java小球循环反弹编程
Control Flow
控制流
(1) The Definition of the Control Flow
(1)控制流程的定义
The sequence of statements that are actually executed in a program. Conditionals and loops enable us to choreograph control flow. For example,
在程序中实际执行的语句序列。 条件和循环使我们能够编排控制流。 例如,
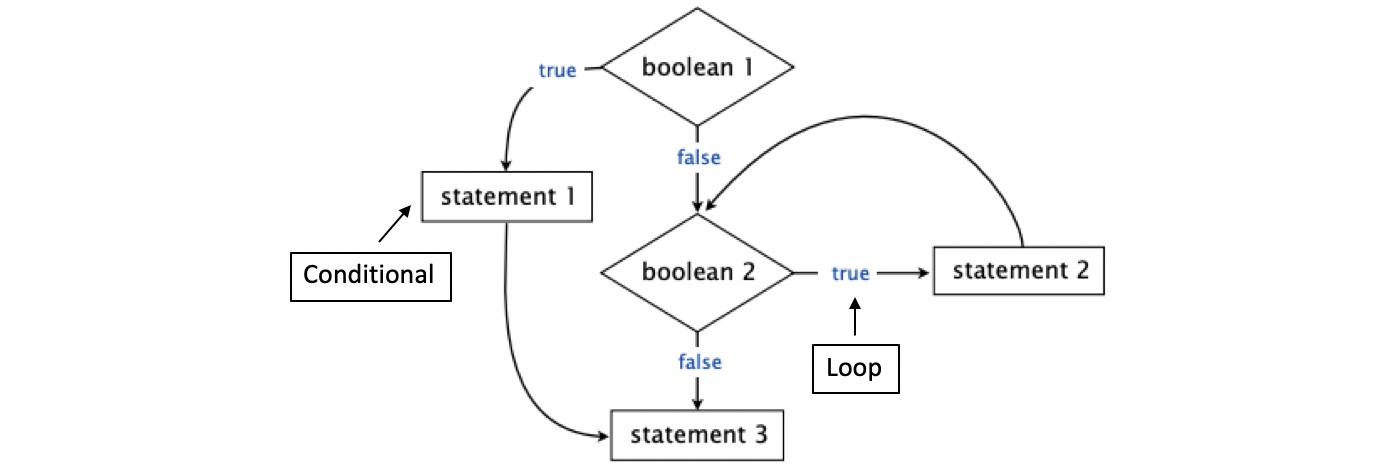
2. Conditionals: the if statement
2.条件:if语句
(1) The if Statement
(1)if语句
The if statement executes certain statements depending on the values of certain variables. It follows the following steps:
if语句根据某些变量的值执行某些语句。 它遵循以下步骤:
- Evaluate a boolean expression. 评估布尔表达式。
- If the boolean is true, execute a statement. 如果布尔值为true,则执行一条语句。
- If the boolean is false, execute the statement behind else. 如果布尔值为假,则执行其他后面的语句。
(2) The if Statement: Example #1 Simulate
(2)if语句:示例1模拟
The following code simulates a flip coin.
以下代码模拟了一个掷硬币。
public class Flip
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
if (Math.random() < 0.5)
System.out.println("Heads");
else
System.out.println("Tails");
}
}(3) The if Statement: Example #2 Sort
(3)if语句:示例#2排序
The following code to swap two integers if the first one is greater than the second one.
以下代码在第一个大于第二个整数时交换两个整数。
public class TwoSort
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
if (b < a)
{
int t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}(4) The if Statement: Example #3 Sort
(4)if语句:示例#3排序
The following code to sort three integers a, b, and c.
以下代码对三个整数a , b和c进行排序。
public class ThreeSort
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(args[2]);
if (b < a)
{ int t = a; a = b; b = t; }
if (c < a)
{ int t = a; a = c; c = t; }
if (c < b)
{ int t = b; b = c; c = t; }
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
}
}(5) The if Statement: Example #4 Error Checks
(5)if语句:示例4错误检查
Sometimes, we can use the if statement to check the variables.
有时,我们可以使用if语句检查变量。
public class IntOps1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int sum = a + b;
int prod = a * b;
System.out.println(a + " + " + b + " = " + sum);
System.out.println(a + " * " + b + " = " + prod);
if (b == 0) System.out.println("Division by zero");
else System.out.println(a + " / " + b + " = " + a / b);
if (b == 0) System.out.println("Division by zero");
else System.out.println(a + " % " + b + " = " + a % b);
}
}3. Loops: The while Loop
3.循环:while循环
(1) The Definition of the while Loop
(1)while循环的定义
Execute certain statements repeatedly until certain conditions are met.
重复执行某些语句,直到满足某些条件为止。
- Evaluate a boolean expression 评估布尔表达式
- If true, execute a sequence of statements如果为true,则执行一系列语句
- Repeat重复
(2) The while Loop: Example #1 Power
(2)while循环:示例1电源
Prints the powers of two from 2⁰ to 2ⁿ.
