1、Linux时钟框架
上图是linux时钟框架一个经典的描述。本质上linux各种时钟架构和服务是基于硬件提供的两种timer而构建的。
1、定时Timer这类timer每个cpu都有一个独立的,称为local timer。这类timer的中断一般都是PPI(Private Peripheral Interrupt)类型,即每个cpu都有独立一份中断。 与PPI对应的是SPI(Shared Peripheral Interrupt,即多个cpu共享同一个中断。
这类timer一般是32bit宽度count,最重要的它会频繁的溢出并产生timer到期中断。
这类timer服务于tick timer(低精度)或者hrtimer(高精度)。
低精度模式,local timer工作在PERIODIC模式。即timer以tick时间(1/HZ)周期性的产生中断。在tick timer中处理任务调度tick、低精度timer、其他时间更新和统计profile。在这种模式下,所有利用时间的进行的运算,精度都是以tick(1/HZ)为单位的,精度较低。比如HZ=1000,那么tick=1ms。
高精度模式,local timer工作在ONESHOT模式。即系统可以支持hrtimer(high resolution)高精度timer,精度为local timer的计数clk达到ns级别。这种情况下把tick timer也转换成一种hrtimer。
2、时间戳Timer这类timer一个系统多个cpu共享一个,称为global timer。
这类timer一般是32bit/64bit宽度count,一般不会溢出产生中断,系统实时的去读取count的值来计算当前的时间戳。
这类timer服务于clocksource/timekeeper。本文的代码分析基于linux kernel 4.4.22,最好的学习方法还是”RTFSC”
1.1、Exynos MCT(Multi-Core Timer)
我们以samsung exynos架构为例来说明linux对timer的使用。
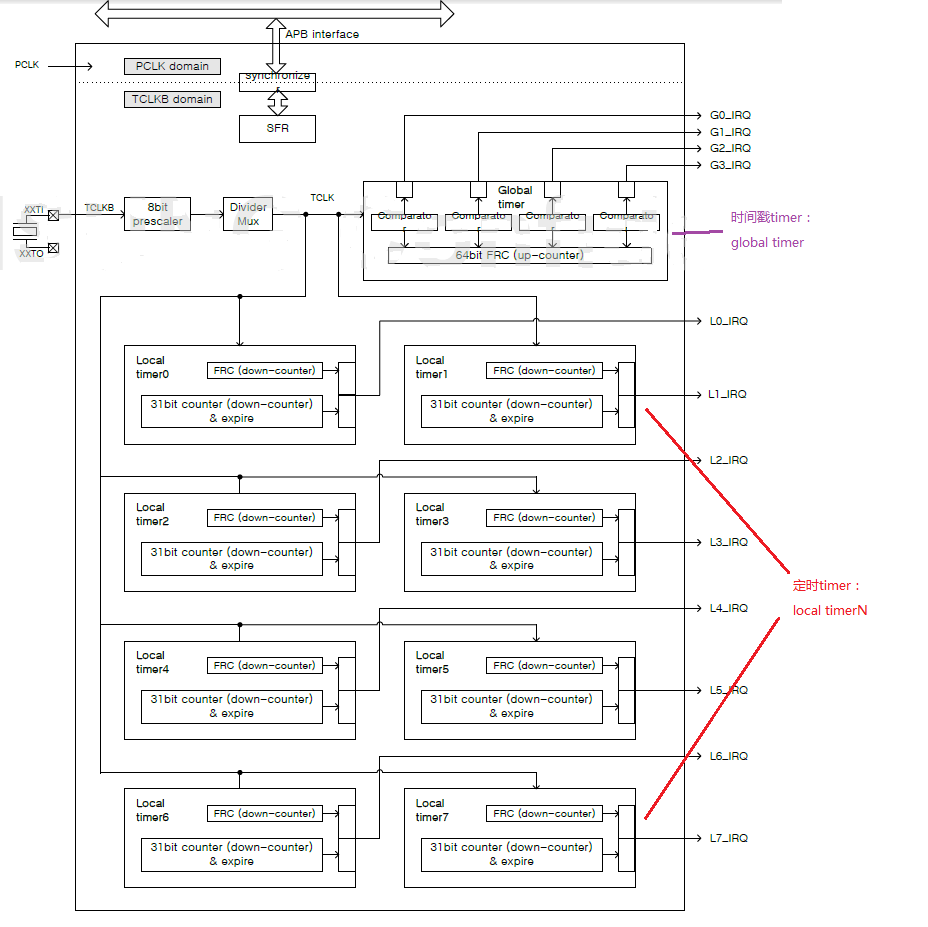
从上图可以看到,exynos有1个64bit global timer用来做时间戳timer,有8个31bit localtimer用来做定时timer,每个cpu拥有一个localtimer。
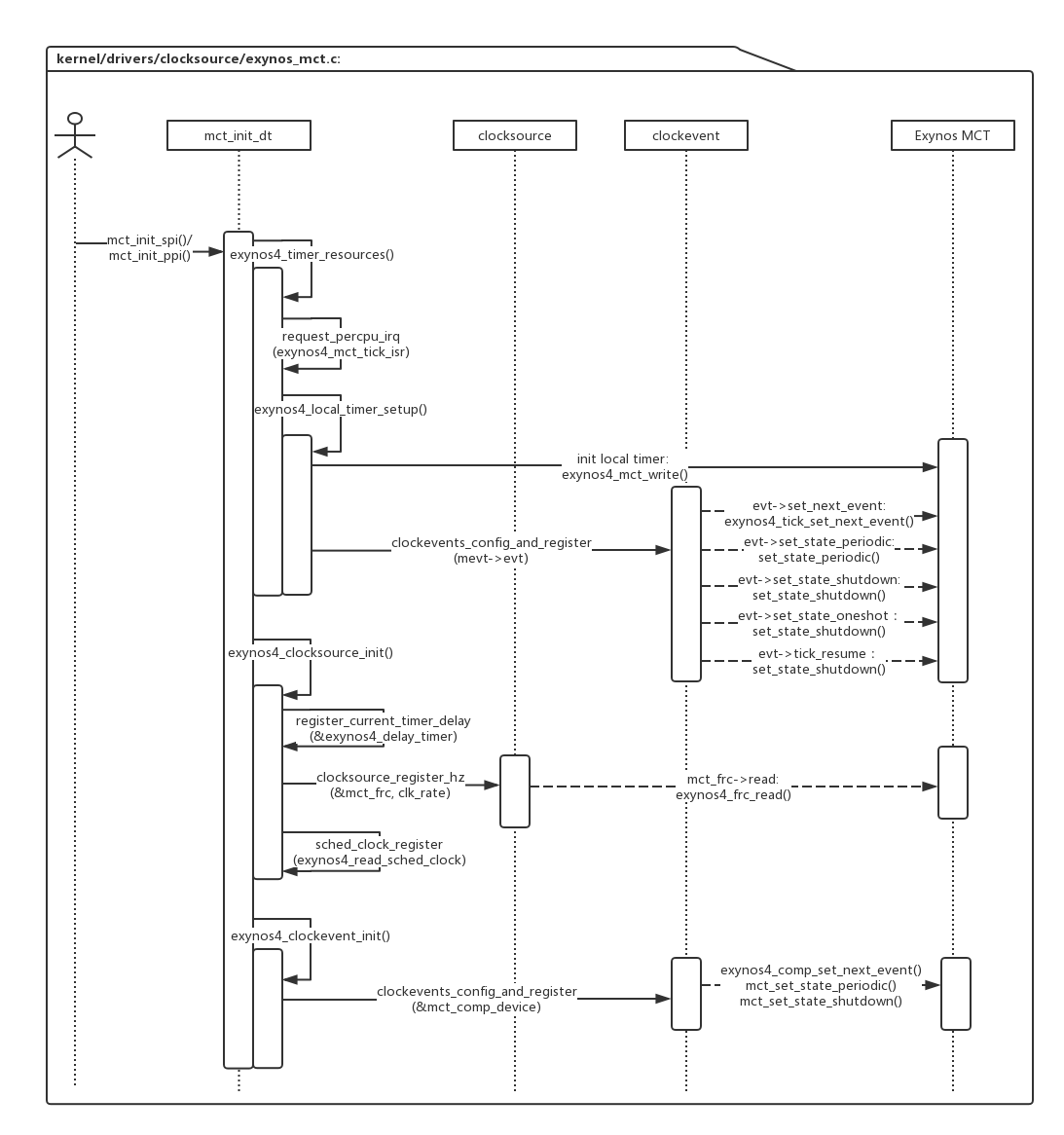
上图是exynos driver的初始化流程,mct_init_dt()中包含了主要的初始化流程:
static void __init mct_init_dt(struct device_node *np, unsigned int int_type)
{
exynos4_timer_resources(np, of_iomap(np, 0)); //(1)初始化localtimer,并将其注册成clockevent
exynos4_clocksource_init(); //(2)初始化globaltimer,并将其注册成clocksource
exynos4_clockevent_init(); //(3)将globaltimer的comparator 0注册成一个clockevent,一般不会使用
}
后面结合clocksource和clockevent的子系统的解析,再来详细描述exynos系统的具体实现。
2、clocksource & timekeeper
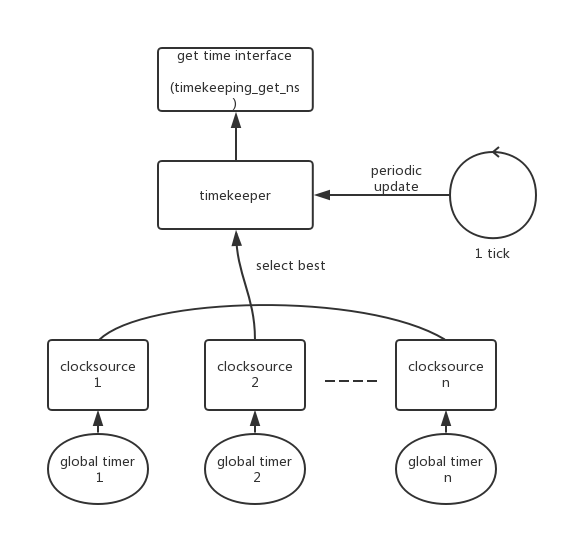
上图描述的是clocksource和timekeeper的关系:一个global timer对应注册一个clocksource。
一个系统中可以有多个clocksource,timekeeper选择精度最高的那个来使用。
用户使用timekeeper提供的接口来获取系统的时间戳。
为了避免无人主动获取时间clocksource定时器的溢出,timekeeper需要定期的去获取clocksource的值来更新系统时间,一般是在tick处理中更新。
2.1、clocksource
下面来看一看clocksource的定义:
static struct clocksource mct_frc = {
.name= "mct-frc",
/* (1) .rating = 精度,数值越大越好,
select_best会选择精度最大的clocksource给timekeeper使用 */
.rating= 400,
/* (2) .read = 读取clocksource的timer当前计数 */
.read= exynos4_frc_read,
/* (3) .mask = timer的位宽 */
.mask= CLOCKSOURCE_MASK(32),
.flags= CLOCK_SOURCE_IS_CONTINUOUS,
.resume= exynos4_frc_resume,
};
看一下clocksource的注册过程:
static void __init exynos4_clocksource_init(void)
{
// 启动global timer
exynos4_mct_frc_start();
// 注册timer_delay
exynos4_delay_timer.read_current_timer = &exynos4_read_current_timer;
exynos4_delay_timer.freq = clk_rate;
register_current_timer_delay(&exynos4_delay_timer);
// (1) 注册clocksource
if (clocksource_register_hz(&mct_frc, clk_rate))
panic("%s: can't register clocksource\n", mct_frc.name);
// 注册sched_clock
sched_clock_register(exynos4_read_sched_clock, 32, clk_rate);
}
|→
static inline int clocksource_register_hz(struct clocksource *cs, u32 hz)
{
return __clocksource_register_scale(cs, 1, hz);
}
||→
int __clocksource_register_scale(struct clocksource *cs, u32 scale, u32 freq)
{
/* Initialize mult/shift and max_idle_ns */
/* (1.1) 根据timer的频率freq,计算cs->mult、cs->shift
这两个字段是用来把timer的计数转换成实际时间单位ns
ns = (count * cs->mult) >> cs->shift */
__clocksource_update_freq_scale(cs, scale, freq);
/* Add clocksource to the clocksource list */
mutex_lock(&clocksource_mutex);
/* (1.2) 将新的clocksource加入全局链表 */
clocksource_enqueue(cs);
clocksource_enqueue_watchdog(cs);
/* (1.3) 从全局链表中重新选择一个best
clocksource给timekeeper使用 */
clocksource_select();
clocksource_select_watchdog(false);
mutex_unlock(&clocksource_mutex);
return 0;
}
|||→
void __clocksource_update_freq_scale(struct clocksource *cs, u32 scale, u32 freq)
{
u64 sec;
/*
* Default clocksources are *special* and self-define their mult/shift.
* But, you're not special, so you should specify a freq value.
*/
if (freq) {
/*
* Calc the maximum number of seconds which we can run before
* wrapping around. For clocksources which have a mask > 32-bit
* we need to limit the max sleep time to have a good
* conversion precision. 10 minutes is still a reasonable
* amount. That results in a shift value of 24 for a
* clocksource with mask >= 40-bit and f >= 4GHz. That maps to
* ~ 0.06ppm granularity for NTP.
