要实现的任何接口上。在接口上使用 @Transactional 注解,只能当你设置了基于接口的代理时它才生效。因为注解是 不能继承 的,这就意味着如果正在使用基于类的代理时,那么事务的设置将不能被基于类的代理所识别,而且对象也将不会被事务代理所包装。
6. @Transactional 的事务开启 ,或者是基于接口的 或者是基于类的代理被创建。所以在同一个类中一个方法调用另一个方法有事务的方法,事务是不会起作用的。
public interface PersonService {
//删除指定id的person
public void delete(Integer personid) ;
//删除指定id的person,flag
public void delete(Integer personid,boolean flag) ;
}
public class PersonServiceBean implements PersonService {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void delete(Integer personid){
try{
this.delete(personid,true)
System.out.println("delete success");
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("delete failed");
}
}
@Transactional
//此时,事务根本就没有开启, 即数据库会默认提交该操作,即记录别删除掉 public void delete(Integer personid,boolean flag){
if(flag == ture){
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from person where id=?", new Object[]{personid},
new int[]{java.sql.Types.INTEGER});
throw new RuntimeException("运行期例外");
}
}
}
public class PersonServiceBeanTest{
PersonService ps = new PersonServiceBean ();
ps.delete(5);
}
7. Spring使用声明式事务处理,默认情况下,如果被注解的数据库操作方法中发生了unchecked异常,所有的数据库操作将rollback;如果发生的异常是checked异常,默认情况下数据库操作还是会提交的。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public interface PersonService {
//删除指定id的person
public void delete(Integer personid) ;
//获取person
public Person getPerson(Integer personid);
}
//PersonServiceBean 实现了PersonService 接口,则基于接口的还是基于类的代理 都可以实现事务
@Transactional public class PersonServiceBean implements PersonService {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//发生了unchecked异常,事务回滚, @Transactional
public void delete(Integer personid){
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from person where id=?", new Object[]{personid},
new int[]{java.sql.Types.INTEGER});
throw new RuntimeException("运行期例外");
}
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public interface PersonService {
//删除指定id的person
public void delete(Integer personid) throws Exception;
//获取person
public Person getPerson(Integer personid);
}
@Transactional
public class PersonServiceBean implements PersonService {
//发生了checked异常,事务不回滚,即数据库记录仍能被删除,
//checked的例外,需要我们在外部用try/catch语法对调用该方法的地方进行包含 @Transactional
public void delete(Integer personid) throws Exception{
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from person where id=?", new Object[]{personid},
new int[]{java.sql.Types.INTEGER});
throw new Exception("运行期例外");
}
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
但是,对于checked这种例外,默认情况下它是不会进行事务回滚的,但是如果我们需要它进行事务回滚,这时候可以在delete方法上通过@Transaction这个注解来修改它的行为。
@Transactional
public class PersonServiceBean implements PersonService {
@Transactional(rollbackFor=Exception.class)
//rollbackFor这属性指定了,既使你出现了checked这种例外,那么它也会对事务进行回滚
public void delete(Integer personid) throws Exception{
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from person where id=?", new Object[]{personid},
new int[]{java.sql.Types.INTEGER});
throw new Exception("运行期例外");
}
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
在PersonServiceBean这个业务bean里面,有一些事务是不需要事务管理的,好比说获取数据的getPersons方法,getPerson方法。因为@Transactional 放在了类的上面。
此时,可以采用propagation这个事务属性@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED),propagation这个属性指定了事务传播行为,我们可以指定它不支持事务,当我们这么写了之后,Spring容器在getPersons方法执行前就不会开启事务.
@Transactional
public class PersonServiceBean implements PersonService {
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED)
//则此方法 就不会开启事务了
public Person getPerson(Integer personid)
{
}
}






















 5682
5682

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