从2⁰到2ⁿ打印2的幂。
public class PowersOfTwo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int i = 0;
int v = 1;
while (i <= n)
{
System.out.println(v);
i = i + 1;
v = 2 * v;
}
}
}(3) The while Loop: Example #2 Implement Square Root
(3)while循环:示例2:实现平方根
The Newton-Raphson method to compute sqrt(c) is:
用于计算sqrt(c)的Newton-Raphson方法是:
- Initialize t0 = c 初始化t0 = c
- Set ti+1 to be the average of ti and c / ti 将ti + 1设置为ti和c / ti的平均值
- Repeat until ti = c/ti (up to desired precision)重复直到ti = c / ti(达到所需的精度)
public class Sqrt
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double EPS = 1E-15;
double c = Double.parseDouble(args[0]);
double t = c;
while (Math.abs(t - c/t) > t*EPS)
t = (c/t + t) / 2.0;
System.out.println(t);
}
}4. Loops: The for Loop
4.循环:for循环
(1) The Definition of the for Loop
(1)for循环的定义
The for loop is an alternative repetition structure.
for循环是另一种重复结构。
- Evaluate an initialization statement 评估初始化语句
- Evaluate a boolean expression评估布尔表达式
- If true, execute a sequence of statements, then execute an increment statement如果为true,则执行一系列语句,然后执行一个增量语句
- Repeat重复
(2) The for Loop: Example #1 Ruler
(2)for循环:#1标尺示例
public class Ruler1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
String ruler = " ";
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
ruler = ruler + i + ruler;
System.out.println(ruler);
}
}5. Nested Conditionals and Loops
5.嵌套条件和循环
(1) The Definition of Nesting
(1)嵌套的定义
Any “statement” within a conditional or loop may itself be a conditional or a loop statement.
条件或循环中的任何“声明”本身都可以是条件或循环语句。
- Enables complex control flows 实现复杂的控制流程
- Adds to the challenge of debugging增加了调试的挑战
(2) Nesting: Example #1 Gamber’s Ruin Problem
(2)嵌套:示例#1甘伯的废墟问题
The following code will show us the result of a type of gambling. Look into the result, you can find out that it will never be a good idea to do gambling.
以下代码将向我们展示一种赌博的结果。 查看结果,您会发现赌博永远不是一个好主意。
public class Gamble {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for (int t = 0; t < 5; t++)
{
int goal = 10;
int cash = 5;
while (cash > 0 && cash < goal)
if (Math.random() < 0.45) cash++;
else cash--;
if (cash == goal) System.out.println("You win");
else System.out.println("You lose");
}
}
}(3) Nesting: Example #2 Income Tax Calculator
(3)嵌套:示例2所得税计算器
Based on the following code, we can calculate the income tax and our real salary automatically.
根据以下代码,我们可以自动计算所得税和实际工资。
public class IncomeTax {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double income = Double.parseDouble(args[0]);
double rate = 0.35;
if (income < 47450) rate = 0.22;
else if (income < 114650) rate = 0.25;
else if (income < 174700) rate = 0.28;
else if (income < 311950) rate = 0.33;
System.out.println("The income tax is: " + rate * income);
System.out.println("The real salary is: " + (1 - rate) * income);
}
}6. Debugging
6.调试
Is your program a legal Java program? Think about the following sets to debug your program.
您的程序是合法的Java程序吗? 考虑以下设置以调试程序。
- Java compiler can help you find out. Java编译器可以帮助您找到答案。
- Find the first compiler error (if any) 查找第一个编译器错误(如果有)
- Repeat 重复
- Result: An executable Factors.class file结果:可执行的Factors.class文件
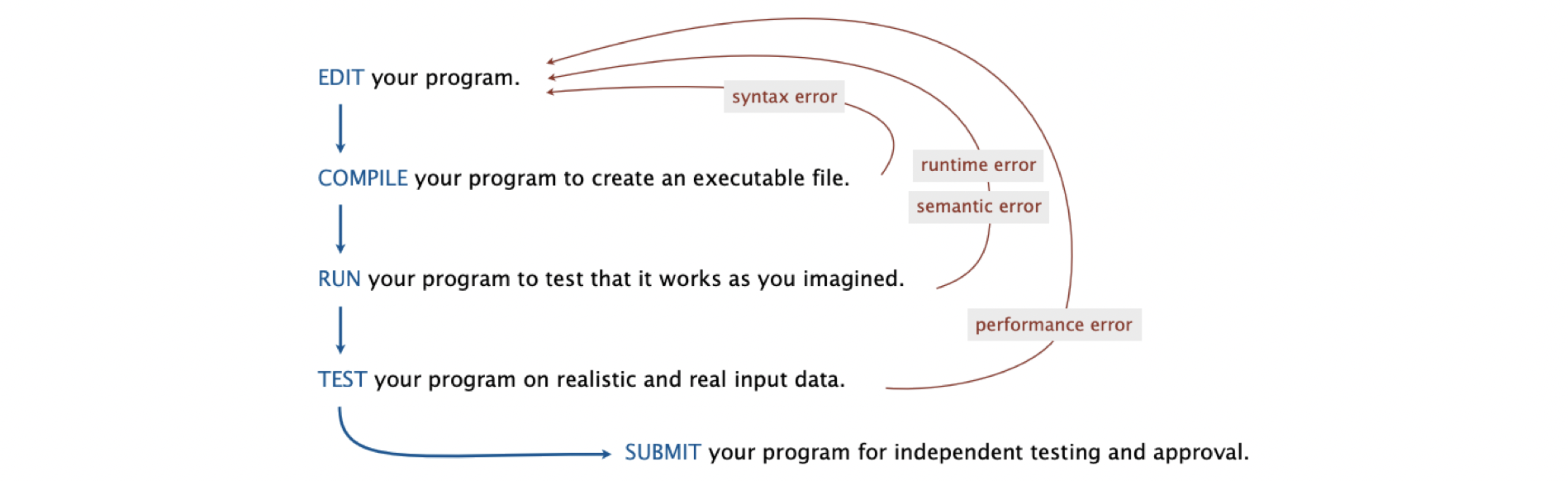
翻译自: https://medium.com/adamedelwiess/java-programming-2-conditionals-loops-and-debugging-d6782a0d018e
java小球循环反弹编程





















 388
388

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