*/
/* (1.1.1) 计算timer计数器到溢出,
最大能计数多少秒 = sec */
sec = cs->mask;
do_div(sec, freq);
do_div(sec, scale);
if (!sec)
sec = 1;
else if (sec > 600 && cs->mask > UINT_MAX)
sec = 600;
/* (1.1.2) 根据1s内的频率数freq,和1s内的ns数NSEC_PER_SEC
计算freq和ns之间的转换公式:
ns = (freq * cs->mult) >> cs->shift
目的是把mult和shift算到最大值,最大可能的保留精度 */
clocks_calc_mult_shift(&cs->mult, &cs->shift, freq,
NSEC_PER_SEC / scale, sec * scale);
}
/*
* Ensure clocksources that have large 'mult' values don't overflow
* when adjusted.
*/
cs->maxadj = clocksource_max_adjustment(cs);
while (freq && ((cs->mult + cs->maxadj < cs->mult)
|| (cs->mult - cs->maxadj > cs->mult))) {
cs->mult >>= 1;
cs->shift--;
cs->maxadj = clocksource_max_adjustment(cs);
}
/*
* Only warn for *special* clocksources that self-define
* their mult/shift values and don't specify a freq.
*/
WARN_ONCE(cs->mult + cs->maxadj < cs->mult,
"timekeeping: Clocksource %s might overflow on 11%% adjustment\n",
cs->name);
/* (1.1.3) 根据mult和shift的值,计算最大能进入idle的时间max_idle_ns
才能保证idle时timer不会溢出*/
clocksource_update_max_deferment(cs);
pr_info("%s: mask: 0x%llx max_cycles: 0x%llx, max_idle_ns: %lld ns\n",
cs->name, cs->mask, cs->max_cycles, cs->max_idle_ns);
}
|||→
static void clocksource_select(void)
{
__clocksource_select(false);
}
static void __clocksource_select(bool skipcur)
{
bool oneshot = tick_oneshot_mode_active();
struct clocksource *best, *cs;
/* Find the best suitable clocksource */
/* (1.3.1) 选择best clocksource */
best = clocksource_find_best(oneshot, skipcur);
if (!best)
return;
/* Check for the override clocksource. */
list_for_each_entry(cs, &clocksource_list, list) {
if (skipcur && cs == curr_clocksource)
continue;
if (strcmp(cs->name, override_name) != 0)
continue;
/*
* Check to make sure we don't switch to a non-highres
* capable clocksource if the tick code is in oneshot
* mode (highres or nohz)
*/
if (!(cs->flags & CLOCK_SOURCE_VALID_FOR_HRES) && oneshot) {
/* Override clocksource cannot be used. */
pr_warn("Override clocksource %s is not HRT compatible - cannot switch while in HRT/NOHZ mode\n",
cs->name);
override_name[0] = 0;
} else
/* Override clocksource can be used. */
best = cs;
break;
}
/* (1.3.2) 通知timekeeper更新clocksource,tick-sched更新 */
if (curr_clocksource != best && !timekeeping_notify(best)) {
pr_info("Switched to clocksource %s\n", best->name);
curr_clocksource = best;
}
}
||||→
int timekeeping_notify(struct clocksource *clock)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
if (tk->tkr_mono.clock == clock)
return 0;
stop_machine(change_clocksource, clock, NULL);
tick_clock_notify();
return tk->tkr_mono.clock == clock ? 0 : -1;
}
2.1.1、exynos4_clocksource_init()
exynos将global timer注册成clocksource,虽然global timer拥有64bit的位宽,但是注册的时候把其当成32bit的clocksource注册。
static u32 notrace exynos4_read_count_32(void)
{
return readl_relaxed(reg_base + EXYNOS4_MCT_G_CNT_L);
}
static cycle_t exynos4_frc_read(struct clocksource *cs)
{
return exynos4_read_count_32();
}
static struct clocksource mct_frc = {
.name= "mct-frc",
.rating= 400,
.read= exynos4_frc_read,
.mask= CLOCKSOURCE_MASK(32),
.flags= CLOCK_SOURCE_IS_CONTINUOUS,
.resume= exynos4_frc_resume,
};
static void __init exynos4_clocksource_init(void)
{
exynos4_mct_frc_start();
exynos4_delay_timer.read_current_timer = &exynos4_read_current_timer;
exynos4_delay_timer.freq = clk_rate;
register_current_timer_delay(&exynos4_delay_timer);
/* (1) exynos将global timer注册成clocksource */
if (clocksource_register_hz(&mct_frc, clk_rate))
panic("%s: can't register clocksource\n", mct_frc.name);
sched_clock_register(exynos4_read_sched_clock, 32, clk_rate);
}
2.2、timekeeper
timerkeeper提供了几种时间:xtime、monotonic time、raw monotonic time、boot time。xtime 即是wall time,和RTC时间一样可以表示当前的时刻,它的起始时间是公元0世纪0秒,精度大于RTC时间;
monotonic time 从系统开机后到现在的累计时间,不过不计算系统休眠的时间;
raw monotonic time 和monotonic time含义一样,不过更纯粹,不会受到NTP时间调整的影响;
boot time 在monotonic time的基础上加上了系统休眠的时间,它代表着系统上电后的总时间。时间种类精度(统计单位)访问速度累计休眠时间受NTP调整的影响获取函数RTC低慢YesYes
xtime高快YesYesdo_gettimeofday()、ktime_get_real_ts()、ktime_get_real()
monotonic高快NoYesktime_get()、ktime_get_ts64()
raw monotonic高快NoNoktime_get_raw()、getrawmonotonic64()
boot time高快YesYesktime_get_boottime()
2.2.1、timekeeper的定义
虽然clocksource定时器只有一个,但是timekeeper提供了xtime、monotonic time、raw time、boot time等几种时间,所以timekeeper结构体中定义了多个变量来记住这些差值。
/**
* struct timekeeper - Structure holding internal timekeeping values.
* @tkr_mono:The readout base structure for CLOCK_MONOTONIC
* @tkr_raw:The readout base structure for CLOCK_MONOTONIC_RAW
* @xtime_sec:Current CLOCK_REALTIME time in seconds
* @ktime_sec:Current CLOCK_MONOTONIC time in seconds
* @wall_to_monotonic:CLOCK_REALTIME to CLOCK_MONOTONIC offset
* @offs_real:Offset clock monotonic -> clock realtime
* @offs_boot:Offset clock monotonic -> clock boottime
* @offs_tai:Offset clock monotonic -> clock tai
* @tai_offset:The current UTC to TAI offset in seconds
* @clock_was_set_seq:The sequence number of clock was set events
* @next_leap_ktime:CLOCK_MONOTONIC time value of a pending leap-second
* @raw_time:Monotonic raw base time in timespec64 format
* @cycle_interval:Number of clock cycles in one NTP interval
* @xtime_interval:Number of clock shifted nano seconds in one NTP
*interval.
* @xtime_remainder:Shifted nano seconds left over when rounding
*@cycle_interval
* @raw_interval:Raw nano seconds accumulated per NTP interval.
* @ntp_error:Difference between accumulated time and NTP time in ntp
*shifted nano seconds.
* @ntp_error_shift:Shift conversion between clock shifted nano seconds and
*ntp shifted nano seconds.
* @last_warning:Warning ratelimiter (DEBUG_TIMEKEEPING)
* @underflow_seen:Underflow warning flag (DEBUG_TIMEKEEPING)
* @overflow_seen:Overflow warning flag (DEBUG_TIMEKEEPING)
*
* Note: For timespec(64) based interfaces wall_to_monotonic is what
* we need to add to xtime (or xtime corrected for sub jiffie times)
* to get to monotonic time. Monotonic is pegged at zero at system
* boot time, so wall_to_monotonic will be negative, however, we will
* ALWAYS keep the tv_nsec part positive so we can use the usual
* normalization.
*
* wall_to_monotonic is moved after resume from suspend for the
* monotonic time not to jump. We need to add total_sleep_time to
* wall_to_monotonic to get the real boot based time offset.
*
* wall_to_monotonic is no longer the boot time, getboottime must be
* used instead.
*/
struct timekeeper {
struct tk_read_basetkr_mono;
// tkr_mono.xtime_nsec:xtime/monotonic time 的ns
// tkr_mono.base:monotonic time的base部分
struct tk_read_basetkr_raw;
// tkr_mono.base:raw time的base部分
u64xtime_sec; // xtime的sec
unsigned longktime_sec; // monotonic time 的整sec
struct timespec64wall_to_monotonic; // xtime + wall_to_monotonic = monotonic time
ktime_toffs_real; // monotonic time + offs_real = xtime,
// 和wall_to_monotonic是相反的值
ktime_toffs_boot; // monotonic time + offs_boot = boot time
ktime_toffs_tai;
s32tai_offset;
unsigned intclock_was_set_seq;
ktime_tnext_leap_ktime;
struct timespec64raw_time; // raw time
/* The following members are for timekeeping internal use */
cycle_tcycle_interval;
u64xtime_interval;
s64xtime_remainder;
u32raw_interval;
/* The ntp_tick_length() value currently being used.
* This cached copy ensures we consistently apply the tick
* length for an entire tick, as ntp_tick_length may change
* mid-tick, and we don't want to apply that new value to
* the tick in progress.
*/
u64ntp_tick;
/* Difference between accumulated time and NTP time in ntp
* shifted nano seconds. */
s64ntp_error;
u32ntp_error_shift;
u32ntp_err_mult;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_TIMEKEEPING
longlast_warning;
/*
* These simple flag variables are managed
* without locks, which is racy, but they are
* ok since we don't really care about being
* super precise about how many events were
* seen, just that a problem was observed.
*/
intunderflow_seen;
intoverflow_seen;
#endif
};
2.2.2、timekeeper的初始化
timekeeper在初始化的过程中,读取当前的RTC值和clocksource的值,来初始化xtime、monotonic time、raw time、boot time,以及各种offset。
void __init timekeeping_init(void)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
struct clocksource *clock;
unsigned long flags;
struct timespec64 now, boot, tmp;
read_persistent_clock64(&now);
if (!timespec64_valid_strict(&now)) {
pr_warn("WARNING: Persistent clock returned invalid value!\n"
" Check your CMOS/BIOS settings.\n");
now.tv_sec = 0;
now.tv_nsec = 0;
} else if (now.tv_sec || now.tv_nsec)
persistent_clock_exists = true;
read_boot_clock64(&boot);
if (!timespec64_valid_strict(&boot)) {
pr_warn("WARNING: Boot clock returned invalid value!\n"
" Check your CMOS/BIOS settings.\n");
boot.tv_sec = 0;
boot.tv_nsec = 0;
}
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
write_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
ntp_init();
clock = clocksource_default_clock();
if (clock->enable)
clock->enable(clock);
tk_setup_internals(tk, clock);
tk_set_xtime(tk, &now);
tk->raw_time.tv_sec = 0;
tk->raw_time.tv_nsec = 0;
if (boot.tv_sec == 0 && boot.tv_nsec == 0)
boot = tk_xtime(tk);
set_normalized_timespec64(&tmp, -boot.tv_sec, -boot.tv_nsec);
tk_set_wall_to_mono(tk, tmp);
timekeeping_update(tk, TK_MIRROR | TK_CLOCK_WAS_SET);
write_seqcount_end(&tk_core.seq);
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
}
timekeeper原理上的初始化是在timekeeping_init()函数中完成的,但是read_persistent_clock64()、read_boot_clock64()都是空函数,所以实际上的初始化是另外的路径:rtc_hctosys() -> do_settimeofday64(),rtc初始化的时候重新配置timekeeper。
static int __init rtc_hctosys(void)
{
int err = -ENODEV;
struct rtc_time tm;
struct timespec64 tv64 = {
.tv_nsec = NSEC_PER_SEC >> 1,
};
struct rtc_device *rtc = rtc_class_open(CONFIG_RTC_HCTOSYS_DEVICE);
if (rtc == NULL) {
pr_info("unable to open rtc device (%s)\n",
CONFIG_RTC_HCTOSYS_DEVICE);
goto err_open;
}
/* (1) 读取当前的rtc时间 */
err = rtc_read_time(rtc, &tm);
if (err) {
dev_err(rtc->dev.parent,
"hctosys: unable to read the hardware clock\n");
goto err_read;
}
tv64.tv_sec = rtc_tm_to_time64(&tm);
tv64.tv_nsec = tm.tm_cnt * (1000000000 / 32768);
/* (2) 根据rtc时间配置xtime */
err = do_settimeofday64(&tv64);
dev_info(rtc->dev.parent,
"setting system clock to "
"%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d UTC (%lld)\n",
tm.tm_year + 1900, tm.tm_mon + 1, tm.tm_mday,
tm.tm_hour, tm.tm_min, tm.tm_sec,
(long long) tv64.tv_sec);
err_read:
rtc_class_close(rtc);
err_open:
rtc_hctosys_ret = err;
return err;
}
|→
int do_settimeofday64(const struct timespec64 *ts)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
struct timespec64 ts_delta, xt;
unsigned long flags;
int ret = 0;
if (!timespec64_valid_strict(ts))
return -EINVAL;
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
write_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
timekeeping_forward_now(tk);
/* (2.1) 读取当前的xtime,计算rtc time和xtime之间的差值 */
xt = tk_xtime(tk);
ts_delta.tv_sec = ts->tv_sec - xt.tv_sec;
ts_delta.tv_nsec = ts->tv_nsec - xt.tv_nsec;
if (timespec64_compare(&tk->wall_to_monotonic, &ts_delta) > 0) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out;
}
/* (2.2) 将差值追加到offset;tk->wall_to_monotonic、tk->offs_real */
tk_set_wall_to_mono(tk, timespec64_sub(tk->wall_to_monotonic, ts_delta));
/* (2.3) 更新xtime */
tk_set_xtime(tk, ts);
out:
timekeeping_update(tk, TK_CLEAR_NTP | TK_MIRROR | TK_CLOCK_WAS_SET);
write_seqcount_end(&tk_core.seq);
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
/* signal hrtimers about time change */
clock_was_set();
notify_time_update();
return ret;
}
2.2.3、timekeeper的update
clocksource定时器的值要定时的读出来,并且把增量加到timekeeper中,不然clocksource定时器会溢出。这个定时更新的时间一般是1 tick,调用的函数是update_wall_time():
void update_wall_time(void)
{
struct timekeeper *real_tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
struct timekeeper *tk = &shadow_timekeeper;
cycle_t offset;
int shift = 0, maxshift;
unsigned int clock_set = 0;
unsigned long flags;
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
/* Make sure we're fully resumed: */
if (unlikely(timekeeping_suspended))
goto out;
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_USES_GETTIMEOFFSET
offset = real_tk->cycle_interval;
#else
/* (1) 获取clocksource和上一次update之间的offset */
offset = clocksource_delta(tk->tkr_mono.read(tk->tkr_mono.clock),
tk->tkr_mono.cycle_last, tk->tkr_mono.mask);
#endif
/* Check if there's really nothing to do */
if (offset < real_tk->cycle_interval)
goto out;
/* Do some additional sanity checking */
timekeeping_check_update(real_tk, offset);
/*
* With NO_HZ we may have to accumulate many cycle_intervals
* (think "ticks") worth of time at once. To do this efficiently,
* we calculate the largest doubling multiple of cycle_intervals
* that is smaller than the offset. We then accumulate that
* chunk in one go, and then try to consume the next smaller
* doubled multiple.
