汉诺塔递归算法进阶
When something is specified in terms of itself, it is called recursion. The recursion gives us a new idea of how to solve a kind of problem and this gives us insights into the nature of computation. Basically, many of computational artifacts are naturally self-referential, for example:
如果根据自身指定某些内容,则称为递归。 递归为我们提供了有关如何解决一种问题的新思路,这使我们可以洞悉计算的本质。 基本上,许多计算工件自然都是自引用的,例如:
- File system 文件系统
- Fractal graph 分形图
- Algorithms 演算法
Any recursion function consists of two parts:
任何递归函数都包括两个部分:
Base case: the last case of the recursion. For every recursion, the last step must be the base case and it is going to return a specific value to us.
基本情况:递归的最后一种情况。 对于每次递归,最后一步必须是基本情况,它将为我们返回一个特定值。
Reduction step: Assuming that the recursion works for smaller values of its argument, then use the function to compute a new return value.
归约步骤:假定递归适用于其参数的较小值,然后使用该函数计算新的返回值。
Now think about the following examples:
现在考虑以下示例:
To compute a recursion function of a positive integer N as its parameter,
要计算正整数 N作为其参数的递归函数,
Base case: The ending case with N equals a specific number (usually 1 or 0) and this will give us a specific return result under this condition.
基本情况: N的结束情况等于一个特定的数字(通常为1或0),在这种情况下,这将为我们提供特定的返回结果。
Reduction step: For each of the steps of this recursion, we use N-t as its new parameter (t could be any constant based on the question).
归约步骤:对于该递归的每个步骤,我们将N- t用作其新参数(根据问题, t可以是任何常数)。
In this case, the positive integer N is called the depth of this recursion.
在这种情况下,正整数N称为此递归的深度。
To compute a recursion function of a sequence Seq as its parameter,
要计算序列 Seq的递归函数作为其参数,
Base case: The ending case with Seq equals an empty set (empty list/empty string/etc.) and this will give us a specific return result under this condition.
基本情况:带有Seq的结束情况等于一个空集(空列表/空字符串等),在这种情况下,这将为我们提供特定的返回结果。
Reduction step: For each of the steps of this recursion, we use a shorter Seq (usually moves one element from the previous one) as its new parameter.
归约步骤:对于此递归的每个步骤,我们都使用较短的Seq(通常将上一个元素移到上一个元素)作为其新参数。
问题1.倒数问题 (Question 1. Counting-down Problem)
Suppose we are working on a project of rocket and we want to count down numbers before the rocket blast off. We count down from 5 and after we count 1, we will then print “Blastoff 🚀”. Write a recursion function about it.
假设我们正在研究一个火箭项目,并且我们想在火箭发射之前计算数量。 我们从5开始倒数,再从1开始倒数,然后打印“ Blastoff🚀”。 编写有关它的递归函数。
问题2.创建斐波那契数列 (Question 2. Create a Fibonacci Sequence)
Fibonacci sequence is a series in which each number is the sum of the two preceding numbers.
斐波那契数列是一个序列,其中每个数字是前面两个数字的总和。
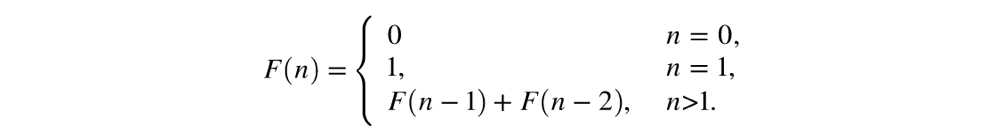
Suppose that we give an index n, then we are going to return the n-th element of this Fibonacci sequence. Write a recursion function to calculate the n-th element. For example, an index n = 7 will give back 13.
假设我们给定索引n ,那么我们将返回此斐波那契数列的第n个元素。 编写一个递归函数以计算第n个元素。 例如,索引n = 7将返回13。
问题3.计算最大公约数 (Question 3. Calculate the Greatest Common Divisor)
The greatest common divisor (GCD), also called the greatest common factor, of two numbers is the largest natural number d that divides both numbers without a remainder. Let’s code up the Euclidean algorithm (one of the oldest algorithms in common use) to find the GCD. Note that this function should also work for negative numbers and the result GCD is always positive!
两个数的最大公除数(GCD),也称为最大公因数,是将两个数除而无余的最大自然数d 。 让我们编码欧几里得算法 (最常用的最古老算法之一)以找到GCD。 注意,该函数也应适用于负数 ,并且结果GCD始终为正 !
Write a recursive function that returns the greatest common divisor for two numbers.
编写一个递归函数,该函数返回两个数字的最大公约数。
4.计算列表的长度 (4. Calculate the Length of a List)
Find a recursive function that returns the number of items in a list. In other words, write a function that reimplements the len function for lists with recursion.
查找一个返回列表中项目数的递归函数。 换句话说,编写一个函数,为带有递归的列表重新实现len函数。
5.反转字符串 (5. Reverse a string)
Suppose we have a string and we would like to reverse it by recursion. Write a function to implement this.
假设我们有一个字符串,我们想通过递归来反转它。 编写一个函数来实现这一点。
翻译自: https://medium.com/adamedelwiess/advanced-python-1-recursion-5e4a5b71f17
汉诺塔递归算法进阶





















 299
299

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








