1. 简述
题目描述:
Str1中可能包含的字符:除了'*'和'?'以外的任意字符。
Str2中可能包含的字符:任意字符。其中,'?'表示匹配任意一个字符,'*'表示匹配任意字符0或者多次。
给出这样两个字符串,判断Str2是否是Str1的子串,如果是输出第一个匹配到的子串,如果不是,输出"不是子串"。
2. 分析
对于'?'的处理,只要在匹配的时候将代码由:if(str1[i]==str2[j]) 改为 if(str1[i]==str2[j] || str2[j]=='?')即可。
对于'*'的处理,可以将str2根据其中的'*'分为若干个片段,然后依次在str1中分别匹配这几个片段即可,而且对于这几个片段分别匹配,如果第k个片段在str1中匹配不到,后面也可以结束了。这里举例说明一下:对于str1="Oh year.Totay is weekend!",str2=*ye*a*e*",实际上就是在str1中匹配"ye","a","e"这三个片段。
Oh year.Totay is weekend!
yea e
yea e
yea e
ye a e
ye a e
ye a e
实际上,能够匹配到上面6种情况,按照我们的如果从左到右的匹配每个片段返回的是第一种情况。这里主要分析这种情况的处理,对于所有情况的输出后面再简单说明一下。
首先处理str2,根据'*'分成若干个部分,然后依次在str1中进行匹配,使用kmp算法即可。这样判断能否匹配或者只找第一个匹配的子串的负责度是O(m+n)
3. 代码实现
其中利用了kmp算法,为了使用方便,稍微改了下kmp算法的输入参数,即pat字符串的长度不用'\0'确定,用指定参数确定。
#include < deque >
using namespace std;
// KMP算法,pat长度由len_pat指定
void get_next( const char pat[], int next[], int pat_len) {
// int len = strlen(pat);
int len = pat_len;
int i,j; next[ 0 ] = - 1 ;
for (i = 1 ; i < len; i ++ ) {
for (j = next[i - 1 ]; j >= 0 && pat[i - 1 ] != pat[j]; j = next[j])
;
if (j < 0 || pat[i - 1 ] != pat[j])
next[i] = 0 ;
else
next[i] = j + 1 ; // if (pat[i]==pat[next[i]]) next[i]=next[next[i]];
}
for ( int i = 0 ; i < len; i ++ ) {
if (pat[i] == pat[next[i]])
next[i] = next[next[i]];
}
}
// KMP算法,str长度由'\0'判断,pat长度由len_pat指定
int kmp_next( const char text[], const char pat[], int pat_len) {
int t_length = strlen(text);
// int p_length = strlen(pat);
int p_length = pat_len;
int t,p; int * next = new int [p_length];
get_next(pat, next, p_length);
for (t = 0 ,p = 0 ; t < t_length,p < p_length; ) {
if (text[t] == pat[p])
t ++ ,p ++ ;
else
if (next[p] == - 1 ) // 说明此时p=0,而且pat[0]都匹配不了
t ++ ;
else
p = next[p];
}
delete []next;
return t < t_length ? (t - p_length): - 1 ;
}
// 切分pat的结构
struct PAT_INFO {
char * pat;
int len;
};
// 可以匹配通配符的KMP,返回第一个匹配子串在str中的下标
void KMP_WildCard( char * str, char * pat) {
int len_str = strlen(str);
int len_pat = strlen(pat);
int i,j;
deque < PAT_INFO > store;
// 切分pat到store中
PAT_INFO info;
bool new_info = true ;
for (i = 0 ; i < len_pat; i ++ ) {
if (pat[i] == ' * ' ) {
if (new_info == false ) // 有info需要保存
store.push_back(info);
new_info = true ;
}
else {
if (new_info) { // 需要新建一个info
info.pat = pat + i;
info.len = 1 ;
new_info = false ;
}
else { // 不需要新建一个info
info.len ++ ;
}
}
} // for
// 测试切分结果
/*
while(store.size() > 0) {
info = store.front();
for(i=0; i<info.len; i++)
cout << info.pat[i];
cout << endl;
store.pop_front();
} */
// 根据切分后的pat序列进行匹配
int first_index = - 1 ; // 起始的下标
int last_index = 0 ; // 最后的下标后面的一个位置
int next_index = 0 ; // 下一次开始匹配的下标
while (store.size()) {
info = store.front();
next_index = kmp_next(str + next_index, info.pat, info.len);
if (next_index == - 1 ) { // 这个片段没找到,查找任务失败
break ;
}
else { // 这个片段找到了,继续找
if (first_index == - 1 ) { // 找到的第一个片段
first_index = next_index;
}
last_index += next_index + info.len;
next_index = last_index;
}
store.pop_front();
// cout << last_index << endl;
}
if (store.size())
cout << " not found " << endl;
else {
for (i = first_index; i < last_index; i ++ )
cout << str[i];
cout << endl;
}
}
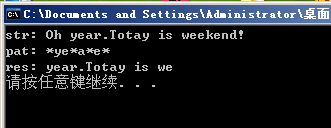
int main() {
char * str = " Oh year.Totay is weekend! " ;
char * pat = " *ye*a*e* " ;
cout << " str: " << str << endl;
cout << " pat: " << pat << endl;
cout << " res: " ;
KMP_WildCard(str, pat);
system( " PAUSE " );
return 0 ;
}
4. 所有匹配结果输出
例子:
Oh year.Totay is weekend!
yea e
yea e
yea e
ye a e
ye a e
ye a e
首先是所有结果是什么:如果我们要的是str1匹配到的字符串,那么可见实际上上面6个有3个是重复的,因此对于这种情况,只有得到匹配字符串在str1中的开始index和结束index,然后对于重复的去掉即可。如果要的是str1匹配到的字符的下标,那么这是不会重复的。
然后说一下匹配方法,基本上与匹配一个的差不多,不过要加上回溯的过程。比如第一次匹配成功后,继续在新的位置匹配最后一个片段,如果成功了就是第二次匹配成功了,否则就要回溯取在新的位置去匹配倒数第二个片段了,依次类推。直到第一个片段都没法再匹配到,不再回溯了。此外值得注意的是,如果第一次匹配都没成功,就不必回溯了,这种情况下,说明不可能存在匹配结果,因为匹配是从左到右的顺序,都会尽量在左边找到合适的片段,如果第一次都没成功,假设在第k个片段上匹配失败了,那么再回溯的话,轮到k片段是空间实际上只会与上次相同或者更小,大的空间都匹配不到,小的空间更不用说了。
还有一点值得注意:有的一些博文采用的是用str2中一个字符一个字符的匹配,感觉效率会低,而且也没有片段这个方法中的第一次匹配失败就可以停止的规律,也用不了kmp(准确的说是体现不出kmp的优势)。
5. 参考
带通配符*的字符串匹配 http://www.slimeden.com/2010/10/algorithm/stringmatchwithasterisk
hdu 3901 Wildcard 带通配符的字符串匹配 http://blog.csdn.net/kongming_acm/article/details/6656583




















 5704
5704











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