*/
shift = ilog2(offset) - ilog2(tk->cycle_interval);
shift = max(0, shift);
/* Bound shift to one less than what overflows tick_length */
maxshift = (64 - (ilog2(ntp_tick_length())+1)) - 1;
shift = min(shift, maxshift);
/* (2) 如果offset的值是多个cycle_interval,
不要一次update,使用2的n次方cycle_interval的方式逐个update。
tk->cycle_interval的值在tk_setup_internals()时被赋值,默认为1 tick */
while (offset >= tk->cycle_interval) {
/* (3) 将offset更新到timekeeper中 */
offset = logarithmic_accumulation(tk, offset, shift,
&clock_set);
if (offset < tk->cycle_interval<
shift--;
}
/* correct the clock when NTP error is too big */
timekeeping_adjust(tk, offset);
/*
* XXX This can be killed once everyone converts
* to the new update_vsyscall.
*/
old_vsyscall_fixup(tk);
/*
* Finally, make sure that after the rounding
* xtime_nsec isn't larger than NSEC_PER_SEC
*/
clock_set |= accumulate_nsecs_to_secs(tk);
write_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
/*
* Update the real timekeeper.
*
* We could avoid this memcpy by switching pointers, but that
* requires changes to all other timekeeper usage sites as
* well, i.e. move the timekeeper pointer getter into the
* spinlocked/seqcount protected sections. And we trade this
* memcpy under the tk_core.seq against one before we start
* updating.
*/
/* (4) */
timekeeping_update(tk, clock_set);
memcpy(real_tk, tk, sizeof(*tk));
/* The memcpy must come last. Do not put anything here! */
write_seqcount_end(&tk_core.seq);
out:
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
if (clock_set)
/* Have to call _delayed version, since in irq context*/
clock_was_set_delayed();
}
|→
static cycle_t logarithmic_accumulation(struct timekeeper *tk, cycle_t offset,
u32 shift,
unsigned int *clock_set)
{
cycle_t interval = tk->cycle_interval << shift;
u64 raw_nsecs;
/* If the offset is smaller than a shifted interval, do nothing */
if (offset < interval)
return offset;
/* Accumulate one shifted interval */
offset -= interval;
/* (3.1) 更新cycle_last */
tk->tkr_mono.cycle_last += interval;
tk->tkr_raw.cycle_last += interval;
/* (3.2) 更新xtime:
tk->tkr_mono.xtime_nsec
tk->xtime_sec */
tk->tkr_mono.xtime_nsec += tk->xtime_interval << shift;
*clock_set |= accumulate_nsecs_to_secs(tk);
/* Accumulate raw time */
/* (3.3) 更新raw time:
tk->raw_time.tv_nsec
tk->raw_time.tv_sec */
raw_nsecs = (u64)tk->raw_interval << shift;
raw_nsecs += tk->raw_time.tv_nsec;
if (raw_nsecs >= NSEC_PER_SEC) {
u64 raw_secs = raw_nsecs;
raw_nsecs = do_div(raw_secs, NSEC_PER_SEC);
tk->raw_time.tv_sec += raw_secs;
}
tk->raw_time.tv_nsec = raw_nsecs;
/* Accumulate error between NTP and clock interval */
tk->ntp_error += tk->ntp_tick << shift;
tk->ntp_error -= (tk->xtime_interval + tk->xtime_remainder) <<
(tk->ntp_error_shift + shift);
return offset;
}
|→
static void timekeeping_update(struct timekeeper *tk, unsigned int action)
{
if (action & TK_CLEAR_NTP) {
tk->ntp_error = 0;
ntp_clear();
}
tk_update_leap_state(tk);
/* (4.1) update monotonic time */
tk_update_ktime_data(tk);
update_vsyscall(tk);
update_pvclock_gtod(tk, action & TK_CLOCK_WAS_SET);
update_fast_timekeeper(&tk->tkr_mono, &tk_fast_mono);
update_fast_timekeeper(&tk->tkr_raw, &tk_fast_raw);
if (action & TK_CLOCK_WAS_SET)
tk->clock_was_set_seq++;
/*
* The mirroring of the data to the shadow-timekeeper needs
* to happen last here to ensure we don't over-write the
* timekeeper structure on the next update with stale data
*/
if (action & TK_MIRROR)
memcpy(&shadow_timekeeper, &tk_core.timekeeper,
sizeof(tk_core.timekeeper));
}
||→
static inline void tk_update_ktime_data(struct timekeeper *tk)
{
u64 seconds;
u32 nsec;
/*
* The xtime based monotonic readout is:
*nsec = (xtime_sec + wtm_sec) * 1e9 + wtm_nsec + now();
* The ktime based monotonic readout is:
*nsec = base_mono + now();
* ==> base_mono = (xtime_sec + wtm_sec) * 1e9 + wtm_nsec
*/
/* (4.1.1) update tk->tkr_mono.base的值,
= tk->xtime_sec + tk->wall_to_monotonic,
tk->tkr_mono.xtime_nsec 没有计算到base中 */
seconds = (u64)(tk->xtime_sec + tk->wall_to_monotonic.tv_sec);
nsec = (u32) tk->wall_to_monotonic.tv_nsec;
tk->tkr_mono.base = ns_to_ktime(seconds * NSEC_PER_SEC + nsec);
/* Update the monotonic raw base */
/* (4.1.2) update tk->tkr_raw.base的值,
直接转换tk->raw_time */
tk->tkr_raw.base = timespec64_to_ktime(tk->raw_time);
/*
* The sum of the nanoseconds portions of xtime and
* wall_to_monotonic can be greater/equal one second. Take
* this into account before updating tk->ktime_sec.
*/
/* (4.1.3) update tk->ktime_sec的值
nsec += (u32)(tk->tkr_mono.xtime_nsec >> tk->tkr_mono.shift);
if (nsec >= NSEC_PER_SEC)
seconds++;
tk->ktime_sec = seconds;
}
2.2.4、timekeeper的获取xtime/wall time 的获取:
do_gettimeofday()、ktime_get_real_ts()最后调用的getnstimeofday64() -> __getnstimeofday64()获取到xtime:
int __getnstimeofday64(struct timespec64 *ts)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
unsigned long seq;
s64 nsecs = 0;
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
/* (1) sec直接从变量tk->xtime_sec获取到,
即上一tick更新的值 */
ts->tv_sec = tk->xtime_sec;
/* (2) nsec需要更新最新的值:tk->tkr_mono.xtime_nsec + delta
delta是距离上一次tick更新的差值 */
nsecs = timekeeping_get_ns(&tk->tkr_mono);
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&tk_core.seq, seq));
ts->tv_nsec = 0;
timespec64_add_ns(ts, nsecs);
/*
* Do not bail out early, in case there were callers still using
* the value, even in the face of the WARN_ON.
*/
if (unlikely(timekeeping_suspended))
return -EAGAIN;
return 0;
}
|→
static inline s64 timekeeping_get_ns(struct tk_read_base *tkr)
{
cycle_t delta;
s64 nsec;
/* (2.1) 获取距离上一次tick更新,timer的delta值 */
delta = timekeeping_get_delta(tkr);
/* (2.2) delta加上上一次的nsec tkr->xtime_nsec,
即为最新的ns值 */
nsec = (delta * tkr->mult + tkr->xtime_nsec) >> tkr->shift;
/* If arch requires, add in get_arch_timeoffset() */
return nsec + arch_gettimeoffset();
}
||→
static inline cycle_t timekeeping_get_delta(struct tk_read_base *tkr)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
cycle_t now, last, mask, max, delta;
unsigned int seq;
/*
* Since we're called holding a seqlock, the data may shift
* under us while we're doing the calculation. This can cause
* false positives, since we'd note a problem but throw the
* results away. So nest another seqlock here to atomically
* grab the points we are checking with.
*/
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
/* (2.1.1) 使用read函数读取当前timer的计数 */
now = tkr->read(tkr->clock);
last = tkr->cycle_last;
mask = tkr->mask;
max = tkr->clock->max_cycles;
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&tk_core.seq, seq));
/* (2.1.2) 使用公式:(now - last) & mask,
计算delta值 */
delta = clocksource_delta(now, last, mask);
/*
* Try to catch underflows by checking if we are seeing small
* mask-relative negative values.
*/
if (unlikely((~delta & mask) < (mask >> 3))) {
tk->underflow_seen = 1;
delta = 0;
}
/* Cap delta value to the max_cycles values to avoid mult overflows */
if (unlikely(delta > max)) {
tk->overflow_seen = 1;
delta = tkr->clock->max_cycles;
}
return delta;
}
ktime_get_real()使用monotonic time再加上差值timekeeper.offs_real的方法来获取xtime:
static inline ktime_t ktime_get_real(void)
{
return ktime_get_with_offset(TK_OFFS_REAL);
}
|→
static ktime_t *offsets[TK_OFFS_MAX] = {
[TK_OFFS_REAL]= &tk_core.timekeeper.offs_real,
[TK_OFFS_BOOT]= &tk_core.timekeeper.offs_boot,
[TK_OFFS_TAI]= &tk_core.timekeeper.offs_tai,
};
ktime_t ktime_get_with_offset(enum tk_offsets offs)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
unsigned int seq;
ktime_t base, *offset = offsets[offs];
s64 nsecs;
WARN_ON(timekeeping_suspended);
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
/* (1) monotonic time = tk->tkr_mono.base,
offset = timekeeper.offs_real */
base = ktime_add(tk->tkr_mono.base, *offset);
/* (2) nsec需要更新最新的值:tk->tkr_mono.xtime_nsec + delta
delta是距离上一次tick更新的差值 */
nsecs = timekeeping_get_ns(&tk->tkr_mono);
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&tk_core.seq, seq));
return ktime_add_ns(base, nsecs);
}monotonic time 的获取;
ktime_get()直接获取monotonic time:
ktime_t ktime_get(void)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
unsigned int seq;
ktime_t base;
s64 nsecs;
WARN_ON(timekeeping_suspended);
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
/* (1) monotonic time = tk->tkr_mono.base */
base = tk->tkr_mono.base;
/* (2) nsec需要更新最新的值:tk->tkr_mono.xtime_nsec + delta
delta是距离上一次tick更新的差值 */
nsecs = timekeeping_get_ns(&tk->tkr_mono);
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&tk_core.seq, seq));
return ktime_add_ns(base, nsecs);
}
ktime_get_ts64()通过xtime加上差值tk->wall_to_monotonic的方法来获取monotonic time:
void ktime_get_ts64(struct timespec64 *ts)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
struct timespec64 tomono;
s64 nsec;
unsigned int seq;
WARN_ON(timekeeping_suspended);
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
/* (1) 获取xtime */
ts->tv_sec = tk->xtime_sec;
nsec = timekeeping_get_ns(&tk->tkr_mono);
/* (2) 加上xtime和monotonic之间的差值tk->wall_to_monotonic */
tomono = tk->wall_to_monotonic;
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&tk_core.seq, seq));
ts->tv_sec += tomono.tv_sec;
ts->tv_nsec = 0;
timespec64_add_ns(ts, nsec + tomono.tv_nsec);
}raw monotonic time 的获取;
ktime_get_raw()通过tk->tkr_raw.base获取raw monotonic time:
ktime_t ktime_get_raw(void)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
unsigned int seq;
ktime_t base;
s64 nsecs;
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
/* (1) raw monotonic time = tk->tkr_raw.base */
base = tk->tkr_raw.base;
/* (2) nsec需要更新最新的值:tk->tkr_raw.xtime_nsec + delta
delta是距离上一次tick更新的差值 */
nsecs = timekeeping_get_ns(&tk->tkr_raw);
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&tk_core.seq, seq));
return ktime_add_ns(base, nsecs);
}
getrawmonotonic64()通过tk->raw_time获取raw monotonic time:
void getrawmonotonic64(struct timespec64 *ts)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
struct timespec64 ts64;
unsigned long seq;
s64 nsecs;
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
nsecs = timekeeping_get_ns(&tk->tkr_raw);
ts64 = tk->raw_time;
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&tk_core.seq, seq));
timespec64_add_ns(&ts64, nsecs);
*ts = ts64;
}boot time 的获取;
ktime_get_boottime()使用monotonic time再加上差值timekeeper.offs_boot的方法来获取boot time:
static inline ktime_t ktime_get_boottime(void)
{
return ktime_get_with_offset(TK_OFFS_BOOT);
}
|→
static ktime_t *offsets[TK_OFFS_MAX] = {
[TK_OFFS_REAL]= &tk_core.timekeeper.offs_real,
[TK_OFFS_BOOT]= &tk_core.timekeeper.offs_boot,
[TK_OFFS_TAI]= &tk_core.timekeeper.offs_tai,
};
ktime_t ktime_get_with_offset(enum tk_offsets offs)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
unsigned int seq;
ktime_t base, *offset = offsets[offs];
s64 nsecs;
WARN_ON(timekeeping_suspended);
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
/* (1) monotonic time = tk->tkr_mono.base,
offset = timekeeper.offs_boot */
base = ktime_add(tk->tkr_mono.base, *offset);
/* (2) nsec需要更新最新的值:tk->tkr_mono.xtime_nsec + delta
delta是距离上一次tick更新的差值 */
nsecs = timekeeping_get_ns(&tk->tkr_mono);
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&tk_core.seq, seq));
return ktime_add_ns(base, nsecs);
}
2.2.5、timekeeper suspend
系统在进入suspend以后,clocksource不会再工作,这部分时间会计入xtime和boot time,但是不会计入monotonic time。
void timekeeping_resume(void)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
struct clocksource *clock = tk->tkr_mono.clock;
unsigned long flags;
struct timespec64 ts_new, ts_delta;
cycle_t cycle_now, cycle_delta;
sleeptime_injected = false;
read_persistent_clock64(&ts_new);
clockevents_resume();
clocksource_resume();
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
write_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
/*
* After system resumes, we need to calculate the suspended time and
* compensate it for the OS time. There are 3 sources that could be
* used: Nonstop clocksource during suspend, persistent clock and rtc
* device.
