原文:http://www.programcreek.com/2011/08/so-java-passes-object-by-reference-or-by-value/
//注释处为个人见解。。。
This is a classic interview question which confuses novice Java developers. In this post I will use an example and some diagram to demonstrate that: Java is pass-by-value.
1. Some Definitions
Pass by value: make a copy in memory of the actual parameter’s value that is passed in.
Pass by reference: pass a copy of the address of the actual parameter.
Java is always pass-by-value. Primitive data types and object reference are just values.
//java总是值传递。。基本类型和obj都是值
2. Passing Primitive Type Variable
Since Java is pass-by-value, it’s not hard to understand the following code will not swap anything.
swap(Type arg1, Type arg2) {
Type temp = arg1;
arg1 = arg2;
arg2 = temp;
}3. Passing Object Variable
Java manipulates objects by reference, and all object variables are references. However, Java doesn’t pass method arguments by reference, but by value.
Question is: why the member value of the object can get changed?
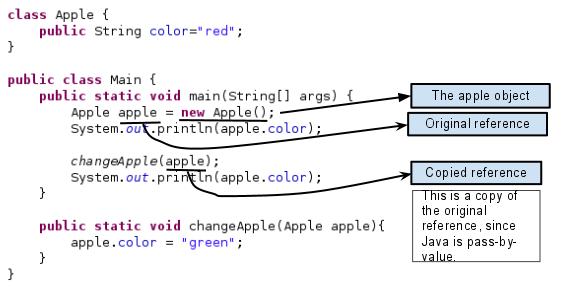
Code:
class Apple {
public String color="red";
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Apple apple = new Apple();
System.out.println(apple.color);
changeApple(apple);
System.out.println(apple.color);
}
public static void changeApple(Apple apple){
apple.color = "green";
}
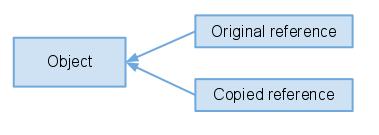
}Since the orignal and copied reference refer the same object, the member value gets changed.
//java没有指针。。java obj对象都是在堆里产生。。栈里保存对其的引用。。这就象指针一样。。(仅仅像。。不=指针);
//java传递变量是永远都是值传递。。。对obj来说。。如上例。。传递的就是 一个指向Apple类型的引用变量。。的副本;如下图
Output:
red green
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a= new String("111");
change(a);
System.out.println(a);
}
public static void change(String a) {
a = "222";
}
//上文说java永远都是值传递。。
//so。。上面例子中传递的就是a的一个副本。。如下图
//调用方法时。。复制了一份引用变量a。。传递给change方法。。然后chuange方法new了一个字符串"222",再把其引用丢给a副本;
//TIP:如果本例为StringBuilder结果为222
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder a= new StringBuilder("111");
change(a);
System.out.println(a);
}
public static void change(StringBuilder a) {
a.append("222");
} //因为a和a副本都引用堆中同一份的 111,so输出为 111222;
//写完收工。。。。。。。。。。。。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








