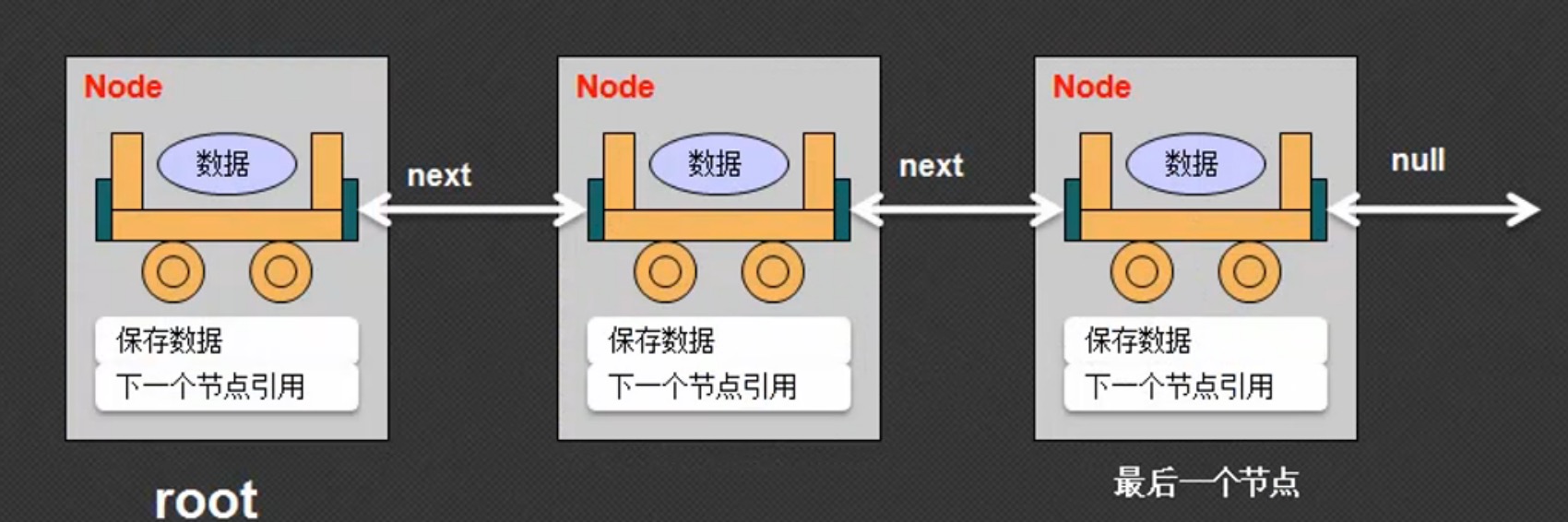
一、链表
链表是一种最简单的数据结构,其主要目的是依靠引用关系来实现多个数据保存,完成一个设置数据和取出数据的过程,
二、设计模式:
Node类:定义一个节点,
对于其节点的操作,由于不知道具体的循环次数,所以只能使用使用while循环,但是在节点操作中,递归的操作比直接使用while循环代码更加直接,习惯性也用递归。
客户端代码只关注于提供Link支持的方法,即数据的保存和输出
Link类的主要功能是控制Node类对象的产生和根节点
Node类主要负责数据的保存和引用关系的分配
三、链表的方法
1、数据增加:public void add(数据类型 变量)
如果要进行数据增加,则有Link类负责节点对象的产生,并且由Link类维护根节点,所有节点匹配由Node类实现
2、取得保存元素个数:public int Size()
3、判断是不是空链表:public boolean isEmpty()
空链表判断实际上可以通过两种方式
1):判断有没有根节点(root是否为null)
2):判断保存的数据量(count是否为0)
4、数据查询:public boolean contains(数据类型 变量)
5、根据索引取得数据: public 数据类型 get(int index)
6、使用新的内容替换掉指定索引的旧内容: public void set(int index,数据类型 变量)
7、数据删除:public void remove(数据类型 变量)
如果删除的是对象,则对象之间要进行比较
情况一:要删除的是根节点,则root变为根节点的next,在Link类处理
情况二:要删除的是普通节点,非根节点,删除数据的最终形式:当前节点的上一个节点.next = 当前节点.next、即:空出了当前节点,在Node类处理,从第二个节点开始判断
8、将链表变成对象数组:public 数据类型 [] toArray()
Link 类
public class Link {
//设置数据
private Node root;
private int count = 0;
private int foot = 0;
private String [] retArray;
public void add(String data) {
// Link link = new Link();
// Node newNode = link.new Node(data);
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//不保存空值
if(data == null) {
return;
}
if(root == null) {
root = newNode;
}else {
root.addNode(newNode);
}
count++;
}
public int size() {
return count;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
}
public boolean contains(String data) {
if(data == null || root == null) {
return false;
}
return this.root.containsNode(data);
}
public String get(int index) {
if(index > count-1) {
return null;
}
this.foot = 0; //表示从前开始查询
return this.root.getNode(index);
}
public void set(int index,String data) {
if(index > count-1) {
return ;
}
this.foot = 0;
this.root.setNode(index, data);
}
public void remove(String data) {
if(this.contains(data)) {
if(data.equals(this.root.data)) {
this.root = this.root.next;
} else {
this.root.next.removeNode(this.root, data);
}
}else {
System.out.println("该数据不存在");
}
}
public String [] toArray() {
if(this.root == null) {
return null;
}
this.foot = 0;
this.retArray = new String[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
return this.retArray;
}
//输出数据
public void print() {
root.printNode();
}
//----------------------内部类-----------------------------
private class Node {
private String data;
private Node next;
public Node(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void addNode(Node newNode) {
if(next == null) {
next = newNode;
}else {
next.addNode(newNode);
}
}
public void printNode() {
System.out.println(data);
if(next != null) {
next.printNode();
}
}
public boolean containsNode(String data) {
if(data.equals(this.data)) {
return true;
}else {
if(this.next != null) {
return this.next.containsNode(data);
}else {
return false;
}
}
}
public String getNode(int index) {
if(Link.this.foot ++ == index) {
return this.data;
}else {
return this.next.getNode(index);
}
}
public void setNode(int index,String data) {
if(Link.this.foot ++ == index) {
this.data = data;
}else {
this.next.setNode(index, data);
}
}
//
public void removeNode(Node previous,String data) {
if(data.equals(this.data)) {
previous.next = this.next;
} else {
this.next.removeNode(this, data);
}
}
public void toArrayNode() {
Link.this.retArray[Link.this.foot ++] = this.data;
if(this.next != null) {
this.next.toArrayNode();
}
}
}
}
LinkDemo
public class LinkDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Link link = new Link();
link.add("火车头");
link.add("车厢一");
link.add("车厢二");
link.set(0, "22");
link.remove("车厢");
String [] data = link.toArray();
for(int x = 0;x < data.length;x++) {
System.out.println(data[x]);
}
link.print();
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