*
* One specific platform may have 1 or 2 or all of them, and the
* preference will be:
*suspend-nonstop clocksource -> persistent clock -> rtc
* The less preferred source will only be tried if there is no better
* usable source. The rtc part is handled separately in rtc core code.
*/
cycle_now = tk->tkr_mono.read(clock);
if ((clock->flags & CLOCK_SOURCE_SUSPEND_NONSTOP) &&
cycle_now > tk->tkr_mono.cycle_last) {
u64 num, max = ULLONG_MAX;
u32 mult = clock->mult;
u32 shift = clock->shift;
s64 nsec = 0;
cycle_delta = clocksource_delta(cycle_now, tk->tkr_mono.cycle_last,
tk->tkr_mono.mask);
/*
* "cycle_delta * mutl" may cause 64 bits overflow, if the
* suspended time is too long. In that case we need do the
* 64 bits math carefully
*/
do_div(max, mult);
if (cycle_delta > max) {
num = div64_u64(cycle_delta, max);
nsec = (((u64) max * mult) >> shift) * num;
cycle_delta -= num * max;
}
nsec += ((u64) cycle_delta * mult) >> shift;
ts_delta = ns_to_timespec64(nsec);
sleeptime_injected = true;
} else if (timespec64_compare(&ts_new, &timekeeping_suspend_time) > 0) {
ts_delta = timespec64_sub(ts_new, timekeeping_suspend_time);
sleeptime_injected = true;
}
if (sleeptime_injected)
__timekeeping_inject_sleeptime(tk, &ts_delta);
/* Re-base the last cycle value */
tk->tkr_mono.cycle_last = cycle_now;
tk->tkr_raw.cycle_last = cycle_now;
tk->ntp_error = 0;
timekeeping_suspended = 0;
timekeeping_update(tk, TK_MIRROR | TK_CLOCK_WAS_SET);
write_seqcount_end(&tk_core.seq);
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
touch_softlockup_watchdog();
tick_resume();
hrtimers_resume();
}
int timekeeping_suspend(void)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
unsigned long flags;
struct timespec64delta, delta_delta;
static struct timespec64old_delta;
read_persistent_clock64(&timekeeping_suspend_time);
/*
* On some systems the persistent_clock can not be detected at
* timekeeping_init by its return value, so if we see a valid
* value returned, update the persistent_clock_exists flag.
*/
if (timekeeping_suspend_time.tv_sec || timekeeping_suspend_time.tv_nsec)
persistent_clock_exists = true;
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
write_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
timekeeping_forward_now(tk);
timekeeping_suspended = 1;
if (persistent_clock_exists) {
/*
* To avoid drift caused by repeated suspend/resumes,
* which each can add ~1 second drift error,
* try to compensate so the difference in system time
* and persistent_clock time stays close to constant.
*/
delta = timespec64_sub(tk_xtime(tk), timekeeping_suspend_time);
delta_delta = timespec64_sub(delta, old_delta);
if (abs(delta_delta.tv_sec) >= 2) {
/*
* if delta_delta is too large, assume time correction
* has occurred and set old_delta to the current delta.
*/
old_delta = delta;
} else {
/* Otherwise try to adjust old_system to compensate */
timekeeping_suspend_time =
timespec64_add(timekeeping_suspend_time, delta_delta);
}
}
timekeeping_update(tk, TK_MIRROR);
halt_fast_timekeeper(tk);
write_seqcount_end(&tk_core.seq);
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
tick_suspend();
clocksource_suspend();
clockevents_suspend();
return 0;
}
/* sysfs resume/suspend bits for timekeeping */
static struct syscore_ops timekeeping_syscore_ops = {
.resume= timekeeping_resume,
.suspend= timekeeping_suspend,
};
和初始化一样的原因,理论上timekeeper的操作在timekeeping_resume()、timekeeping_suspend(),但是实际上在rtc的操作中执行rtc_suspend()、rtc_resume()。
static int rtc_suspend(struct device *dev)
{
struct rtc_device*rtc = to_rtc_device(dev);
struct rtc_timetm;
struct timespec64delta, delta_delta;
int err;
if (timekeeping_rtc_skipsuspend())
return 0;
if (strcmp(dev_name(&rtc->dev), CONFIG_RTC_HCTOSYS_DEVICE) != 0)
return 0;
/* snapshot the current RTC and system time at suspend*/
/* (1.1) 读取suspend时候的rtc时间 */
err = rtc_read_time(rtc, &tm);
if (err < 0) {
pr_debug("%s: fail to read rtc time\n", dev_name(&rtc->dev));
return 0;
}
/* (1.2) 读取当前xtime */
getnstimeofday64(&old_system);
old_rtc.tv_sec = rtc_tm_to_time64(&tm);
old_rtc.tv_nsec = tm.tm_cnt*(1000000000/32768);
/*
* To avoid drift caused by repeated suspend/resumes,
* which each can add ~1 second drift error,
* try to compensate so the difference in system time
* and rtc time stays close to constant.
*/
/* (1.3) 如果rtc时间和xtime有偏差,尝试纠正xtime */
delta = timespec64_sub(old_system, old_rtc);
delta_delta = timespec64_sub(delta, old_delta);
if (delta_delta.tv_sec < -2 || delta_delta.tv_sec >= 2) {
/*
* if delta_delta is too large, assume time correction
* has occured and set old_delta to the current delta.
*/
old_delta = delta;
} else {
/* Otherwise try to adjust old_system to compensate */
old_system = timespec64_sub(old_system, delta_delta);
}
return 0;
}
static int rtc_resume(struct device *dev)
{
struct rtc_device*rtc = to_rtc_device(dev);
struct rtc_timetm;
struct timespec64new_system, new_rtc;
struct timespec64sleep_time;
int err;
if (timekeeping_rtc_skipresume())
return 0;
rtc_hctosys_ret = -ENODEV;
if (strcmp(dev_name(&rtc->dev), CONFIG_RTC_HCTOSYS_DEVICE) != 0)
return 0;
/* snapshot the current rtc and system time at resume */
/* (2.1) 读取resume后的rtc时间和xtime */
getnstimeofday64(&new_system);
err = rtc_read_time(rtc, &tm);
if (err < 0) {
pr_debug("%s: fail to read rtc time\n", dev_name(&rtc->dev));
return 0;
}
new_rtc.tv_sec = rtc_tm_to_time64(&tm);
new_rtc.tv_nsec = tm.tm_cnt*(1000000000/32768);
if (new_rtc.tv_sec < old_rtc.tv_sec) {
pr_debug("%s: time travel!\n", dev_name(&rtc->dev));
return 0;
}
/* calculate the RTC time delta (sleep time)*/
/* (2.2) 计算suspend和resume之间rtc的差值 */
sleep_time = timespec64_sub(new_rtc, old_rtc);
/*
* Since these RTC suspend/resume handlers are not called
* at the very end of suspend or the start of resume,
* some run-time may pass on either sides of the sleep time
* so subtract kernel run-time between rtc_suspend to rtc_resume
* to keep things accurate.
*/
/* (2.3) 使用上一步的差值,再减去,suspend和resume之间xtime的差值
得到实际的sleep时间*/
sleep_time = timespec64_sub(sleep_time,
timespec64_sub(new_system, old_system));
if (sleep_time.tv_sec >= 0)
/* (2.4) 将计算得到的sleep时间,加入到timekeeper中 */
timekeeping_inject_sleeptime64(&sleep_time);
rtc_hctosys_ret = 0;
return 0;
}
|→
void timekeeping_inject_sleeptime64(struct timespec64 *delta)
{
struct timekeeper *tk = &tk_core.timekeeper;
unsigned long flags;
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
write_seqcount_begin(&tk_core.seq);
timekeeping_forward_now(tk);
__timekeeping_inject_sleeptime(tk, delta);
timekeeping_update(tk, TK_CLEAR_NTP | TK_MIRROR | TK_CLOCK_WAS_SET);
write_seqcount_end(&tk_core.seq);
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&timekeeper_lock, flags);
/* signal hrtimers about time change */
clock_was_set();
}
||→
static void __timekeeping_inject_sleeptime(struct timekeeper *tk,
struct timespec64 *delta)
{
if (!timespec64_valid_strict(delta)) {
printk_deferred(KERN_WARNING
"__timekeeping_inject_sleeptime: Invalid "
"sleep delta value!\n");
return;
}
/* (2.4.1) 更新xtime */
tk_xtime_add(tk, delta);
/* (2.4.2) 更新tk->wall_to_monotonic、tk->offs_real */
tk_set_wall_to_mono(tk, timespec64_sub(tk->wall_to_monotonic, *delta));
/* (2.4.3) 更新tk->offs_boot */
tk_update_sleep_time(tk, timespec64_to_ktime(*delta));
tk_debug_account_sleep_time(delta);
}
3、clock_event
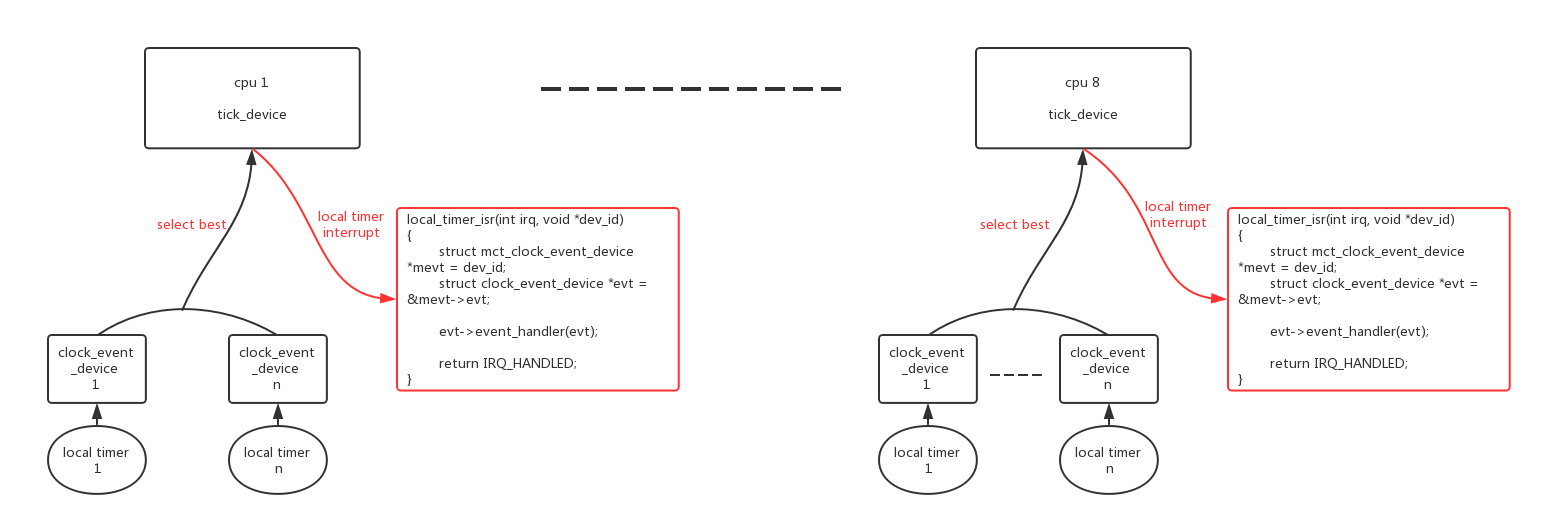
clock_event其实就是对local timer的使用,每个cpu对应一个本地local timer。global timer启动后不需要主动做任何事情,只需要等待timekepper的读取就可以了。而local timer需要触发中断,它的主要价值就体现在定时中断处理了,中断的时间可以是固定的(period mode)也或者是不固定的(oneshot mode)。
3.1、clock_event的注册
3.1.1、exynos clock_event的注册
exynos clock_event的注册分为两部分:第一部分:localtimer中断的注册:
static void __init exynos4_timer_resources(struct device_node *np, void __iomem *base)
{
int err, cpu;
struct mct_clock_event_device *mevt = this_cpu_ptr(&percpu_mct_tick);
struct clk *mct_clk, *tick_clk;
tick_clk = np ? of_clk_get_by_name(np, "fin_pll") :
clk_get(NULL, "fin_pll");
if (IS_ERR(tick_clk))
panic("%s: unable to determine tick clock rate\n", __func__);
clk_rate = clk_get_rate(tick_clk);
mct_clk = np ? of_clk_get_by_name(np, "mct") : clk_get(NULL, "mct");
if (IS_ERR(mct_clk))
panic("%s: unable to retrieve mct clock instance\n", __func__);
clk_prepare_enable(mct_clk);
reg_base = base;
if (!reg_base)
panic("%s: unable to ioremap mct address space\n", __func__);
if (mct_int_type == MCT_INT_PPI) {
/* (1) 大部分的localtimer是PPI模式,
注册中断处理函数:exynos4_mct_tick_isr() */
err = request_percpu_irq(mct_irqs[MCT_L0_IRQ],
exynos4_mct_tick_isr, "MCT",
&percpu_mct_tick);
WARN(err, "MCT: can't request IRQ %d (%d)\n",
mct_irqs[MCT_L0_IRQ], err);
} else {
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
int mct_irq = mct_irqs[MCT_L0_IRQ + cpu];
struct mct_clock_event_device *pcpu_mevt =
per_cpu_ptr(&percpu_mct_tick, cpu);
pcpu_mevt->evt.irq = -1;
irq_set_status_flags(mct_irq, IRQ_NOAUTOEN);
if (request_irq(mct_irq,
exynos4_mct_tick_isr,
IRQF_TIMER | IRQF_NOBALANCING,
pcpu_mevt->name, pcpu_mevt)) {
pr_err("exynos-mct: cannot register IRQ (cpu%d)\n",
cpu);
continue;
}
pcpu_mevt->evt.irq = mct_irq;
}
}
/* (2) 注册cpu hotplug的notifier,
在其他cpu up时调用exynos4_local_timer_setup()注册clock_event */
err = register_cpu_notifier(&exynos4_mct_cpu_nb);
if (err)
goto out_irq;
/* Immediately configure the timer on the boot CPU */
/* (3) 注册本cpu的clock_event */
exynos4_local_timer_setup(mevt);
return;
out_irq:
free_percpu_irq(mct_irqs[MCT_L0_IRQ], &percpu_mct_tick);
}
static irqreturn_t exynos4_mct_tick_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct mct_clock_event_device *mevt = dev_id;
struct clock_event_device *evt = &mevt->evt;
exynos4_mct_tick_clear(mevt);
/* (4) localtimer中断处理函数是固定的也是非常简单的,
调用本cpu clock_event_device的handler函数:evt->event_handler(evt) */
evt->event_handler(evt);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}第二部分:clock_event_device注册:
static int exynos4_local_timer_setup(struct mct_clock_event_device *mevt)
{
struct clock_event_device *evt = &mevt->evt;
unsigned int cpu = smp_processor_id();
mevt->base = EXYNOS4_MCT_L_BASE(cpu);
snprintf(mevt->name, sizeof(mevt->name), "mct_tick%d", cpu);
/* (1) 初始化clock_event_device */
evt->name = mevt->name;
evt->cpumask = cpumask_of(cpu); // 本clock_event_device只服务于一个cpu
evt->set_next_event = exynos4_tick_set_next_event;
evt->set_state_periodic = set_state_periodic;
evt->set_state_shutdown = set_state_shutdown;
evt->set_state_oneshot = set_state_shutdown;
evt->tick_resume = set_state_shutdown;
evt->features = CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_PERIODIC | CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_ONESHOT;
evt->rating = 450;
exynos4_mct_write(TICK_BASE_CNT, mevt->base + MCT_L_TCNTB_OFFSET);
if (mct_int_type == MCT_INT_SPI) {
if (evt->irq == -1)
return -EIO;
irq_force_affinity(evt->irq, cpumask_of(cpu));
enable_irq(evt->irq);
} else {
enable_percpu_irq(mct_irqs[MCT_L0_IRQ], 0);
}
/* (2) 配置并注册clockevent */
clockevents_config_and_register(evt, clk_rate / (TICK_BASE_CNT + 1),
0xf, 0x7fffffff);
return 0;
}
3.1.2、clock_event_device的注册
我们来分析一下clock_event_device的注册过程。
void clockevents_config_and_register(struct clock_event_device *dev,
u32 freq, unsigned long min_delta,
unsigned long max_delta)
{
dev->min_delta_ticks = min_delta; // localtimer可配置的最小定时值
dev->max_delta_ticks = max_delta; // localtimer可配置的最大定时值,
// 比如exynos是31bit的localtimer,最大值就是0x7fffffff
/* (1) 根据localtimer的freq,计算clock_event_device对应的mult、shift,
mult、shift的作用是用来做ns到localtimer cycle之间的转换,
与之相反的是,在clocksource中mult、shift用来转换localtimer cycle到ns */
clockevents_config(dev, freq);
/* (2) 继续注册clock_event_device */
clockevents_register_device(dev);
}
|→
void clockevents_config(struct clock_event_device *dev, u32 freq)
{
u64 sec;
/* (1.1) 如果不支持oneshot模式,只是period模式,
定时周期是固定的,不需要动态计算ns到cycle的转换 */
if (!(dev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_ONESHOT))
return;
/*
* Calculate the maximum number of seconds we can sleep. Limit
* to 10 minutes for hardware which can program more than
* 32bit ticks so we still get reasonable conversion values.
*/
sec = dev->max_delta_ticks;
do_div(sec, freq);
if (!sec)
sec = 1;
else if (sec > 600 && dev->max_delta_ticks > UINT_MAX)
sec = 600;
/* (1.2) 根据localtimer的freq,计算clock_event_device对应的mult、shift */
clockevents_calc_mult_shift(dev, freq, sec);
/* (1.3) 转换min、max的cycle到ns */
dev->min_delta_ns = cev_delta2ns(dev->min_delta_ticks, dev, false);
dev->max_delta_ns = cev_delta2ns(dev->max_delta_ticks, dev, true);
}
|→
void clockevents_register_device(struct clock_event_device *dev)
{
unsigned long flags;
/* Initialize state to DETACHED */
clockevent_set_state(dev, CLOCK_EVT_STATE_DETACHED);
if (!dev->cpumask) {
WARN_ON(num_possible_cpus() > 1);
dev->cpumask = cpumask_of(smp_processor_id());
}
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&clockevents_lock, flags);
/* (2.1) 将clock_event_device加入到全局链表clockevent_devices中 */
list_add(&dev->list, &clockevent_devices);
/* (2.2) 继续尝试向本cpu的tick_device中注册clock_event_device */
tick_check_new_device(dev);
clockevents_notify_released();
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&clockevents_lock, flags);
}
||→
void tick_check_new_device(struct clock_event_device *newdev)
{
struct clock_event_device *curdev;
struct tick_device *td;
int cpu;
cpu = smp_processor_id();
td = &per_cpu(tick_cpu_device, cpu);
curdev = td->evtdev;
/* cpu local device ? */
/* (2.2.1) 新的clock_event_device是否支持本cpu? */
if (!tick_check_percpu(curdev, newdev, cpu))
goto out_bc;
/* Preference decision */
/* (2.2.2) 新的clock_event_device是否比当前clock_event_device更适合?
1.如果curdev已经是oneshot模式,而newdev不支持oneshot,则切换
2.newdev的精度要大于curdev,精度 = dev->rating */
if (!tick_check_preferred(curdev, newdev))
goto out_bc;
if (!try_module_get(newdev->owner))
return;
/*
* Replace the eventually existing device by the new
* device. If the current device is the broadcast device, do
* not give it back to the clockevents layer !
*/
if (tick_is_broadcast_device(curdev)) {
clockevents_shutdown(curdev);
curdev = NULL;
}
/* (2.2.3) 关闭curdev、newdev */
clockevents_exchange_device(curdev, newdev);
/* (2.2.4) 继续clock_event_device注册 */
tick_setup_device(td, newdev, cpu, cpumask_of(cpu));
if (newdev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_ONESHOT)
tick_oneshot_notify();
return;
out_bc:
/*
* Can the new device be used as a broadcast device ?
*/
/* (2.2.5) 如果newdev不适合注册成本cpu的td->evtdev,
尝试将其注册成broadcast clockevent */
tick_install_broadcast_device(newdev);
}
|||→
static void tick_setup_device(struct tick_device *td,
struct clock_event_device *newdev, int cpu,
const struct cpumask *cpumask)
{
ktime_t next_event;
void (*handler)(struct clock_event_device *) = NULL;
/*
* First device setup ?
*/
if (!td->evtdev) {
/* (2.2.4.1) 如果是tick_do_timer_cpu没有被设置,且没有使能tick_nohz_full_cpu
把tick_do_timer_cpu设置成本cpu,
tick_do_timer_cpu负责在tick中update jiffies、update_wall_time */
/*
* If no cpu took the do_timer update, assign it to
* this cpu:
*/
if (tick_do_timer_cpu == TICK_DO_TIMER_BOOT) {
if (!tick_nohz_full_cpu(cpu))
tick_do_timer_cpu = cpu;
else
tick_do_timer_cpu = TICK_DO_TIMER_NONE;
tick_next_period = ktime_get();
tick_period = ktime_set(0, NSEC_PER_SEC / HZ);
}
/*
* Startup in periodic mode first.
*/
/* (2.2.4.2) 如果tick_device是第一次设置clock_event_device,
把tick_device设置成period模式 */
td->mode = TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC;
} else {
/* (2.2.4.3) 如果tick_device不是第一次设置clock_event_device,
备份原clock_event_deviced的event_handler和next_event */
handler = td->evtdev->event_handler;
next_event = td->evtdev->next_event;
td->evtdev->event_handler = clockevents_handle_noop;
}
/* (2.2.4.4) 更新tick_device->evtdev到new clock_event_deviced */
td->evtdev = newdev;
/*
* When the device is not per cpu, pin the interrupt to the
* current cpu:
*/
if (!cpumask_equal(newdev->cpumask, cpumask))
irq_set_affinity(newdev->irq, cpumask);
/*
* When global broadcasting is active, check if the current
* device is registered as a placeholder for broadcast mode.
* This allows us to handle this x86 misfeature in a generic
* way. This function also returns !=0 when we keep the
* current active broadcast state for this CPU.
*/
/* (2.2.4.5) 如果全局的brodcast clockevent服务已经启动,
本cpu的clockevent注册需要向brodcas服务,
这是为了解决x86的一个失误(misfeature),其他架构不需要? */
if (tick_device_uses_broadcast(newdev, cpu))
return;
/* (2.2.4.6) 根据td->mode安装clock_event_deviced的event_handler,并启动 */
if (td->mode == TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC)
/* (2.2.4.7) period模式 */
tick_setup_periodic(newdev, 0);
else
/* (2.2.4.8) oneshot模式 */
tick_setup_oneshot(newdev, handler, next_event);
}
3.2、tick_device的period mode
接上节,在cpu第一次注册clock_event_deviced的时候,td->mode默认被设置成period模式。event_handler会被初始化成tick_handle_periodic:
void tick_setup_periodic(struct clock_event_device *dev, int broadcast)
{
/* (1) 设置period模式下的event_handler */
tick_set_periodic_handler(dev, broadcast);
/* Broadcast setup ? */
if (!tick_device_is_functional(dev))
return;
/* (2) 如果dev支持period模式,则硬件上启动period模式:
tick_device->mode = TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC
clock_event_device->state_use_accessors = CLOCK_EVT_STATE_PERIODIC */
if ((dev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_PERIODIC) &&
!tick_broadcast_oneshot_active()) {
clockevents_switch_state(dev, CLOCK_EVT_STATE_PERIODIC);
} else {
unsigned long seq;
ktime_t next;
do {
seq = read_seqbegin(&jiffies_lock);
next = tick_next_period;
} while (read_seqretry(&jiffies_lock, seq));
/* (3) 如果dev不支持period模式只支持oneshot模式,则硬件上启动one shot模式,
使用oneshot模式来模拟period模式:
tick_device->mode = TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC
clock_event_device->state_use_accessors = CLOCK_EVT_STATE_ONESHOT */
clockevents_switch_state(dev, CLOCK_EVT_STATE_ONESHOT);
for (;;) {
if (!clockevents_program_event(dev, next, false))
return;
next = ktime_add(next, tick_period);
}
}
}
|→
void tick_set_periodic_handler(struct clock_event_device *dev, int broadcast)
{
if (!broadcast)
/* (1.1) 设置period模式下的event_handler */
dev->event_handler = tick_handle_periodic;
else
dev->event_handler = tick_handle_periodic_broadcast;
}
仔细分析一下tick_handle_periodic:
void tick_handle_periodic(struct clock_event_device *dev)
{
int cpu = smp_processor_id();
ktime_t next = dev->next_event;
/* (1) 周期性的tick任务 */
tick_periodic(cpu);
#if defined(CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS) || defined(CONFIG_NO_HZ_COMMON)
/*
* The cpu might have transitioned to HIGHRES or NOHZ mode via
* update_process_times() -> run_local_timers() ->
* hrtimer_run_queues().
*/
if (dev->event_handler != tick_handle_periodic)
return;
#endif
if (!clockevent_state_oneshot(dev))
return;
/* (2) 如果tick_device是period mode,而clockevent是oneshot模式,
编程oneshot模式clockevent在下一周期触发:
tick_device->mode = TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC
clock_event_device->state_use_accessors = CLOCK_EVT_STATE_ONESHOT */
for (;;) {
/*
* Setup the next period for devices, which do not have
* periodic mode:
*/
next = ktime_add(next, tick_period);
if (!clockevents_program_event(dev, next, false))
return;
/*
* Have to be careful here. If we're in oneshot mode,
* before we call tick_periodic() in a loop, we need
* to be sure we're using a real hardware clocksource.
* Otherwise we could get trapped in an infinite
* loop, as the tick_periodic() increments jiffies,
* which then will increment time, possibly causing
* the loop to trigger again and again.
*/
if (timekeeping_valid_for_hres())
tick_periodic(cpu);
}
}
|→
static void tick_periodic(int cpu)
{
/* (1.1) 如果本cpu是tick_do_timer_cpu,更新全局时间戳类型的任务,
包括update jiffies、update_wall_time */
if (tick_do_timer_cpu == cpu) {
write_seqlock(&jiffies_lock);
/* Keep track of the next tick event */
tick_next_period = ktime_add(tick_next_period, tick_period);
/* (1.1.1) 更新jiffies */
do_timer(1);
write_sequnlock(&jiffies_lock);
/* (1.1.2) 读取clocksource来更新timekeeper */
update_wall_time();
}
/* (1.2) 运行软件timer(run_local_timers())和运行调度tick任务(scheduler_tick()) */
update_process_times(user_mode(get_irq_regs()));
profile_tick(CPU_PROFILING);
}
3.3、运行Mode
关于mode,有几个结构涉及到:tick_device、clock_event_device、tick_sched、hrtimer_cpu_base、。组合起来有以下几种情况:
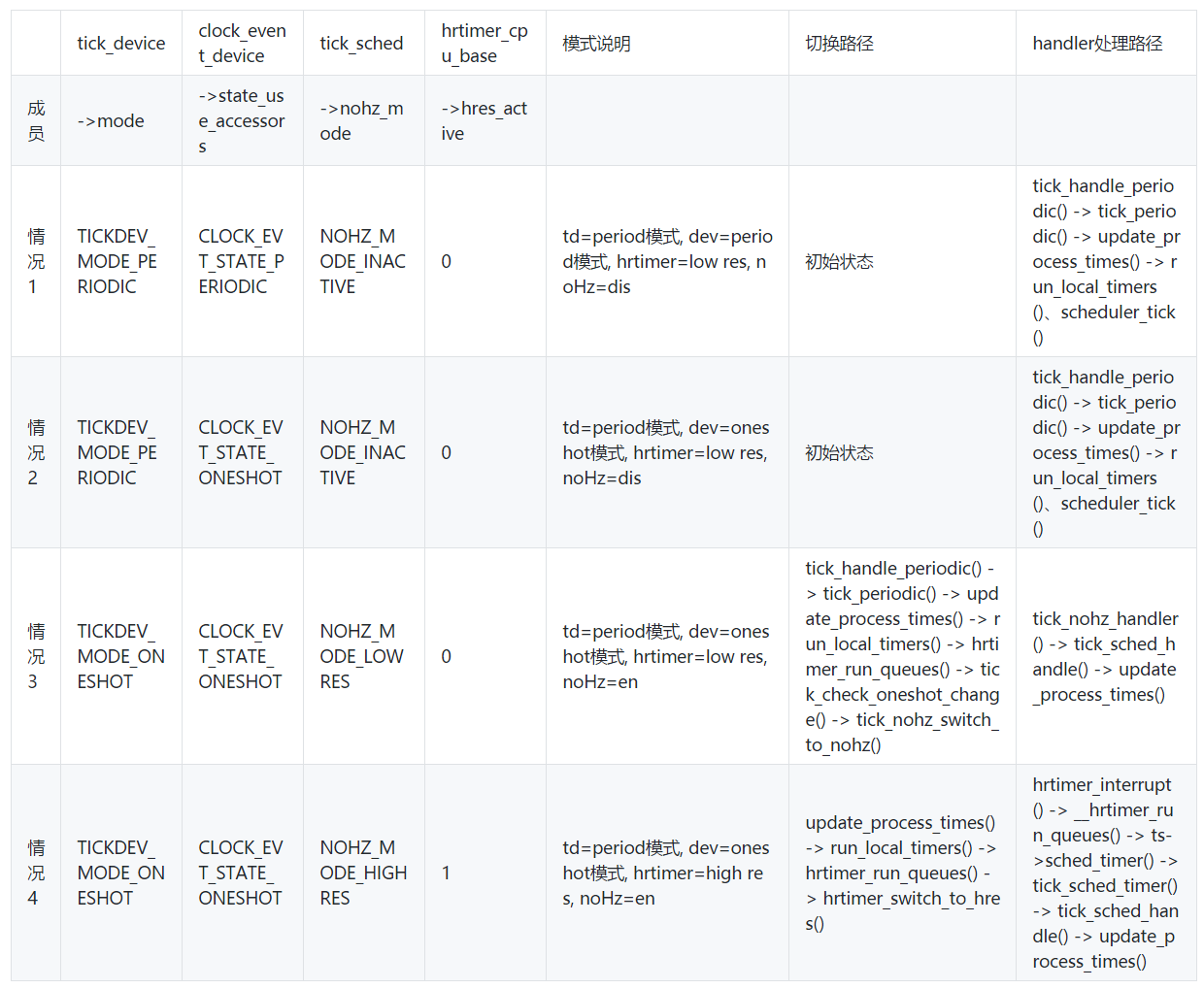
其实归结起来就3种mode:NOHZ_MODE_INACTIVE、NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES、NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES。下面来逐个解析一下。
3.3.1、NOHZ_MODE_INACTIVE
NOHZ_MODE_INACTIVE就是系统初始化时的状态:“td=period模式, dev=period/oneshot模式, hrtimer=low res, noHz=dis”。

NOHZ_MODE_INACTIVE模式:tick_device工作在period模式,HW local timer工作在period/oneshot模式;
noHZ没有使能,进入idle会被tick timer中断打断;
hrtimer工作在低精度模式,和低精度定时器(SW local timer)的精度一样,都是基于tick的;
3.3.2、NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES
在系统的运行过程中系统尝试进入精度更高的模式,如果noHZ可以使能,但是hrtimer高精度不能使能,即进入NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES模式:“td=period模式, dev=oneshot模式, hrtimer=low res, noHz=en”。
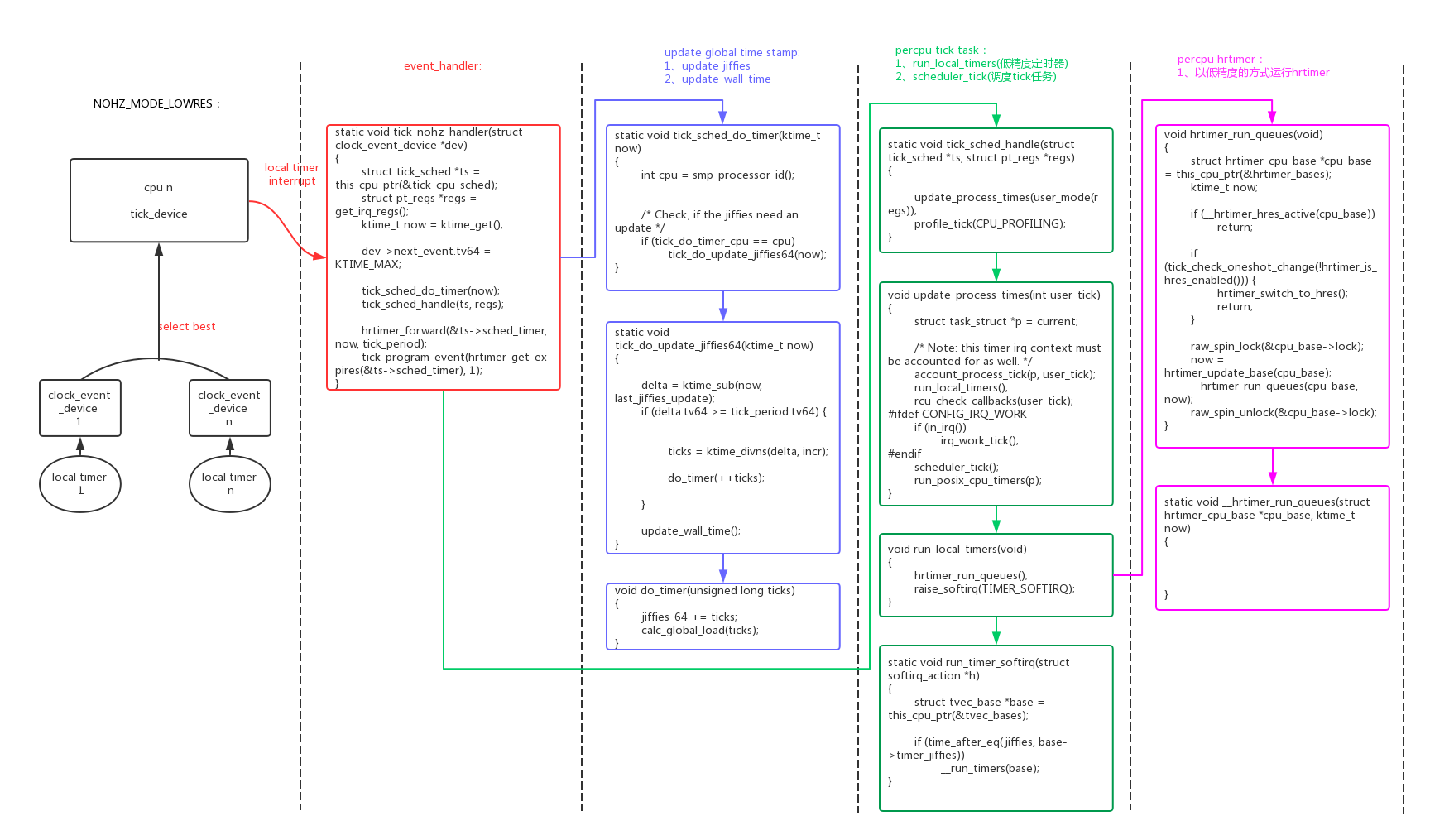
NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES模式:tick_device工作在oneshot模式,HW local timer工作在oneshot模式;
noHZ使能,进入idle不会被tick timer中断打断;
hrtimer工作在低精度模式,和低精度定时器(SW local timer)的精度一样,都是基于tick的;
为了支持noHZ,tick_device必须切换成oneshot模式,在进入idle时停掉tick timer(tick_nohz_idle_enter() -> __tick_nohz_idle_enter() -> tick_nohz_stop_sched_tick()),在离开idle时恢复tick timer(tick_nohz_idle_exit() -> tick_nohz_restart_sched_tick()),这样idle过程就不会被tick中断。就实现了noHZ模式(tickless)。
NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES模式下,没有进入idle时tick_device还是以固定周期工作的:
static void tick_nohz_handler(struct clock_event_device *dev)
{
struct tick_sched *ts = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_sched);
struct pt_regs *regs = get_irq_regs();
ktime_t now = ktime_get();
dev->next_event.tv64 = KTIME_MAX;
tick_sched_do_timer(now);
tick_sched_handle(ts, regs);
/* No need to reprogram if we are running tickless */
if (unlikely(ts->tick_stopped))
return;
/* (1) HW local timer还是以固定周期发生中断 */
hrtimer_forward(&ts->sched_timer, now, tick_period);
tick_program_event(hrtimer_get_expires(&ts->sched_timer), 1);
}
3.3.3、NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES
在系统的运行过程中系统尝试进入精度更高的模式,如果noHZ可以使能,hrtimer高精度可以使能,即进入NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES模式:“td=period模式, dev=oneshot模式, hrtimer=high res, noHz=en”。
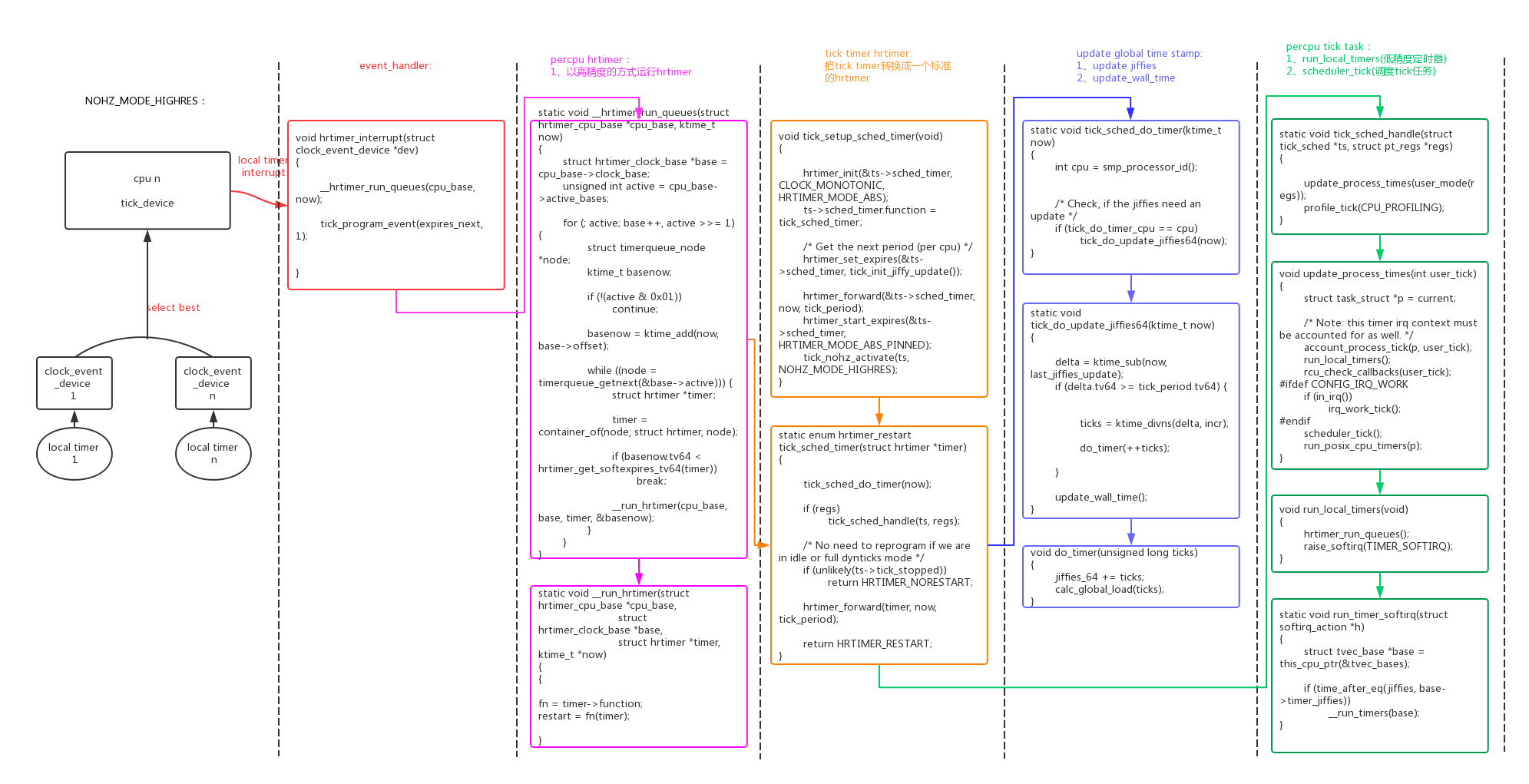
NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES:tick_device工作在oneshot模式,HW local timer工作在oneshot模式;
noHZ使能,进入idle不会被tick timer中断打断;
hrtimer工作在高精度模式,和硬件定时器(HWlocal timer)的精度一样,远大于低精度定时器tick精度;
为了支持hrtimer的高精度模式,hrtimer必须直接使用tick_device的oneshot模式,而常规的tick timer转换成hrtimer的一个子timer。
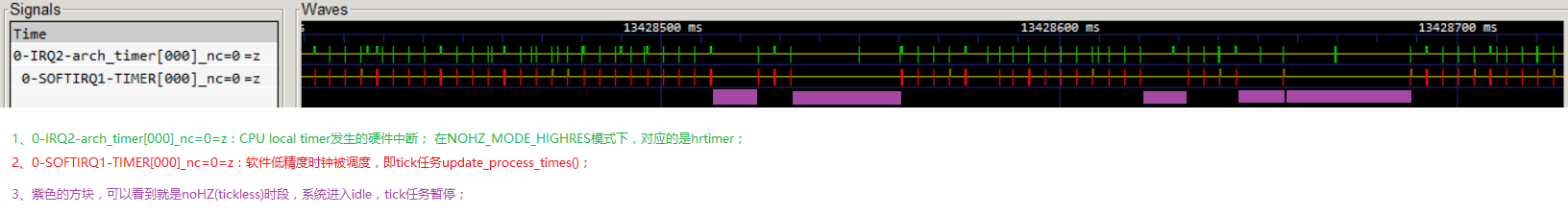
上图是NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES模式下,用ftrace抓取HW timer硬件中断和tick任务的执行情况:tick任务是以固定周期4ms固定执行的;
遇到tick任务超过4ms的间隔,这时就是进入了idle状态,且发生了noHZ(tickless);
硬件timer中断的发生周期是不固定的,是和hrtimer绑定的;
发生tick的时候肯定发生了timer硬中断,因为tick是其中一个hrtimer;
3.3.4、Mode切换
系统初始状态工作在NOHZ_MODE_INACTIVE模式时,会动态检测是否可以进入更高级别的模式NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES、NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES。这个检测工作是在这个路径中做的:tick_device工作在period模式:tick_handle_periodic() -> tick_periodic() -> update_process_times() -> run_local_timers() -> hrtimer_run_queues()
void hrtimer_run_queues(void)
{
struct hrtimer_cpu_base *cpu_base = this_cpu_ptr(&hrtimer_bases);
ktime_t now;
/* (3) 如果hrtimer已经切换到高精度模式,
则不会从run_local_timers()低精度定时器路径来运行hrtimer */
if (__hrtimer_hres_active(cpu_base))
return;
/*
* This _is_ ugly: We have to check periodically, whether we
* can switch to highres and / or nohz mode. The clocksource
* switch happens with xtime_lock held. Notification from
* there only sets the check bit in the tick_oneshot code,
* otherwise we might deadlock vs. xtime_lock.
*/
/* (1) 如果hrtimer没有使能、noHZ使能,
则调用:tick_check_oneshot_change() -> tick_nohz_switch_to_nohz(),
切换到NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES模式 */
if (tick_check_oneshot_change(!hrtimer_is_hres_enabled())) {
/* (2) 如果hrtimer使能、noHZ使能,
则调用:hrtimer_switch_to_hres(),
切换到NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES模式 */
hrtimer_switch_to_hres();
return;
}
raw_spin_lock(&cpu_base->lock);
now = hrtimer_update_base(cpu_base);
/* (4) 低精度hrtimer的运行函数 */
__hrtimer_run_queues(cpu_base, now);
raw_spin_unlock(&cpu_base->lock);
}
4、noHZ
系统在NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES、NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES两种模式下支持noHZ。noHZ是一个功耗优化的feature,在系统负载比较轻的时候没有任务需要调度cpu会进入idle状态,但是系统的tick任务(update_process_times())默认会以固定周期执行,这种固定周期会打断idle状态让系统恢复成正常耗电状态。
tick任务这种不管有没有任务都是固定周期运行的特性是需要改进的,noHZ就是为了解决这一问题而产生的:如果在idle状态的过程中tick任务没有到期需要处理的低精度timer和高精度timer,tick任务可以继续保持睡眠,直到真正有timer到期。
idle进程的主要执行序列如下:
static void cpu_idle_loop(void)
{
while (1) {
/* (1) 进入idle前,noHZ的处理 */
tick_nohz_idle_enter();
while (!need_resched()) {
check_pgt_cache();
rmb();
/* (2) cpu hotplug之cpu_down()的处理 */
if (cpu_is_offline(smp_processor_id())) {
arch_cpu_idle_dead();
}
local_irq_disable();
arch_cpu_idle_enter();
/* (3) cpu idle的进入 */
if (cpu_idle_force_poll || tick_check_broadcast_expired())
cpu_idle_poll();
else
cpuidle_idle_call();
arch_cpu_idle_exit();
}
/* (4) 退出idle后,noHZ的处理 */
tick_nohz_idle_exit();
}
}
可以看到,其中的关键在tick_nohz_idle_enter()/tick_nohz_idle_exit()函数。
4.1、tick_nohz_idle_enter/exit()
tick_nohz_idle_enter()的解析:
void tick_nohz_idle_enter(void)
{
struct tick_sched *ts;
ts = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_sched);
ts->inidle = 1;
__tick_nohz_idle_enter(ts);
}
|→
static void __tick_nohz_idle_enter(struct tick_sched *ts)
{
ktime_t now, expires;
int cpu = smp_processor_id();
now = tick_nohz_start_idle(ts);
/* (1) 判断当前能否stop tick任务 */
if (can_stop_idle_tick(cpu, ts)) {
int was_stopped = ts->tick_stopped;
ts->idle_calls++;
/* (2) 尝试stop tick任务 */
expires = tick_nohz_stop_sched_tick(ts, now, cpu);
if (expires.tv64 > 0LL) {
ts->idle_sleeps++;
ts->idle_expires = expires;
}
if (!was_stopped && ts->tick_stopped)
ts->idle_jiffies = ts->last_jiffies;
}
}
||→
static ktime_t tick_nohz_stop_sched_tick(struct tick_sched *ts,
ktime_t now, int cpu)
{
struct clock_event_device *dev = __this_cpu_read(tick_cpu_device.evtdev);
u64 basemono, next_tick, next_tmr, next_rcu, delta, expires;
unsigned long seq, basejiff;
ktime_ttick;
/* Read jiffies and the time when jiffies were updated last */
do {
seq = read_seqbegin(&jiffies_lock);
basemono = last_jiffies_update.tv64;
basejiff = jiffies;
} while (read_seqretry(&jiffies_lock, seq));
ts->last_jiffies = basejiff;
if (rcu_needs_cpu(basemono, &next_rcu) ||
arch_needs_cpu() || irq_work_needs_cpu()) {
next_tick = basemono + TICK_NSEC;
} else {
/*
* Get the next pending timer. If high resolution
* timers are enabled this only takes the timer wheel
* timers into account. If high resolution timers are
* disabled this also looks at the next expiring
* hrtimer.
*/
/* (2.1) 获取下一个timer的到期时间(包括低精度和高精度timer) */
next_tmr = get_next_timer_interrupt(basejiff, basemono);
ts->next_timer = next_tmr;
/* Take the next rcu event into account */
next_tick = next_rcu < next_tmr ? next_rcu : next_tmr;
}
/*
* If the tick is due in the next period, keep it ticking or
* restart it proper.
*/
/* (2.2) 如果差距小于一个tick,不需要进入noHZ模式 */
delta = next_tick - basemono;
if (delta <= (u64)TICK_NSEC) {
tick.tv64 = 0;
if (!ts->tick_stopped)
goto out;
if (delta == 0) {
/* Tick is stopped, but required now. Enforce it */
tick_nohz_restart(ts, now);
goto out;
}
}
/*
* If this cpu is the one which updates jiffies, then give up
* the assignment and let it be taken by the cpu which runs
* the tick timer next, which might be this cpu as well. If we
* don't drop this here the jiffies might be stale and
* do_timer() never invoked. Keep track of the fact that it
* was the one which had the do_timer() duty last. If this cpu
* is the one which had the do_timer() duty last, we limit the
* sleep time to the timekeeping max_deferement value.
* Otherwise we can sleep as long as we want.
*/
/* (2.3) 根据timekeeper的可能溢出的位宽,得到的idle最大值 */
delta = timekeeping_max_deferment();
if (cpu == tick_do_timer_cpu) {
tick_do_timer_cpu = TICK_DO_TIMER_NONE;
ts->do_timer_last = 1;
} else if (tick_do_timer_cpu != TICK_DO_TIMER_NONE) {
delta = KTIME_MAX;
ts->do_timer_last = 0;
} else if (!ts->do_timer_last) {
delta = KTIME_MAX;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_NO_HZ_FULL
/* Limit the tick delta to the maximum scheduler deferment */
if (!ts->inidle)
delta = min(delta, scheduler_tick_max_deferment());
#endif
/* Calculate the next expiry time */
if (delta < (KTIME_MAX - basemono))
expires = basemono + delta;
else
expires = KTIME_MAX;
/* (2.4) 综合上面条件,得到合理的stop tick的时间 */
expires = min_t(u64, expires, next_tick);
tick.tv64 = expires;
/* Skip reprogram of event if its not changed */
if (ts->tick_stopped && (expires == dev->next_event.tv64))
goto out;
/*
* nohz_stop_sched_tick can be called several times before
* the nohz_restart_sched_tick is called. This happens when
* interrupts arrive which do not cause a reschedule. In the
* first call we save the current tick time, so we can restart
* the scheduler tick in nohz_restart_sched_tick.
*/
if (!ts->tick_stopped) {
nohz_balance_enter_idle(cpu);
calc_load_enter_idle();
ts->last_tick = hrtimer_get_expires(&ts->sched_timer);
ts->tick_stopped = 1;
trace_tick_stop(1, " ");
}
/*
* If the expiration time == KTIME_MAX, then we simply stop
* the tick timer.
*/
if (unlikely(expires == KTIME_MAX)) {
if (ts->nohz_mode == NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES)
hrtimer_cancel(&ts->sched_timer);
goto out;
}
/* (2.5) 实际的stop tick动作:
将local timer的周期改为大于一个tick的时间,将idle时间延长 */
if (ts->nohz_mode == NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES)
hrtimer_start(&ts->sched_timer, tick, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS_PINNED);
else
tick_program_event(tick, 1);
out:
/* Update the estimated sleep length */
ts->sleep_length = ktime_sub(dev->next_event, now);
return tick;
}
tick_nohz_idle_exit()的解析:
void tick_nohz_idle_exit(void)
{
struct tick_sched *ts = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_sched);
ktime_t now;
local_irq_disable();
WARN_ON_ONCE(!ts->inidle);
ts->inidle = 0;
if (ts->idle_active || ts->tick_stopped)
now = ktime_get();
if (ts->idle_active)
tick_nohz_stop_idle(ts, now);
if (ts->tick_stopped) {
/* (1) 重启tick任务 */
tick_nohz_restart_sched_tick(ts, now);
tick_nohz_account_idle_ticks(ts);
}
local_irq_enable();
}
|→
static void tick_nohz_restart_sched_tick(struct tick_sched *ts, ktime_t now)
{
/* Update jiffies first */
tick_do_update_jiffies64(now);
update_cpu_load_nohz();
calc_load_exit_idle();
touch_softlockup_watchdog();
/*
* Cancel the scheduled timer and restore the tick
*/
ts->tick_stopped = 0;
ts->idle_exittime = now;
/* (1.1) 重启local timer */
tick_nohz_restart(ts, now);
}
||→
static void tick_nohz_restart(struct tick_sched *ts, ktime_t now)
{
hrtimer_cancel(&ts->sched_timer);
hrtimer_set_expires(&ts->sched_timer, ts->last_tick);
/* Forward the time to expire in the future */
hrtimer_forward(&ts->sched_timer, now, tick_period);
if (ts->nohz_mode == NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES)
hrtimer_start_expires(&ts->sched_timer, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS_PINNED);
else
tick_program_event(hrtimer_get_expires(&ts->sched_timer), 1);
}
4.2 tick_nohz_irq_enter/exit()
因为在idle退出执行完本tick需要处理的timer后又需要重新关闭tick,系统设计了tick_nohz_irq_enter()/tick_nohz_irq_exit()来处理这种操作。在本次中断处理完timer后,在tick_nohz_irq_exit()中判断是否重新关闭tick任务。
static void cpu_idle_loop(void)
{
while (1) {
/* (1) 关闭tick */
tick_nohz_idle_enter();
while (!need_resched()) {
check_pgt_cache();
rmb();
/* (2) cpu hotplug之cpu_down()的处理 */
if (cpu_is_offline(smp_processor_id())) {
arch_cpu_idle_dead();
}
/* (3) 关中断 */
local_irq_disable();
arch_cpu_idle_enter();
/* (4) 进入idle,
cpu进入暂停状态 */
if (cpu_idle_force_poll || tick_check_broadcast_expired())
cpu_idle_poll();
else
cpuidle_idle_call();
/* (5) cpu被local timer中断唤醒退出idle状态,继续执行;
但是因为irq是disable状态,中断服务程序并不能马上得到执行*/
/* (5.1) 退出idle,并且开中断 */
/* (6) 中断打开后,被阻塞的local timer中断服务得到执行,到期的软件timer得到执行;*/
/* (6.1) 退出中断时调用tick_nohz_irq_exit(),重新计算一个tick可以被stop的值 */
arch_cpu_idle_exit();
}
/* (7) 重启tick */
tick_nohz_idle_exit();
}
}
tick_nohz_irq_enter()/tick_nohz_irq_exit()的代码解析:
static inline void tick_nohz_irq_enter(void)
{
struct tick_sched *ts = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_sched);
ktime_t now;
if (!ts->idle_active && !ts->tick_stopped)
return;
now = ktime_get();
if (ts->idle_active)
tick_nohz_stop_idle(ts, now);
/* (1) 基本就是空操作 */
if (ts->tick_stopped) {
tick_nohz_update_jiffies(now);
tick_nohz_kick_tick(ts, now);
}
}
void tick_nohz_irq_exit(void)
{
struct tick_sched *ts = this_cpu_ptr(&tick_cpu_sched);
if (ts->inidle)
/* (2) 重新判断stop tick任务 */
__tick_nohz_idle_enter(ts);
else
tick_nohz_full_update_tick(ts);
}
4.3、local timer时钟被关闭时的处理
还有一种情况需要考虑,在系统进入深层次的idle状态时,local timer本身的时钟可能会被关闭。比如MTK平台进入soidle状态时,local timer本身会被停止,这时会用一个GPT timer来替代local timer继续工作。
核心函数是timer_setting_before_wfi()/timer_setting_after_wfi():timer_setting_before_wfi()在进入idle前被调用,读出local timer的剩余值并配置到GPT timer中;
timer_setting_after_wfi()在退出idle后被调用,读出GPT timer的值来重新恢复local timer;
static void timer_setting_before_wfi(bool f26m_off)
{
#ifndef USING_STD_TIMER_OPS
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
unsigned int timer_left = 0;
/* (1) 读出local timer的剩余值 */
timer_left = localtimer_get_counter();
/* (2) 根据GPT timer在不同状态下的频率,把剩余值配置到GPT中 */
if ((int)timer_left <= 0)
gpt_set_cmp(IDLE_GPT, 1); /* Trigger idle_gpt Timeout imediately */
else {
if (f26m_off)
gpt_set_cmp(IDLE_GPT, div_u64(timer_left, 406.25));
else
gpt_set_cmp(IDLE_GPT, timer_left);
}
if (f26m_off)
gpt_set_clk(IDLE_GPT, GPT_CLK_SRC_RTC, GPT_CLK_DIV_1);
start_gpt(IDLE_GPT);
#else
gpt_get_cnt(GPT1, &timer_left);
#endif
#endif
}
static void timer_setting_after_wfi(bool f26m_off)
{
#ifndef USING_STD_TIMER_OPS
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
/* (3) 判断当前退出idle状态是否是因为GPT到期引起的 */
if (gpt_check_and_ack_irq(IDLE_GPT)) {
/* (3.1) 如果GPT时间已经到期,证明local timer也已经到期,
触发local timer在下一时钟执行 */
localtimer_set_next_event(1);
if (f26m_off)
gpt_set_clk(IDLE_GPT, GPT_CLK_SRC_SYS, GPT_CLK_DIV_1);
} else {
/* (4) 退出idle是因为GPT以外的中断源唤醒的 */
/* waked up by other wakeup source */
unsigned int cnt, cmp;
/* (4.1) 读出GPT中的剩余到期值,重新配置到local timer中 */
idle_gpt_get_cnt(IDLE_GPT, &cnt);
idle_gpt_get_cmp(IDLE_GPT, &cmp);
if (unlikely(cmp < cnt)) {
idle_err("[%s]GPT%d: counter = %10u, compare = %10u\n",
__func__, IDLE_GPT + 1, cnt, cmp);
/* BUG(); */
}
if (f26m_off) {
localtimer_set_next_event((cmp - cnt) * 1625 / 4);
gpt_set_clk(IDLE_GPT, GPT_CLK_SRC_SYS, GPT_CLK_DIV_1);
} else {
localtimer_set_next_event(cmp - cnt);
}
stop_gpt(IDLE_GPT);
}
#endif
#endif
}
需要特别说明的是,这种GPT timer全局只有一个,进入soidle的状态时cpu也只有一个在线,所以能正常的工作。
5、hrtimer
5.1、hrtimer的组织
hrtimer的组织相对来说还是比较简单的,每个cpu对应一个hrtimer_cpu_base,每个hrtimer_cpu_base中有4类clock_base代表4种时间类型(HRTIMER_BASE_REALTIME、HRTIMER_BASE_MONOTONIC、HRTIMER_BASE_BOOTTIME、HRTIMER_BASE_TAI)的hrtimer,每个clock_base是以红黑树来组织同一类型的hrtimer的:
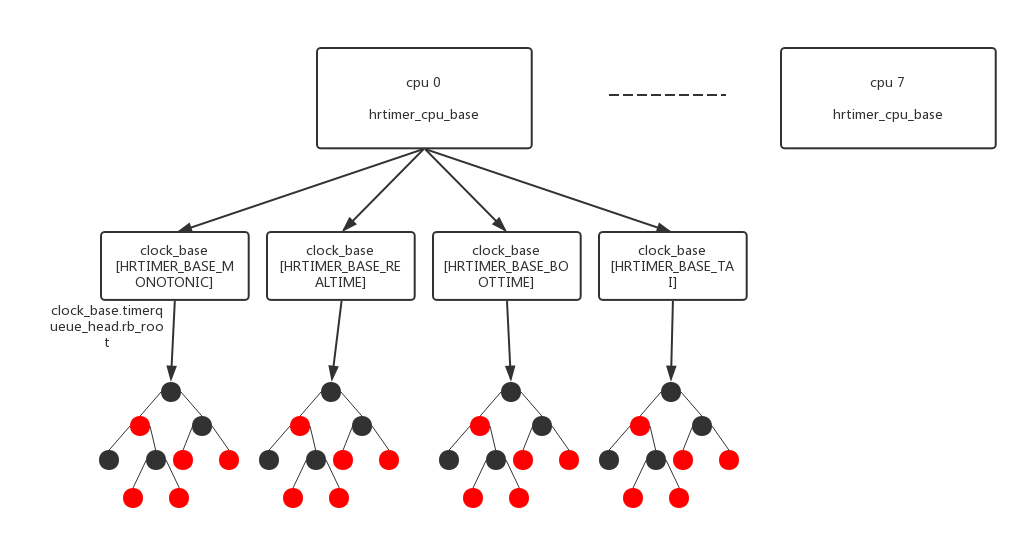
DEFINE_PER_CPU(struct hrtimer_cpu_base, hrtimer_bases) =
{
.lock = __RAW_SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED(hrtimer_bases.lock),
.seq = SEQCNT_ZERO(hrtimer_bases.seq),
.clock_base =
{
{
.index = HRTIMER_BASE_MONOTONIC,
.clockid = CLOCK_MONOTONIC,
.get_time = &ktime_get,
},
{
.index = HRTIMER_BASE_REALTIME,
.clockid = CLOCK_REALTIME,
.get_time = &ktime_get_real,
},
{
.index = HRTIMER_BASE_BOOTTIME,
.clockid = CLOCK_BOOTTIME,
.get_time = &ktime_get_boottime,
},
{
.index = HRTIMER_BASE_TAI,
.clockid = CLOCK_TAI,
.get_time = &ktime_get_clocktai,
},
}
};
5.2、低精度模式(NOHZ_MODE_INACTIVE/NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES)
前面几章已经详细描述了执行路径,在低精度模式下hrtimer的实际精度和低精度定时器是一样的,都是基于tick精度的。他的执行路径如下。
NOHZ_MODE_INACTIVE模式:
tick_handle_periodic()
↓
tick_periodic()
↓
update_process_times()
↓
run_local_timers()
↓
hrtimer_run_queues()
↓
__hrtimer_run_queues()
NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES模式:
tick_nohz_handler()
↓
tick_sched_handle()
↓
update_process_times()
↓
run_local_timers()
↓
hrtimer_run_queues()
↓
__hrtimer_run_queues()
5.3、高精度模式(NOHZ_MODE_HIGHRES)
在高精度模式下hrtimer才能发挥出真正的精度,他的可以精确定时到小于一个tick,精度依赖于硬件local timer。
NOHZ_MODE_LOWRES模式:
hrtimer_interrupt()
↓
__hrtimer_run_queues()
6、低精度timer(lowres timer)
低精度timer在系统中的应用范围更广,若非特别声明是hrtimer其他都是使用低精度timer,类如schedule_timeout()、msleep()。他有以下特点:精度低,以tick为单位计时;
执行上下文,低精度timer执行时是在softirq中,而hrtimer的实际执行是在中断当中。所以低精度的执行精度更小于hrtimer;
对系统的实时影响小,softirq比irq对系统的实时性影响更小;
6.1、低精度timer的组织
低精度timer的组织形式和hrtimer类似,只是timer的链接不是采用红黑树,而是采用tv1 - tv5等一系列的链表。
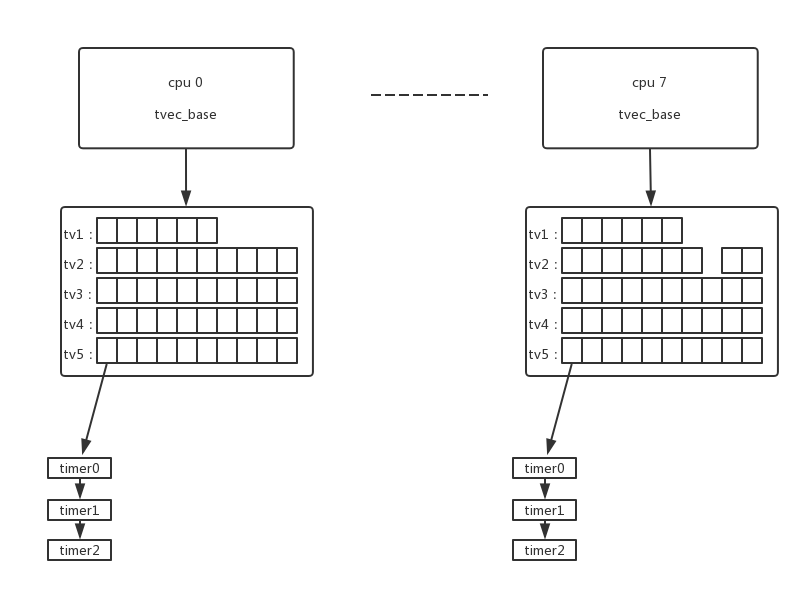
tv1 - tv5中保留着一系列槽位,每个槽位代表一个超时时间,把相同超时时间的低精度timer链接到同一槽位当中。
6.2、低精度timer的执行路径
低精度timer的实际执行时在softirq中执行的,在中断中的动作只是简单触发softirq。
中断中:
tick_handle_periodic()/tick_nohz_handler()/hrtimer_interrupt()
↓
run_local_timers()
↓
raise_softirq(TIMER_SOFTIRQ);
软中断中:
run_timer_softirq()
↓
__run_timers()
参考资料




















 877
877











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








